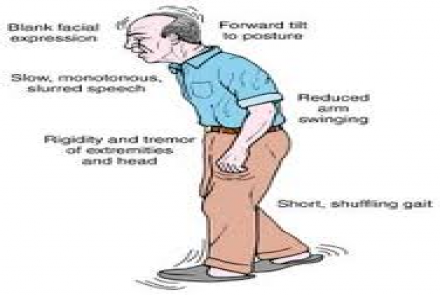
Most of us know that Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder that affects our body movement. The disease progresses slowly and gradually the quality of life is affected. The rate of progression generally varies from person to person and is very individualized. As is the case with most diseases, medication is prescribed to control the progression of the disease.
Nutrition is particularly important in Parkinson’s disease for many reasons:
- The disorder itself slows transition through the gut affecting absorption of the medications and nutrients.
- These patients may also have other medical problems or diseases that puts them at a greater risk of malnutrition. Poor nutrition can worsen other conditions like diabetes and hypertension which in turn can worsen function in Parkinson’s.
- In addition, good nutrition promotes overall brain health and may have some protective benefits.
Diet and Medication:
Our Indian diet consists of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Taken on a percentage basis, 60 – 65 % of the calories in our diet should be provided from carbohydrates, 12 – 15 % from proteins and 25 to 30% from fats. The recommended daily allowance of proteins for an Indian adult male is 60 g and for an Indian adult female is 50 g (or 1g / kg Ideal body weight). Patients who are just beginning to take Levodopa are often asked to take it with food to decrease the nausea that sometimes results. Later on, as the disease progresses, many patients note that their levodopa does not work as well when taken at or near meal times. This could be so because proteins and levodopa compete for intestinal absorption and transport across the blood brain barrier thus reducing the effectiveness of L dopa. Hence reducing the intake of proteins in the diet helps to increase the absorption of the drug.
Understanding our food:
Proteins are present in non-vegetarian foods like egg, chicken, fish and meat. Vegetarian sources of proteins include milk and milk products like paneer, cheese and all pulses and dals (e.g. chole, rajma, moong, tuvar) which should be preferably avoided. Unfortunately even carbohydrates (e.g. rice, jowar, wheat, bread, poha) contain a small amount of protein. Rice has a lower protein content than wheat and the only foods which do not contain any proteins are sago, arrowroot, fruits and simple sugar.
Hence this brings us to the next question – what can we eat ? What to eat ?
From the above it is clear that fruits and vegetables may be taken and rice is preferred over chapattis. Hence one may take chapattis made from rice flour along with a vegetable, steamed or boiled rice or a vegetable pulav. Alternatively, sago khichdi (sabudana khichdi) can also be taken with minimum addition of peanuts. All the root vegetables like potatoes, sweet potato & raw banana are high in starch and contain negligible amounts of protein. Since all non vegetarian foods are high in protein, the quantum or portion size needs to be reduced and taken along with rice, bread or pasta. Mince cutlets may be made with a small quantity of mince and a larger quantity of potatoes. Likewise chicken or fish may be taken in a very small quantity with a generous helping of sauted vegetables.
Antioxidants & Parkinson’s :
Besides restricting the intake of proteins at the time of medication, patients are also advised to increase the intake of antioxidants. Antioxidants are substances that prevent oxidative damage. Oxidative or free radical damage is thought to be part of the mechanism of cell death in some neurodegenerative disorders. Research studies have suggested that a diet rich in antioxidants may help in preventing some of this damage. Anti oxidants include vitamins such as vitamin A, C, E and substances such as lycopene and polyphenols.
- Vitamin A is found in vegetarian foods as Beta carotene which is converted to Vitamin A in the body. It is present in yellow orange fruits and vegetables like papaya, red pumpkin, leafy vegetables like spinach, fenugreek and carrots.
- Vitamin C on the other hand is present in guavas, strawberries and citrus fruits like oranges, sweetlime, lime and capsicum. Vitamin E can be obtained from nuts, grains and wheat germ.
- Lycopene is a red coloured carotenoid present in certain fruits and vegetables. Rich sources of lycopene include tomatoes, guava, watermelon, papaya, grapefruit, carrots, purple cabbage and asparagus.
- Polyphenols once again are non-vitamin natural antioxidants. Good sources of non-vitamin natural antioxidants include red wine, berries, grapes, fresh turmeric, sesame seeds and tea. Tea which is one of the most widely consumed beverages in India is rich in polyphenols. Green tea does not undergo a fermentation process during manufacture and contains catechins which are particularly helpful for Parkinson’s disease patients.
Diet to handle Constipation:
A high intake of fruits and vegetables is also beneficial in overcoming constipation which is a common problem in Parkinson’s disease. Try and include as much fibre in the diet as possible. Whenever possible, eat fruits without peeling, a tossed salad, sprouted pulses and oats all of which are high fibre foods. In place of refined flour(maida), oats may be used to thicken gravies and soups. If chewing the vegetables is a problem due to poor dentition, then puree them, juice them or drink as a soup as all these will to a certain extent help in reducing the constipation. Plenty of other liquids and exercise will also be beneficial.
Orthostatic hypotension:
Another condition that people with Parkinson’s need to be aware of is orthostatic hypotension. Orthostatic hypotension is a condition in which there is a sharp drop in blood pressure that occurs when a person gets up from the bed or chair causing dizziness or even loss of consciousness. Both Parkinson’s and the medication used to treat it may cause this condition. Moreover these patients may also be on certain blood pressure medication. Thus it is necessary for patients to have a basic understanding of orthostatic hypotension, be well hydrated at all times, eat small meals frequently and avoid a sudden change in position.
Thus in summary it can only be said that good nutrition will help to a certain extent in improving the quality of life, which is so badly affected in this debilitating neurological disease.
Couple of useful recipes:
High fibre low protein cutlets:
Ingredients
- ½ cup cauliflower (Boiled)
- 1 cup mixed vegetables (carrots, frenchbeans, potato, peas) (Boiled)
- 1/3 cup oats
- ½ cup oat flour (grind in mixer)
- Coriander leaves - few
- Ginger garlic paste
- Green chili paste
- Garam masalas
- Oil for frying
Mix the boiled vegetables with the oats and the masalas. Coat with oat powder and fry in a non-stick pan using oil as required. Serve hot with green chutney or tomato ketchup .
Skillet chicken with Veggies:
Ingredients
- 1 onion (cut into 8 pieces)
- 1 carrot (cut lengthwise)
- 1 red bell pepper (capsicum) (cut lengthwise)
- 1 small broccoli / cauliflower (cut into florets & boil)
- 30 – 50 g of boneless chicken (boiled)
- 1 tomato / 4 -5 cherry tomatoes
- 1 small pieces of ginger
- 3 - 4 pods of garlic Ingredients for sauce
- 1 tsp red chilli flakes ½ tsp soy sauce
- 2 - 3 tsp honey
- 1 tsp lemon juice
- 2 tsp oil / butter
- 3 – 4 tbsp hot water
Take a little oil in a thick bottomed pan. Add the ginger garlic pieces, onion and saute. Add the boiled chicken and vegetables and stir fry for a while on a low flame Mix all the ingredients for the sauce and add to the chicken vegetable mixture Cook for 2 – 3 minutes and serve topped with cherry tomatoes This dish may be taken along with tomato / spinach soup In place of chicken, tofu or paneer may also be used
Popular articles: Diet for elderly and people with chronic conditions