Subclinical and overt hyperthyroidism is present in 1.6% and 1.3% of the Indian population according to one study. The equivalent number is 1% in an American population.
Hyperthyroidism or thyrotoxicosis is an overactive thyroid where the thyroid gland produces too much of the thyroid hormones. Hyperthyroidism can accelerate your body's metabolism, causing unintentional weight loss and a rapid or irregular heartbeat.

What is Hyperthyroidism
The thyroid is an endocrine gland situated at the base of the neck. It is a vital gland that produces three major hormones : T3 (Triiodothyronine), T4 (Thyroxine) and Calcitonin. These hormones play a major role in the growth, metabolism and development of the human body.
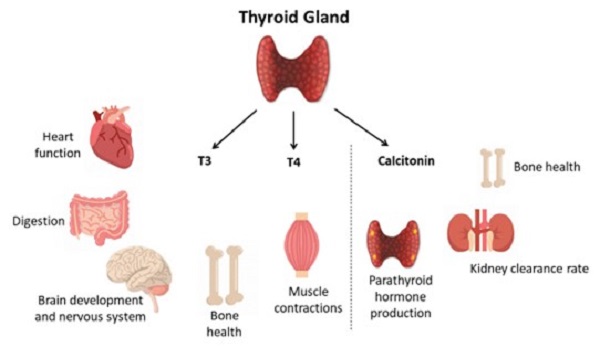
When there is an oversecretion of the T3 and T4 hormones, it leads to a condition termed Hyperthyroidism or Overactive Thyroid or Thyrotoxicosis. The term thyrotoxicosis is used to refer to the clinical manifestation of symptoms owing to excess T3 and T4 action in peripheral tissues.
If you are looking for HypoThyroidism: Click here
Community
Condition
















