Riddhi Shah, MPT , a Cardio-pulmonary physiotherapist in Ahmedabad, Gujarat helps us understand the basics of Pulmonary Rehabilitation and what it entails for patients with Chronic Lung Diseases.
1. What is Pulmonary Rehabilitation (PR)?
Pulmonary rehabilitation is “the art of medical practice wherein an individually tailored, multidisciplinary program is formulated, which through accurate diagnosis, therapy, emotional support and education stabilizes or reverses both the physio- and psychopathology of pulmonary diseases and attempts to return the patient to the highest possible functional capacity allowed by his or her pulmonary handicap and overall life situation.”
The goals of pulmonary rehabilitation are to control symptoms, restore functional capabilities of patients as much as possible, and improve their quality of life. Pulmonary rehabilitation does not reverse or stop progression of the disease, but it can improve a patient’s overall quality of life.
2. Which conditions can benefit from Pulmonary rehab?
In general, patients with any respiratory problem such as shortness of breath should go for rehabilitation. It is beneficial for but not restricted to patients with obstructive and restrictive type of lung diseases. These Obstructive diseases include:
COPD or Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a term that is often utilised for patients who have a combination of chronic bronchitis and emphysema which frequently occur together and may also include asthma).
Chronic Bronchitis is characterized as a daily cough with sputum lasting at least 3 months of the year for at least two consecutive years. There is airway obstruction due to inflammation of the bronchial linings.
Emphysema: is a condition of the lung typified by permanent inflation of the air sacs or alveoli.
Asthma is a clinical syndrome characterised by attacks of wheezing and breathlessness due to narrowing of the intrapulmonary airways.
Bronchiectasis is persistent cough with sputum due to abnormal dilatation of the bronchi associated with obstruction mucus build-up and infection.
Cystic Fibrosis (CF) is a hereditary disorder of exocrine glands, that affects the lungs and digestive system. There is excessive mucus production in the lining of bronchi, which predisposes the patient to chronic broncho-pulmonary infection.
Restrictive diseases include:
- Pneumonia is an acute inflammation of the lung tissue - the alveoli and adjacent airways.
- Pleurisy is a process whereby inflammation occurs between the chest wall and lungs which come into direct contact with each other to cause pain.
- Pleural effusion is an excessive accumulation of fluid in the lung cavity.
- Empyema is a collection of pus in the pleural cavity.
- Pneumothorax occurs when air collects between the lung and chest wall allowing the lung to move away and partially deflate.
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a severe and acute form of respiratory failure precipitated by a wide range of catastrophic events - including shock, septicaemia, major trauma, or aspiration or inhalation of noxious substances.
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis or Fibrosing alveolitis is a progressive life-threatening condition with scarring and hardening of the lung tissue.
- Lung abscess is the localised formation of pus within lung tissue.
- Pulmonary tuberculosis is a serious infection caused by the bacillus Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
3. For whom is Pulmonary Rehabilitation prescribed?
Pulmonary rehabilitation programme can be prescribed for young as well as old patients. Patients suffering from chronic or acute lung issues can also benefit from it.
It is prescribed for patients with Obstructive diseases like COPD, Chronic Bronchitis, Emphysema, Combined Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema, Asthma, Bronchiectasis, and Cystic Fibrosis.
Also beneficial for patients with Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases like Pneumonia, pleurisy, pleural effusion, empyema, pneumothorax, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) like Covid-19, Fibrosing Alveolitis ,pulmonary fibrosis, lung abscess ,pulmonary tuberculosis, Bronchial and Lung Tumours, metastasis, Respiratory failure, and Interstitial lung diseases.
| In Obstructive lung diseases, the ability to exhale all the air from the lungs is hindered. While in Restrictive lung disease, there is difficulty in inhaling air. |
4. What are the advantages of PR?
- It can relieve bronchospasm(tightening of the airways) and facilitate the removal of secretions.
- Improve the pattern of breathing, breathing control and control dyspnoea (difficulty breathing).
- Improve chest expansion and pulmonary functions. Improves posture too.
- To increase knowledge of the patient's lung condition and control of the symptoms.
- To improve exercise tolerance and ensure a long term commitment to exercise.
- Can help patients with self-management in activities of daily living.
- Induce relaxation and help reduce fear and anxiety.
5. What does a routine program entail?
Before commencing PR, each patient is assessed for current health status with a look at their complete medical history and test results. Every rehabilitation sessions involves a warm-up, exercise followed by a cool down.
| PR is contraindicated and must not be done for patients who are agitated, confused, unable to follow instructions or not breathing spontaneously. |
The aim of the exercises is to be able to release mucus secretions. Exercises below mention a few of the techniques used.
- Active cycle of breathing technique (ACBT) is a breathing technique taught to patients that can aide in mobilising and clearing mucus secretions, thus helping to reduce cough and improve ventilation. It should be done for 10 minutes ideally and only once or twice a day. If you have more sputum, you need to do shorter and more frequent cycles. ACBT consists of 3 components which can be used individually or in a cycle (see image). The 3 components include:
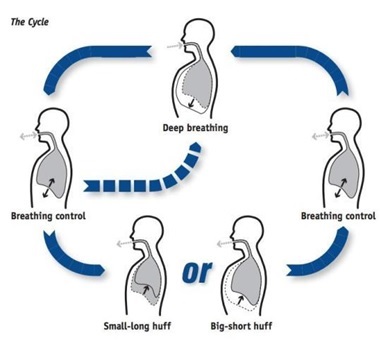
- Breathing Control helps relax the airways and relive symptoms of wheezing and coughing. Patients are taught to breathe through the nose or mouth (if nasal breathing not possible) with pursed lips and eyes closed. The breaths should gradually become slower, longer and relaxed.
- Thoracic expansion exercises consists of deep breathing combined with a 3-second hold on inspiration. Manual techniques like shaking, vibrations, chest clapping, can also aid in removal of secretions.
- Forced Expiratory technique manoeuvre involves huffing which is exhaling with an open mouth and throat instead of coughing.
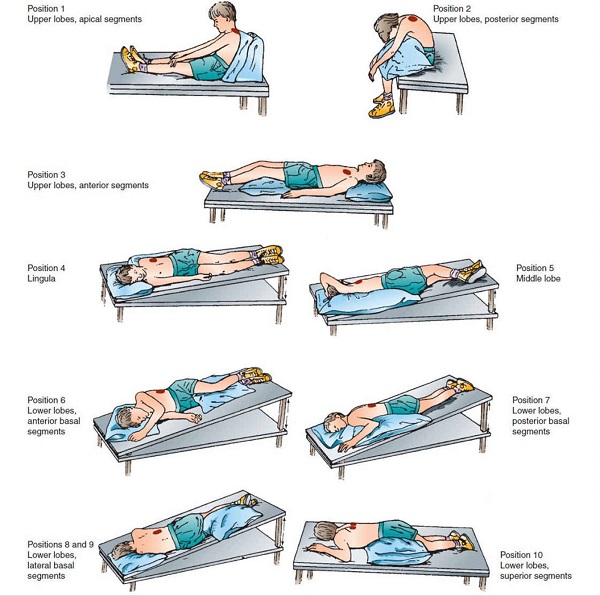
- Postural drainage is the use of different positions allowing gravity to move mucous from the lungs up. It can also be combined with the ACBT technique. Patients are advised to lie down in specific positions depending on which part of their lung needs to be drained.
- Humidification: If the secretions are very thick and tenacious the patient may be given humidification via a nebuliser.
- Steam Inhalation with pine oil added to boiling water can also be given prior to treatments to remove excessive bronchial secretions.
- Improving the breathing pattern. The patient is taught how to relax the shoulder girdle muscles in a supported position such as crook half-lying or supported sitting. Breathing control is taught following clearance of secretions. If the patient is breathless, respiratory control is regained starting with short respiratory phases and allowing the rate to slow as the patient's breathing pattern improves.
6. What is the six-minute test?
The 6 Minute Walk Test is a sub-maximal exercise test used to assess aerobic capacity and endurance. The distance covered over a time of 6 minutes is used as the outcome by which therapist can compare changes in performance capacity.
7. What are the basic exercises that lung patients require?
These basic exercises are taught to all patients as part of their rehabilitation routine, which they can continue and practice at home:
- Deep breathing exercises.
- Pursed lip breathing exercises.
- Chest expansion exercises.
- Thoracic mobility exercises.
- Strengthening exercises of upper limb and lower limb.
- Aerobic exercises like walking, jogging, marching, stair climbing.
Also read: Five exercises to improve lung function
8. How is improvement assessed and monitored?
As per the instructions by the Pulmonologist, routine and regular tests can help us monitor and assess how a patient is faring. These include pulmonary function tests such as FEV1,FVC,PEFR,SVC,MVV. Functional capacity testing can also be done within the Rehab clinic itself. These include the 6 minute walk test, 12 minute walk test, shuttle walk test, step test, treadmill test.
9. Where is PR usually conducted? Can it be done at home?
Usually PR is conducted in an outdoor physiotherapy clinical setup or a pulmonary rehabilitation centre. Yes, it can also be conducted at home with proper supervision and monitoring of physiotherapist.
10. What lifestyle changes do you suggest for patients with lung diseases?
Patients with lung diseases should be regularly engaged in pulmonary rehabilitation programme. Regular walking and aerobic exercise should be practised. Healthy diet with good amount of protein intake should be taken.
References:
- Egan’s, fundamental of respiratory care,11th edition.
- Tidy’s physiotherapy,13th edition.
- Physiopedia: Active Cycle of Breathing Technique. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Active_Cycle_of_Breathing_Technique