Maintaining good oral health is more than just about keeping cavities at bay. Your dental health has far-reaching consequences on your body, with oral bacteria being linked to many life-threatening conditions, like cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, renal health and even brain abcess.
Oral hygiene and overall good health
Like many areas of the body, your mouth is teeming with bacteria, most of them harmless. Normally the body's natural defences and good oral health can keep these bacteria under control. However, without proper oral hygiene, bacteria can reach levels that might lead to oral infections, such as tooth decay and gum disease, and, in fact, may affect your overall health if bacteria invades your body through the blood stream.
Related Reading: 10 Tips for Good Oral Health by Dr. Mariya Khambati, UK
What oral diseases or treatments can cause bacteria to invade our bodies?
- Periodontitis: This is an inflammatory disease of the tissues that surround and support teeth. It is caused by micro-organisms that grow on the tooth surface, and these can enter the blood stream through the blood supply to the tissues surrounding the tooth.
- Inflammatory conditions due to infectious micro-organisms in the apical root portion of the tooth, like periapical abscess, periapical granuloma or periapical cyst. (The apical root and other parts of the tooth are shown in the diagram below.)

- Dental plaque (pale-white to yellowish deposits on tooth surface) on tooth with more than 1011 (10, 00000000000) micro-organisms.
- Tooth extraction
- Dental scaling: During removal of dental plaque (pale-white to yellowish deposits on tooth surface) from tooth and root surfaces, inflamed tissues surrounding the tooth may be injured and bleed, paving the way for entry of bacteria into the blood stream.
- Root canal treatment: Tooth is drilled to remove infected pulp tissue, which contains blood vessels and nerves. During the treatment, bacteria from the infected tooth may be pushed below the apical root portion of the tooth, into the blood stream.

- Brushing: During brushing, inflamed tissues surrounding the tooth may be injured and bleed, paving the way for entry of bacteria into the blood stream.
- Dental surgical procedures
What diseases may be linked to oral health?
Cardiovascular diseases
- Some research suggests that heart attack, clogged arteries and stroke may be linked to the inflammation and infections that oral bacteria can cause. Some suggest that the bacteria causing oral diseases can clot blood and block arteries leading to cardiovascular diseases.
- Endocarditis is an infection of the inner lining of your heart (endocardium). Endocarditis typically occurs when bacteria (like streptococcus – common bacteria causing dental infection, or other germs) from another part of your body, such as your mouth, spread through your bloodstream and attach to damaged areas in your heart.
Respiratory disease
- Bacterial pneumonia: This is an inflammatory condition of the lung caused by bacteria, leading to cough, chest pain and difficulty in breathing. This can be caused by bacteria in the oral cavity entering the lung through the following mechanisms:
- Aspiration of oral contents (sucking or breathing in of oral contents contaminated with bacteria, e.g. dental plaque)
- Bacteria, which has entered the blood stream from the above mentioned oral diseases or treatments
Pregnancy
- Oral micro flora can increase the level of prostaglandins, which cause physiologic uterine contraction, thereby leading to pre-term low-birth weight infants. Gum disease is a common risk factor for pre-term low birth weight.
Diabetes Mellitis
Periodontitis may cause insulin resistance by immunologic reactions, thereby causing diabetes.
Gastrointestinal diseases
- Swallowing micro-organisms may lead to a variety of gastrointestinal diseases
- Gastric and duodenal ulcers are produced by infection from streptococci, which is associated with oral infection (dental caries, throat infection, tonsillitis)
Septic Arthritis
- The streptococci bacteria causing septic arthritis is also associated with oral infection (dental caries, throat infection, tonsillitis). Treatment of oral infections has led to drastic improvement in septic arthritis in some individuals.
Central nervous system disorders
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Oral infection can cause blood clot and block veins that carry blood from face and head to heart, affecting the eye and causing headaches and seizures.
- Brain abscess may be caused by streptococci, fusobacterium and staphylococcus - micro-organisms that cause oral infections.
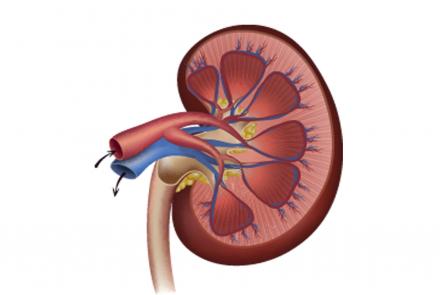
Renal diseases
- Renal diseases and oral diseases are caused by the same type of bacteria. The oral diseases and treatments described above can cause harmful bacteria from the oral cavity to enter the blood stream and affect the kidneys.
Under normal circumstances, the body’s barrier systems work together to inhibit and eliminate bacteria in the oral cavity from penetrating tissues. For example:
- Physical barrier composed of the surface epithelium of oral mucosa. This is the mucous membrane lining the mouth.
- Defensins are a type of proteins present in oral mucous membrane lining, which has anti-microbial properties.
- Immune cells in the blood stream
- Salivary cleansing action
- Immunoglobulins and enzymes in saliva with antimicrobial properties
But certain conditions put you at risk of bacteria or their toxins entering the body through the blood stream. For instance:
- Trauma to the surface epithelium
- Immunosuppression (e.g. If you are on medication that suppresses your immune system, such as Corticosteroid therapy, treatment for AIDS, malignancy, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Poor oral hygiene can lead to accumulation of dental plaque, which is a habitat for micro-organisms
- Decreased salivary flow due to some systemic illness or damage to salivary glands will reduce the cleansing function of saliva leading to plaque accumulation
- Other risk factors can be smoking, tobacco chewing and alcohol, which increases dental plaque build-up on tooth surfaces, increases dental caries formation and gum diseases.
How to prevent complications of oral diseases
- Maintain good oral hygiene by committing to daily oral hygiene procedures, like:
- Brush your teeth twice a day, once during the day and once before bed-time.
- Use fluorinated tooth paste
- Floss your teeth everyday
- Avoid sugary and acidic food/drink between meals.
- Undergo routine dental check-up once in 6 months
- Get your physician’s consent before undergoing dental treatments if you fall into any of the following categories: If you are suffering from any systemic illness, like hypertension, diabetes, asthma; have undergone any major surgeries; are under drug therapy for cardiac diseases; under corticosteroid therapy
- Avoid chewing tobacco, smoking and alcohol due to its risk factors as mentioned above.
Know your support team:
- Dentist
- General physician
Diagrams Courtesy: Dr. Meenakshi Krishnan