Skin allergies affect a large percentage of people and can be difficult to deal with. Learn about Skin allergies, types of skin allergies and how to test for it.
An allergy is an abnormal reaction or increased sensitivity to certain substances. The allergic individual produces symptoms when exposed to these substances, which are harmless to non-allergic people.
Normally, the body's defence system fights against foreign bodies. In most allergic reactions, it is a false alarm which induces the body’s defence mechanism to fight against the substance.
The prevalence of allergic diseases has been increasing and both genetic and environmental factors play a role in creating allergic symptoms.
There are different types of allergies an individual can suffer from, one of which is skin allergy. This can be extremely uncomfortable and can also lead to cosmetic impairment.
TYPES OF SKIN ALLERGIES
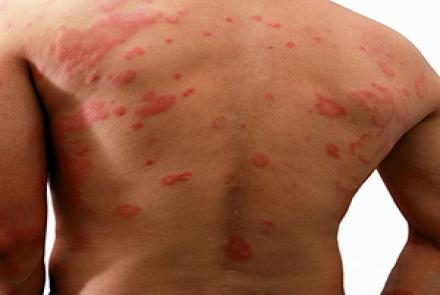
1) ATOPIC DERMATITIS (ECZEMA)
This is the most common skin allergic condition in infants and children. It usually affects the face, elbows and knees. It appears as a red, scaly, itchy rash. It is not a contagious condition, so cannot be transmitted from one person to another. It is possible for eczema to become secondarily infected with skin bacteria, especially if skin is broken due to scratching.
Causes:
- Abnormal amounts of Immunoglobulins IgE (antibody) leads to overactitivity of immune reaction. This is not something the indvidual is born with but develops subsequently.
- Food allergy or intolerance
- Contact of skin with airborne allergens like pollens, dust mites, animal hairs
- Worsening of eczema due to stress
Treatment:
- Use of moisturisers
- Topical steroid and antiseptic creams
- Oral antihistamines
- If secondarily infected, topical antibiotic and antifungal creams can be used
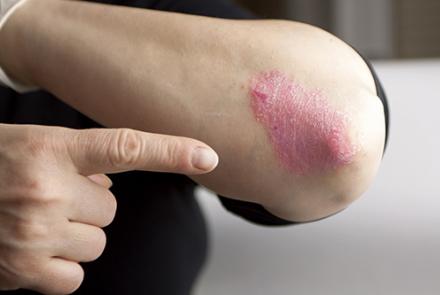
2) ALLERGIC CONTACT DERMATITIS
This is an allergic skin reaction which appears like an eczema. This condition is more painful than itchy. Allergic contact dermatitis reactions can happen within 24 to 48 hours after contact. Once a reaction starts, it takes around 14 to 28 days to cure, even with treatment.
Cause:
It is caused by direct contact with certain substances that cause allergic reaction. The substances are as following:
- Resin of poison Ivy plant
- Hair dyes
- Textile dyes
- Chemical preservatives in cosmetics
- Nickel in jewellery, spectacle frames, wrist watches
- Rubber products in gloves, boots, waistbands
- Chromium in cement, leather
- Medications like neomycin in antibiotic creams
Prevention:
Patch testing to identify the allergen and future avoidance of this trigger.
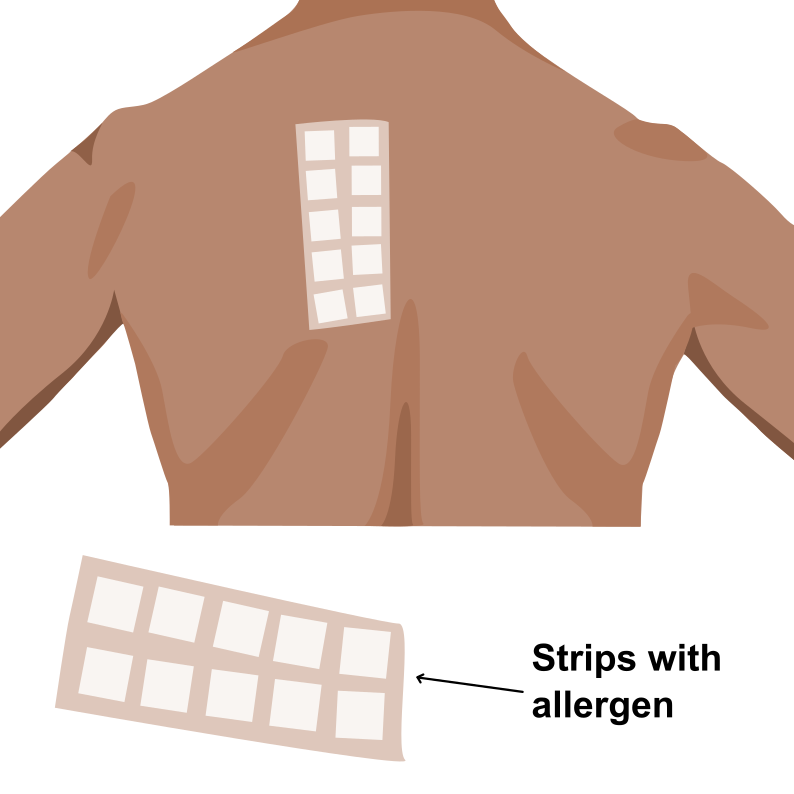
What is patch testing?
Patch testing is a method for diagnosing allergic contact dermatitis. Strips, either commercially available or custom-made with allergens are placed on the patient’s back for 48 hours. After 48 hours the strips are removed and area is marked with a marker pen on the patient’s back with respect to contact of allergen on the skin. The patient is advised not to wet the area of patch testing. The patient is recalled after 48 hours and examined to check for the presence of any localised skin reaction in respect to the allergen.
Treatment:
- Discontinuation of use of substances suspected of causing allergy
- Moisturiser
- Topical steroid
- Oral antihistamines
3) SUN SENSITITVITY: (POLYMORPHIC LIGHT ERUPTION)
This is an itchy skin rash that occurs due to sun exposure. It must not be confused with sun burn. These rashes are short-lived, about a week. Commonly affects fair skinned women of 20 to 30 years of age. Commonly found in temperate climates as in Europe and America. It has a tendency to recur on sunlight exposures.
Causes:
Both visible light and ultraviolet light (UVA and UVB) can cause sun sensitivity. As UV light can pass through glass, you can get it even when indoors. Even 20 minutes of strong sunlight can cause rashes. It is said to be related to immune reaction of the skin to sun exposure.
Prevention:
To reduce sun exposure:
- Avoid unnecessary sun exposure
- Wear long sleeved close-weave clothing
- Use hats
- Use sunblock creams of at least 30 SPF (Sun Protection Factor) with UVA and UVB protection
Treatment:
- Topical steroids
- Oral antihistamines
- Light therapy: Treatment with UV light in gradual increasing doses to make skin gradually resistant to polymorphic light eruption when exposed to natural light.
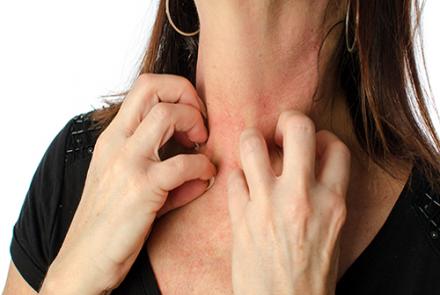
4) URTICARIA
This is also known as hives. It consists of wheals (raised area surrounded by a red base) that are itchy and painful but not contagious. Women are more commonly affected than men. There are two types of utricaria.
- Acute urticaria: Occurs due to consumption of a particular food or coming in contact with a particular material. Can also be caused by non-allergic causes such as heat or exercise or insect bites. Gets cleared within 1 hour.
- Chronic urticarial: Cause is unknown. This is rarely caused by allergy to any specific material. It can last for many months or years. It can be accompanied by angioedema (swelling of various parts of the body).
Treatment:
- Usage of allergic triggers of utricaria must be avoided
- Oral antihistamines
5) ANGIOEDEMA
This is a swelling present in the deeper layers of skin, especially in arms, legs, trunk and face. It can also affect the eyelids, genitals, tongue, mouth, throat and upper airway thereby causing difficulty in respiration. It can be accompanied by urticarial rash. There are three types:
- Acute angioedema: Caused by an allergic reaction to medications or foods.
- Chronic recurrent angioedema: Present for a long time with recurrence. It does not have an identifiable cause.
- Hereditary angioedema (HAE): A rare, serious genetic condition involving swelling in various body parts including the hands, feet, face, intestinal wall and airways. It does not respond to treatment with antihistamines or adrenaline so warrants specific medical attention.
Management:
Oral antihistamines can be used for treatment of acute and chronic angioedema
ARE YOU AT RISK OF DEVELOPING ALLERGY
Anyone can develop an allergy but the probability is increased if one or both parents suffer from some kind of allergic condition. Indeed, the presence of another allergic individual in the family is the strongest factor for predicting allergy in a child.
It must be noted, though, that even when both parents are affected, a child may not be. Conversely, allergic children are born to normal parents and in such cases other factors, such as environmental factor, may be responsible for the development of the allergy.
Repeated exposure to a substance is required before the body can recognise it as foreign and mount an allergic response.
TESTS TO DIAGNOSE SKIN ALLERGY
- Blood investigations can be done to identify abnormal amounts of IgE
- To identify the causative agent for allergic reaction the followings tests are done:
- Skin Test
- Patch Test ( Discussed under Allergic Contact Dermatitis)
Skin Tests:
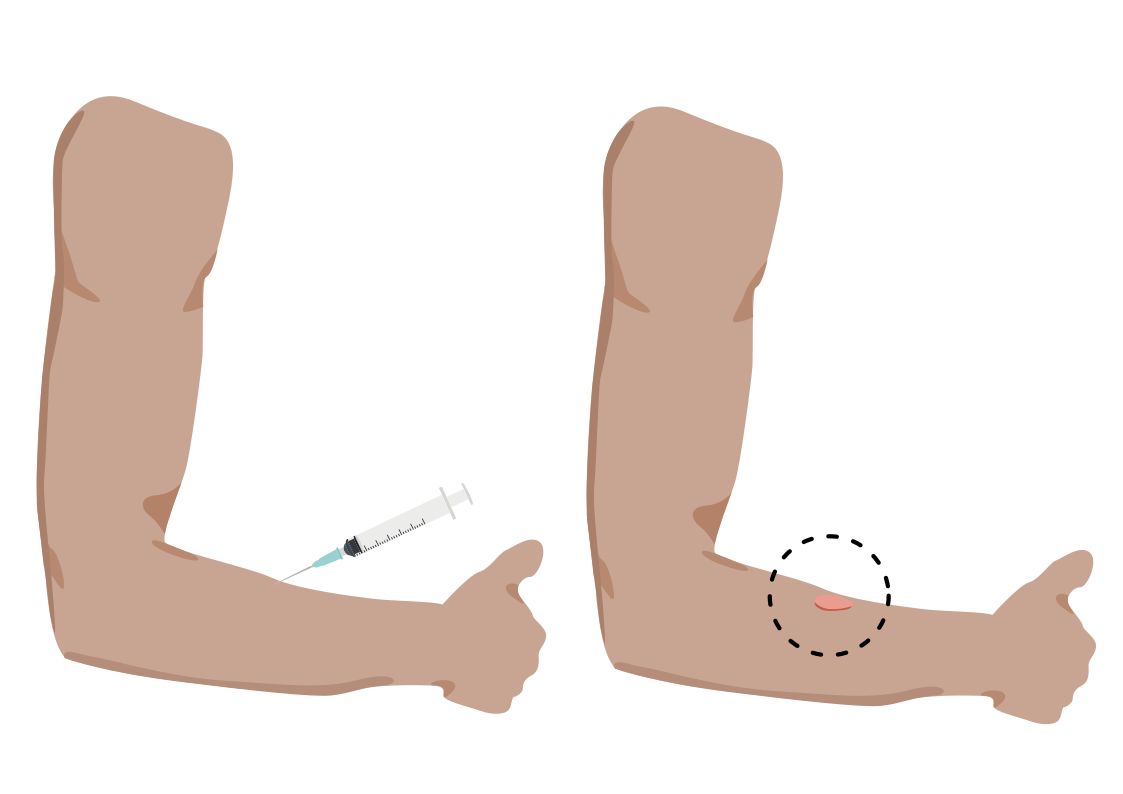
- Prick or scratch test: Drops of the suspected allergens are put on the skin of the forearm and the skin is either pricked or scratched through the drops.
- Intradermal skin test: Suspected allergens can also be injected into the skin of the back
After 15-20 minutes, if there is an allergy to one or more of the substances, a round wheal with a flare forms on the spots where the substances were injected. This may identify and confirm the allergen.
Guidelines for allergy-free life:
- Identify the allergy causing ingredients in your food and avoid them.
- If you are allergic to any medication, make sure you inform your physician prior to prescription
- Avoid usage of substances like hair dye, nickel based articles, rubber, leather etc, if they cause allergic reaction.
- Avoid contact with pets, if you are prone to allergy.
- Wear hats and sun screen regularly to avoid allergic reaction from sun exposure.
Know your support team: Who can help you stay healthy?
- General physician
- Dermatologist
- Dietitian
----ends----