What is a Bone Scan? What do the results of the scan indicate? When do you need a Bone Scan? How often should you get a Bone Scan? We give you information that will help you discuss your options with your doctor.
What is a Bone Scan
A Bone scan is done to check the bone mineral density (BMD) so as to assess strength of the bones and probability of any fractures. The scan helps identify any mild (osteopenia) or serious bone loss (osteoporosis). The most common bone density test is the DEXA scan. Here, the entire body is scanned after a tiny amount of radioactive substance called a tracer is injected into a vein. Since the DEXA test scans the entire body, it is able to detect and diagnose a wide range of bone disorders.
Since the bone scan is a nuclear medicine test, excessive exposure to tracers is not recommended. Although, some doctors may argue that the amount of radiation exposure is minute and hence not harmful. The bone scan generally has no side-effects and follow-up care is not required. Any radioactivity from the tracers used get eliminated within two days post the scan.
So who should get a DEXA scan:
- Women above the age of 65
- Men above the age of 70
If you are younger than the above age group, your doctor may suggest it if you have the following risk factors:
- Early menopause or late-onset of menstrual periods.
- You smoke or drink heavily
- You have a history of rheumatoid arthritis
- You have a parent who had hip or other fractures
- You have low body weight or small body frame
- Take medications that cause bone loss such as steroids, anti-seizure drugs etc.
- You have been on cancer treatment like hormonal treatment, chemotherapy
- Have low estrogen levels
- Have hyperparathyroidism
- Have hyperthyroidism
- Have chronic Vitamin D deficiency.
Let’s look at some other instances when a bone scan is required:
- If a patient complains of unexplained skeletal pain.
- Fractures from minor accidents.
- History of corticosteroid use for more than 3 months.
- Paget’s disease of bone.
- Suspicion of a bone infection or bone disease that is unclear on a regular X-ray.
- To find any cancer originating from the bone
- To check for metastasis (spread of cancer) in the bones from other areas.
- To monitor progress of treatment for Bone Cancer.
What do the DEXA Test results mean:
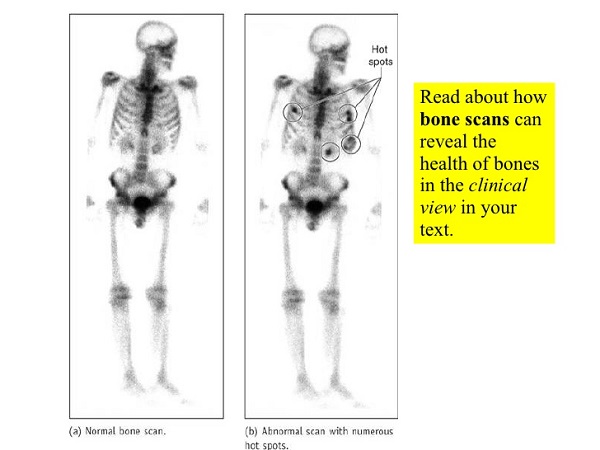
A Radiologist will look for abnormal bone shadows on the images. Dark areas which take up more tracer are termed “hot spots” and light ones with less tracer are the “cold spots”. Areas of fast bone growth, cancer, infections, trauma or repair show up as dark spots (figure b).
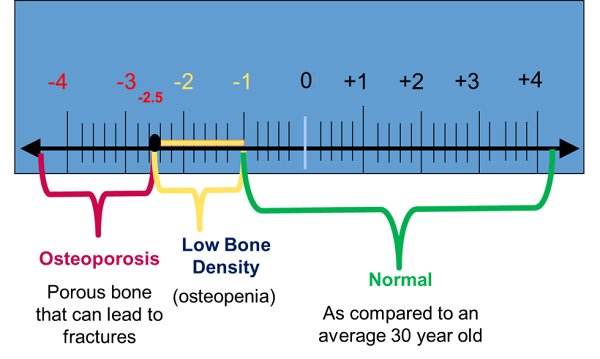
The scan also compares the patient’s bone mineral density values (T-score) to those of a young 30 year old normal adult (Z-score). The image below shows what your T-score result means.
How often should you get a bone scan?
There is no fixed interval for scanning of bone density. If your bones are healthy, your doctor may suggest a scan after 15 years. This comes from a 2012 study that reported that bone loss in average women above 65 is quite slow i.e. a woman with normal bone density only loses 5% of bone density in 10 years. Women who show low or moderate density in the initial scan are likely to be more osteoporotic. For such women, testing is recommended every 5 to 1 year depending on their T-score. Best to follow your doctor’s recommendations on when to get a scan depending on your risk factors and medical history.
Updated for cancer treatment on 12th January 2019
















