It is estimated that nearly 15 lakh prostate cancer cases among men are detected in India every year, of which 85 per cent are stage four cancers. We speak to Dr Ajay Mehta, Director & Oncosurgeon, HCG-NCHRI Cancer Centre, Nagpur, on prostate cancer diagnosis, treatment and how to reduce risks with healthy diet and lifestyle.
What is prostate cancer?
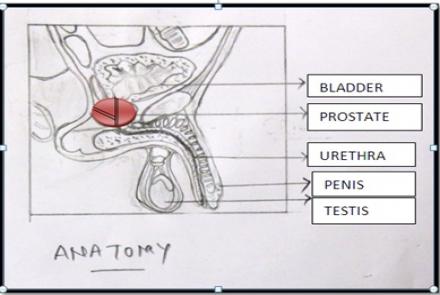
Prostate is a walnut sized gland located between the bladder and the penis. Prostate Cancer is the most common cancer in men. Prostate produces protein -Prostate -specific antigen (PSA) which helps semen retain its liquid state. An excess of this protein in the blood is one of the first signs of prostate cancer.
What causes prostate cancer?
Cancer starts in the glandular cells and is known as adenocarcinoma. Small changes occur in the size and shape of prostate gland cells known as prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia [ PIN]. 50 % of men above 50 yrs have PIN. High grade PIN is considered as precancerous where as low grade is not a cause for concern.
Related Reading: Is an enlarged prostate a sign of cancer?
What are the symptoms and signs of prostate cancer?
EARLY CANCER:
- Increased frequency of urination, including night
- Difficulty in starting and poor flow
- Dribbling, painful urination
- Difficulty in achieving or maintaining an erection
ADVANCED CANCER:
- Cancer can spread to bones causing pain often in spine, femur, pelvis or ribs. There can be fractures of the bones called as “pathological fractures”.
- Spinal cord compression due to metastasis can lead to leg weakness, paralysis, loss of urinary and fecal control.
How is prostate cancer diagnosed?
- Digital rectal examination is carried out by the doctor and blood sent for tumour marker ---PSA (prostate specific Antigen)
- Urine for PCA3 ( PCA3 gene is found only in prostate cancer cells)
- Transrectal Ultrasound and BIOPSY (12-14 small tissue samples)
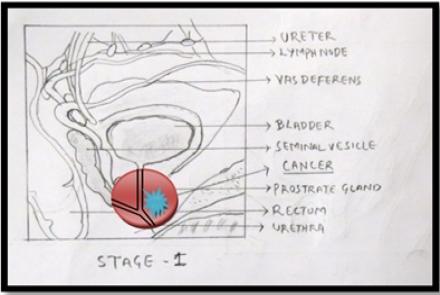
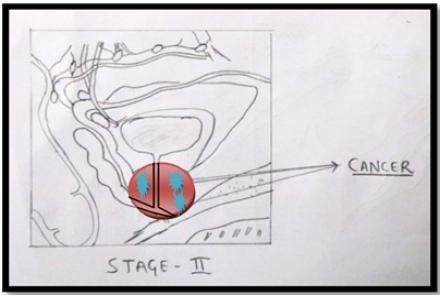
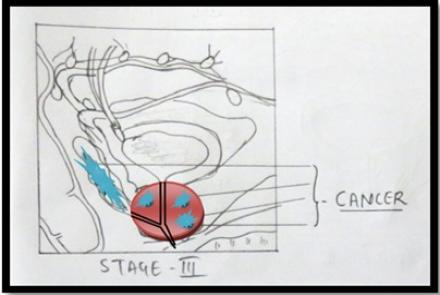
To confirm STAGE of the cancer CT scan / MRI scan /PET Scan are done.
Where is prostate cancer most likely to spread?
Prostate cancer usually spreads to bones –spine, femur, pelvic and ribs. It can spread to lymph nodes in the pelvis and nearby organs like urinary bladder and rectum.
What are some of the treatment options for prostate cancer?
In early stage:
- Regular PSA monitoring is done
- Radical prostatectomy by traditional surgery or by Robotic can be done
- Steriotactic Radio Surgery by Linear Accelerator
- Brachytherapy: Radioactive seeds to prostate gland
- Hormonal treatment
Advanced Cancer:
- Chemotherapy may be recommended if the cancer is wide spread
- Hormonal drugs
- Bilateral Orchidectomy (removal of testis) can be offered
- Local Radiotherapy to control pain
How does prostate cancer and treatment affect testosterone level and sexual function?
Prostate is directly involved with sexual reproduction and surgical removal affects semen production and fertility. Radiation and hormonal treatment affects sperm production and cause fertility issues.
Urologist answers questions on Erectile Dysfunction and other issues
What type of prostate cancer screening schedule is recommend for someone, based on his individual medical profile and family history?
Screening should start at age 45 yrs and if more than one first degree relative having prostate cancer then screening should be at age 40 yrs. If brother or father has prostate cancer, then the risk is almost twice as compared to other men.
Does lifestyle increase risks of prostate cancer?
Diet high in red meat or high-fat dairy products may increase persons chances of developing prostate cancer. Obesity and sedentary life style increases the risk of prostate cancer.
The following changes help reduce risk of prostate cancer
- Folate is found in variety of foods including green vegetables, beans, oranges and other fruits.
- Intake of these foods may reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
- Eating fish like Salmon, tuna, herring which contains omega 3 fatty acids can reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
It is estimated that nearly 15 lakh prostate cancer cases among men are detected in India every year of which 85 per cent are stage four cancers. Are Indian men genetically more predisposed to developing aggressive prostate cancer?
In India, 70-80 % prostate cancer are detected in advance stage due to lack of regular screening. They could be genetically predisposed.