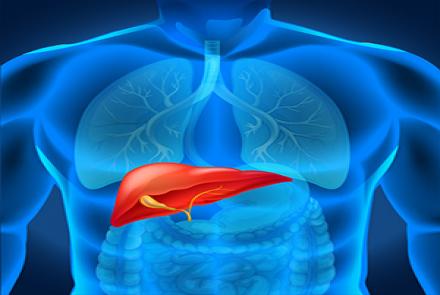
Dr. Shital Patel explains MASLD (Metabolic dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver disease) formerly termed NAFLD (Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease), the signs to watch out for, the treatment options, how to prevent it and the benefits of early diagnosis.
Any condition that damages your liver is termed Liver Disease. Normally, liver does not contain more than 0-5% fat. The range of liver diseases that are due to build-up of more than 5% fat in the liver, without the intake of excess alcohol, are called Metabolic dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Fat accumulation occurs overtime and progressively damages the liver. To this end, recognising the disease early on is beneficial for better treatment options, management and prevention of long term complications.
Related Reading: Difference between MASLD and NASH
Common signs & symptoms of MASLD
Early stages of Fatty liver disease rarely cause any noticeable signs or symptoms making it hard to detect. These subtle changes early on include weakness, feeling tired even after resting, lack of appetite, unwanted weight loss, some abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting.
In later stages, signs become more pronounced, watch out for:
- Jaundice or yellowing of the skin and eyes
- Severe itching of the skin
- Easy bleeding or bruising
- Confusion or disorientation
- Fluid accumulation in the abdomen and/or limbs
- Dark colour of urine
- Pale colour of stool
- Blood in stools or vomit
Stages of MASLD
The stages of Fatty liver disease are based on the inability of the liver to function properly. Four stages of liver damage or disease are:
- Inflamed or fatty liver. In this early stage liver may become enlarged or inflamed but not project any signs or symptoms. Hence many people do not get diagnosed early on.
- Fibrosis/scarring starts to occur when the inflammation begins to form scars. Scarred tissue impairs liver functioning but is not enough to present with symptoms or signs.
- Cirrhosis or severe scarring is accumulation of scar tissue overtime. This when symptoms may begin to present.
- Chronic liver failure is a broad term that indicates end-stage liver disease (ESLD), liver cancer or advanced cirrhosis. Liver function and shape is significantly and permanently damaged.
Prognosis:
Prognosis in liver disease depends directly on the stage at time of diagnosis. This provides a much wider range of treatment options; hence early detection is crucial.
If a person also suffers from Diabetes, their outcome is worse. A 2020 study published in the World journal of Hepatology showed that Typ2 Diabetes reduces the life expectancy of patients with cirrhosis by up to 40% after 5 years.
Treatment:
There is no cure for MASLD but it can be managed with medications and lifestyle alterations. This can help arrest the progression of the disease and prevent further complications.
Alteration to daily lifestyle should include:
- No smoking
- No alcohol. MASLD is not caused by alcohol but drinking will make it worse.
- Weight loss if overweight
- More regularly exercising
- Being more active
When Diabetes and liver disease occur together, the goal of treatment is to control the blood glucose levels, maintain a low HbA1C level (below 6.5%), monitor the liver regularly and making the lifestyle changes mentioned above.
Prevention:
In order to prevent liver damage and progression of existing liver disease, modifications to lifestyle along with a few precautions are necessary.
Here are some ways in which liver health can be improved and kept in check:
- Limited or no intake of alcohol
- No smoking
- Maintaining diabetes, hypertension and any other chronic conditions
- Weight control and healthy diet
- Regular exercising
- Taking prescribed medications on time
- Getting vaccinated against Hepatitis A and B
- Performing liver function tests regularly
References:
Loria P, Lonardo A, Anania F. Liver and diabetes. A vicious circle. Hepatol Res. 2013 Jan;43(1):51-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2012.01031.x. PMID: 23332087; PMCID: PMC3733501.
Garcia-Compean D, Jaquez-Quintana JO, Gonzalez-Gonzalez JA, Maldonado-Garza H. Liver cirrhosis and diabetes: risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical implications and management. World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Jan 21;15(3):280-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.280. PMID: 19140227; PMCID: PMC2653324.
James Myhre & Dennis Sifris, M.D. (no date) Can diabetes causes liver cirrhosis or cancer?, Verywell Health. Available at: https://www.verywellhealth.com/diabetes-and-liver-disease-6753885.
The Liver & Blood Sugar :: Diabetes Education Online. (n.d.). The Liver & Blood Sugar :: Diabetes Education Online.