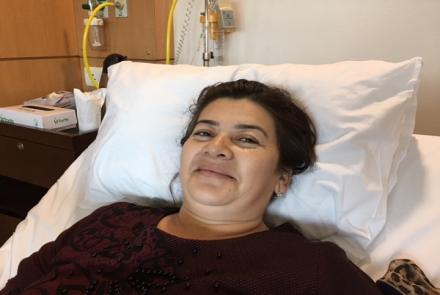
Depending on the individual patient, treatment options may include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery or a combination. It is important to understand the purpose of the treatment, which may vary. In some cases, the treatment aims to ‘cure’ the cancer or ensure ‘remission’. (Doctors tend to use the word ‘remission’ rather than ‘cure’ as in some cases the cancer returns after months or years.) In some cases, treatment aims to control the cancer – limit its growth and keep you free of symptoms for a while, or treat the symptoms to keep the patient pain-free. Speak with your doctor about the pros and cons of every treatment option, likely success rate and possible side-effects.
Read this to understand the role of adjuvant therapy
Chemotherapy
This is a treatment using anti-cancer drugs that kill cancer cells, or stop them from multiplying. Chemotherapy may be given in addition to radiotherapy or surgery in certain situations. Possible side-effects of chemotherapy include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, hair loss, mouth sores, anaemia and diarrhoea.
Laser therapy
Laser therapy is sometimes called laser ablation. This is an outpatient treatment. The doctor applies local anaesthesia to the cervix to numb it and then a laser is used to burn away the abnormal cells. You can go home as soon as this treatment is over. Any side effects? NO
Cryotherapy
For this treatment, the specialist uses a cold probe to freeze away the abnormal cells. You shouldn't feel the probe on the cervix, but you might get a period type pain while you are being treated and for a short while afterwards.
Diathermy
This is done under local anaesthetic. The treatment uses an electric current to cut away the tissue containing the abnormal cells. It is quite quick and you will be able to go home afterwards. Bring a sanitary towel with you. You will have some bleeding or discharge for about 4 weeks after the treatment. You shouldn't wear tampons or have sex for 4 weeks because this will increase your risk of infection.
The advantage of diathermy over laser treatment is that the piece of cervical tissue that the doctor removes can be sent for examination under a microscope. With laser ablation, the cells are destroyed, so the pathologist can't examine them after the treatment.
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is a treatment that uses high-energy beams of radiation focused on cancerous tissue. This kills cancer cells, or stops cancer cells from multiplying. Radiotherapy alone can be curative for early-stage cervical cancer and may be an alternative to surgery. For more advanced cancers, radiotherapy may be advised in addition to other treatments.
Two types of radiotherapy are used for cervical cancer - external and internal. In many cases both types are used:
External radiotherapy: This is where radiation is targeted on the cancer from a machine. (This is the common type of radiotherapy used for many types of cancer.)
Internal radiotherapy (brachytherapy): This treatment involves placing a small radioactive implant next to the cancerous tumour (in the vagina) for a short time.
Even if the cancer is advanced and a cure is not possible, radiotherapy may still have a place to ease symptoms. For example, radiotherapy may be used to shrink secondary tumours that have developed in other parts of the body and are causing pain.
Surgery
An operation to remove the cervix and uterus (hysterectomy) is a common treatment. If the cancer is at an early stage and has not spread, then surgery alone can be curative. In some cases, where the cancer is at a very early stage, it may be possible to just remove the part of the cervix affected by the cancer without removing the entire uterus. This would mean that the patient could still have children.
If the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, surgery may still be advised, often in addition to other treatments. For example, in some cases where the cancer has spread to other nearby structures, extensive surgery may be an option. This may be to remove not only the cervix and uterus but also nearby structures that may have become affected such as the bladder and/or bowel.
Even if the cancer is advanced and a cure is not possible, some surgical techniques may still have a place to ease symptoms. For example, to relieve a blockage of the bowel or urinary tract caused by the spread of the cancer.