
Lymphoedema can be caused by cancer, surgery of any kind, radiotherapy or even infection and can result in swelling, pain and discomfort. Dr. Subathra Muthukumaran of Lakshmi Pain and Palliative Care Trust shares how it can be managed by simple exercises and what to avoid in such a situation.
The goal of palliative care is to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life of those with chronic illnesses since people go through not just pain but various other symptoms. One such distressing symptom is lymphoedema!
Lymphoedema

What was her problem? Lymphoedema - which is the accumulation of lymph (tissue fluid) below the skin. It was not her fault. Lymph is normally drained by the Lymphatic system, which when obstructed can lead to accumulation of the lymph. This may happen if the lymph nodes are damaged, removed or blocked by diseases such as cancer, surgery, radiotherapy or infection.
It commonly affects the hands, legs or face depending on the site of the disease.
Check out the video below on Lymphedema management after you have read this article
It can have a devastating impact on the quality of life with physical, psychosocial, spiritual, vocational and financial issues.
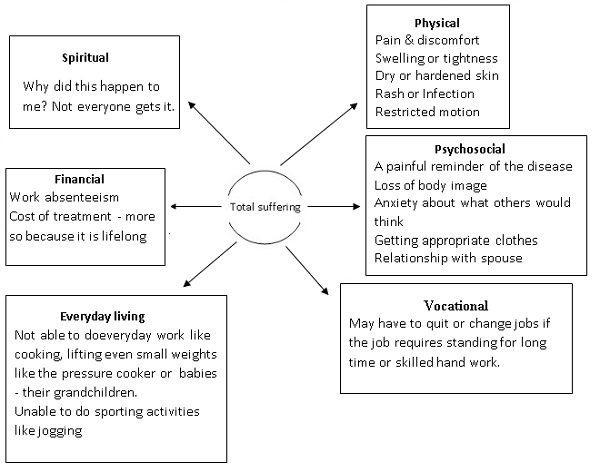
Mrs. T who had undergone mastectomy came to us when the swelling in her hand was barely discernible. She came from a small town. She was very anxious and said that her relatives and others did not know about her disease. What will she tell them if her limb was swollen. Her son was yet to get married. Nobody will come forward to marry him if people knew about her disease and with a swollen limb everyone would get curious.
Can we help these women?
Prevention of Lymphoedema
Patient education is of prime importance. Everyone who is treated for malignancy and certain infections must be forewarned and also taught about the symptoms so that they can be vigilant. They should be given a list of do’s and don’ts and must be encouraged to do simple exercises regularly to prevent lymphoedema. The challenge is to keep them motivated to adhere to these instructions as they have to follow them lifelong.
Upper limb – People at risk are those who have had surgery/radiotherapy for breast cancer.
- Do not carry more than 5kg weight and for extended periods.
- Avoid needle pricks/injections which means no chemotherapy, IV fluids or taking blood for testing -from the affected limb.
- Do not record blood pressure on the affected limb.
- If you notice any swelling, tightening of clothes/ jewellery, feeling of heaviness or discomfort in the arm, inform your doctor.
Lower limb – At risk are those who have had surgery/radiotherapy for gynaecological cancers, prostate cancer or been affected by certain infections like filariasis.
If you notice any swelling, feeling of heaviness or discomfort in the leg, inform your doctor.
Treatment of Lymphoedema
The four our cornerstones of treatment of lymphoedema are : Skincare, Massage, Containment and Exercise
Once patients start having oedema, treatment should be started immediately! Treatment consists of skin care, massage, applying a sleeve or bandaging and exercises to keep it under control.
Given below are some tips on skin care and exercises. These are general guidelines so always get an approval from your doctor before starting them. Consult a Lymphoedema expert or nurse to learn about the right exercise & massage techniques along with appropriate compression garments.
Skin Care
Appropriate skin care helps keep the skin healthy. Take meticulous care of your skin as the swollen limb is prone to infection. It may become dry and cracked allowing germs to enter easily. Could be followed regularly as a precaution even if there is no oedema
- Inspect the swollen limb regularly
- Wash daily and dry softly with a towel. Do not rub.
- Apply coconut oil/moisturisers from finger or toes upwards 2-3 times a day if necessary and at night to avoid dryness.
- Wear loose clothes and jewellery.
- Take care while cutting nails. Try to avoid cuts, injuries or scrapes.
- Apply insect repellants to avoid bites and scratching.
- If you notice redness on the skin, increase in swelling or cuts, show these to your doctor.
Exercises
- Should be done regularly after treatment for cancer to prevent oedema.
- Apply oil or moisturiser regularly.
- Apply bandage or sleeve/ stocking before exercising.
- Exercies should be done at least once every day, preferably twice.
- Slow rhythmic movements.
- Start and finish exercise with deep breathing which helps move the lymph.
Upper limb
I Neck
- Look down; then slowly raise the neck to look up toward the ceiling. 10 times
II Shoulder
- Bring each arm up and down alternately as if pulling up water from a well ×10 times each arm.
- Spread arms sideways; bring up above head and join hands as in namaste position; then place hands on head and slide them behind the head down to the neck ×10 times
- Rotation: Rotate the shoulder up to the ears, then back down and forward ×5times. Repeat in reverse direction ×5 times
III Elbow
- Place hand on table. Make a fist and slowly strengthen the arm and bend at the elbow as far as possible. Open out the hand and place it back on the table×10 times
IV Wrist
- Bend the elbow and move the wrist from side to side ×10 times. Avoid movement at the elbow.
V Fingers
- Join hands in prayer position and push matching fingers from one side to another × 5 times each finger.
Always end with deep breathing ×10 times
Lower limb
I Hip
- Keep the feet on pillows; then bend one leg at the knee and hip and slowly bring the knee close to the chest as you breathe out; then straighten knee and hip so that leg is raised as you breathe in; then bring it down to the pillow. Repeat with other leg ×10 times each leg
- Bend at the hip and make cycling movements in the air ×5 times; then reverse direction
II Ankle
- Point the toes downwards; Slowly bring them up and back as far as possible ×10 times
- Rotate the ankle with toes pointed downwards ×5times; reverse direction ×5 times
III Toes
- Bend each toe upward, downward and then rotate clockwise and anti clockwise slowly ×5times in each toe Stand up. Hold on to something for light support and stand on toes; count slowly up to 5 and then go back to standing position. Repeat ×10 times.
- If job requires you to stand for a long time, do the last exercise × 10 times every hour.
Always end with deep breathing ×10 times
Containment
Positioning
| Arm | Leg |
|---|---|
|
|
Using pneumatic machines regularly can help move the lymph fluid away from the toes/fingers, thus reducing the swelling. However such machines are not always affordable. Some physiotherapy centres may have them.

Massage
For lymphatic massage, its best to contact an expert
This article is contributed by Lakshmi Pain and Palliative Care Trust, which was started by a group of five doctors with the mission of relieving suffering and improving quality of life in patients with cancer.
Dr. Mallika Tiruvadanan, Dr. Subathra Muthukumaran, Dr. A.K. Mrunalini, Dr. Amrutha Deivanayagam, Dr. S. Thayalan
The objectives of the trust:
To provide skilled palliative care and relieve suffering in people with cancer by
- Treating pain and other distressing symptoms like vomiting and breathlessness
- Giving emotional and social support
- To provide education and training for doctors, nurses, social workers and volunteers
- To create awareness about palliative care in the society
- To help with rehabilitation of patient and family
References
- https://www.lymphnet.org/le-faqs - Check out for more details
- Twycross R, Jenns K, Todd J (Eds). Lymphoedema. Ausmed publications.
















