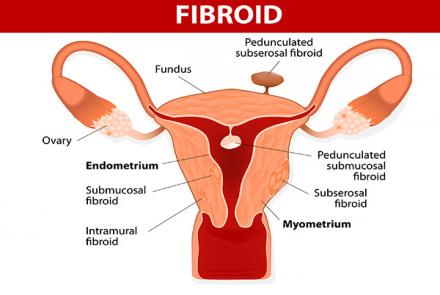
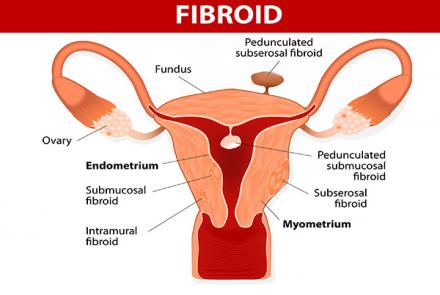
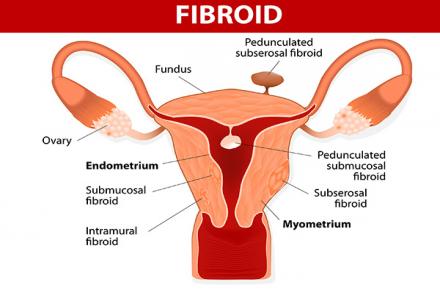
Types of Uterine Fibroids:
Submucosal: These fibroids are located just underneath the lining of uterus, protruding into the uterus. They cause heavy bleeding, long periods and irregular bleeding between the cycles.
Subserosal: These fibroids are located outside the uterus either in the muscle or hanging outside the uterine wall. They cause bulk symptoms, such as pain and pressure in the pelvis, abnormal and excessive menstrual bleeding, pressure on spinal cord.
Intramural: These fibroids are…
Latest Stories
- The exact cause of fibroids is not known. Our body is made-up of cells that regularly undergo turnover i.e production of new cells and removal of old and damaged cells. Sometimes, this regular process is disturbed causing more cells to be produced than destroyed. This results in the formation of abnormal mass of tissue, which is called tumour. The tumour can be benign or malignant. Fibroids are a kind of benign tumour. Normal cell production and destruction may be disturbed by genetic,…
- Fibroids are non-cancerous, i.e. harmless or benign tumours that grow in the smooth muscle layers of the wall of uterus (womb). Synonyms: Uterine fibroids, Myomas, Fibromyomas Fibroids grow singly or appear in clusters. They are slow growing and may be as small as a peanut to as large as a melon. They are most common among women in their 30s or 40s, with four out of every five women developing fibroids. About 70% of Asian women develop fibroids at some point in their lives…
- Hallucination and Delusion in Parkinson's Hallucinations and Delusions are two types of Neuropsychiatric symptoms which affect people with Parkinson’s, and result in disturbance of perception and thought. They can occur due to two reasons - as a symptom of the condition or as a side effect of the medication. A Hallucination involves a sensation (seeing, hearing, smelling, tasting or feeling) about something that does not exist. It is experienced when the person is in a wakeful state and very…
- Unity walk for Parkinson…in Nasik A Unity walk was organized in Nashik on Saturday, December 5, 2015 to promote awareness of Parkinson’s disease by PDMDS with support from several other leading organizations. In addition to the patients and representatives of these organizations, citizens of Nashik also came out in large numbers to show their support. Approximately 300 participants started assembling bright and early and the walk commenced at 5:15 PM, originating at Nasik City Center Mall to…
- But often overlooked, says Porrselvi A.P. a cognitive and psychosocial interventions specialist. Here, she offers a case study and practical strategies to guide you back to normal life. The patient: Mrs. K, a 67-year-old woman had a stroke in the left side of her brain in September last year. Her condition: Mrs K was referred for cognitive and psychological evaluation following complaints of social withdrawal, memory disturbances and increased irritability…
- A excellent video in Hindi from the UK. Covers the following aspects: What is Dementia Types of Dementia - Alzheimer's, Vascular Dementia, Lewy Body, etc.. Difference between Dementia and Ageing Medication and treatment Management of Dementia Importance of a support network so you realise you are not alone Advise to caregivers and carers: Share your worries and concerns with friends and family members Join support groups Involve the family, even children Use care services whenever…
- What can you do when you have Early Stage Parkinson's Taking Control of Parkinson’s: Make a decision today to take control of your life with Parkinson’s. The key to living an optimally healthy, happy and fulfilling life is in your hands. Here are some pointers to help you take control. Acceptance: It is important that you accept that you have Parkinson’s. Then only will you be able to take control of it. Acceptance does not mean you’re “giving up” instead it is the first hurdle you must…
- As the temperature plummets, asthma attacks and pneumonia cases rise. Family practitioner and paediatrician Dr Gita Mathai tells you why this is so and how to protect yourself. Asthma What is asthma? Asthma refers to a condition that causes shortness of breath with a whistling sound from the chest. It is also called "reactive airway disease". What causes asthma symptoms? The whistling sound is caused by the narrowing of the tubes through which the air passes…