Nausea and vomiting during a migraine attack can be extremely distressing. Dr. Shital Raval suggests several safe and effective options that can provide much needed relief from both migraine and nausea
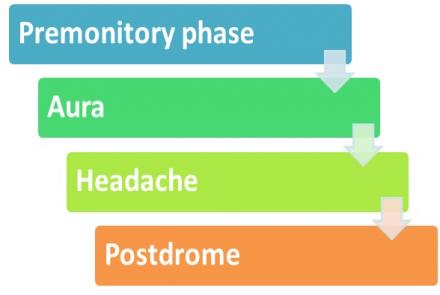
When muscles in your scalp, neck, and face tighten and contract, it causes spasms and pain called Headache. Besides physical strain, headaches can be triggered by lack of sleep, dehydration, sinus congestion, vision problems, stress, anxiety and fatigue.
What is Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome (CVS)
Millions of people around the world are affected by headaches including migraines. Migraine headaches appear with symptoms of one-sided throbbing pain along with nausea, vomiting, aura, sensitivity to light & sound etc. Unfortunately, for many people, headaches are accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. The most common being nausea and vomiting. It is known that a high percentage of migraine sufferers experience nausea, upset stomach, and vomiting. Cyclic vomiting syndrome or CVS is typical of migraine attacks! Triggers such as stress and anxiety may also be factors for inducing CVS. Researchers are not completely sure what the underlying cause of this association is but there are a few theories which may explain it better.
- Since nausea and vomiting also occur with vertigo or dizziness, the link may be due to some inner ear disturbances.
- There is a center in the brain that if affected would lead to nausea and vomiting.
- During a headache, the arteries in the head become wide initiating pain and the Sympathetic nervous system. This is the body’s “fight or flight” response system which then prompts increase in heart rate and blood pressure to mobilize the body and also slow the digestive system. Consequently, the stomach relaxes and stops digesting which may cause the nausea and vomiting as the food stays longer in the stomach. This may also explain why oral medications taken during an intense headache are less effective.
- Some belive that estrogen fluctuations trigger brain signal that control nausea and vomiting. This explains why more women than men suffer from migraines.
- Serotonin (chemical in the brain) which is related to motion sickness may also play a role because many migraine patients also experience motion sickness.
Tips to handle nausea during migraine headaches?
Because migraines can last anywhere from 4 to 24 hours, early treatment is important. The most effective method is to cut down on migraine attacks by avoiding triggers such as certain foods, wine, chocolate, smoking and stress.
- Step out for some fresh air.
- Warm alternating with cold wash cloth/ compresses on the face, forehead and back of neck help in relaxing the muscles.
- Slicing a lemon and sucking on it is known to work like a charm.
- Sip on ginger or chamomile tea, water and clear broth to stay hydrated.
- Get some rest.
- Massage the temples with peppermint or lavender oil.
- Try over-the-counter pain-reducing drugs such as Paracetamol* or Ibuprofen.
- Try anti-emetics or anti-nausea drugs such as Prochloperazine or Promethazine.
*Only Generic names of medications have been provided. In severe cases, please see your doctor for prescription drugs.