There are two main types of cervical cancer:
- Squamous cell cancer
- Adenocarcinoma
They are named after the type of cell that becomes cancerous.
Squamous cell cancer
Squamous cells are the flat, skin-like cells lining the ectocervix, which connects to the vagina. Around 7 to 8 out of 10 cervical cancers are squamous cell cancer (70 to 80%).
Adenocarcinoma
Adenomatous cells are gland cells that produce mucus. The cervix has these gland cells scattered along the inside of the passageway that runs from the cervix to the womb (the endocervical canal). Adenocarcinoma is a cancer of these gland cells. It is less common than squamous cell cancer, but has become more common in recent years. More than 1 in 10 cervical cancers are adenocarcinoma (10 to 15%). It is treated in the same way as squamous cell cancer of the cervix.
Other rarer types of cancer:
Very rarely, other types of cancer can occur in the cervix. An example is lymphoma, which is a cancer of the lymphatic system.
Stages of cervical cancer
Cervical cancer staging is the assessment of cervical cancer to decide how far the disease has progressed. There are different ways of classifying the stage.
One of these is TNM Staging: T describes the size or extent of the tumour. N describes the spread of tumour to nearby lymph nodes. M describes the presence of distant metastasis.
TNM and FIGO Classifications for Cervical Cancer:
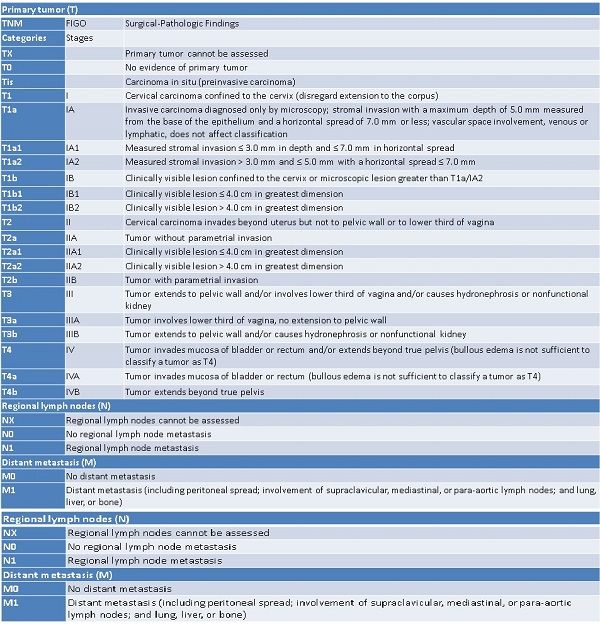
Primary tumor
TX
Primary tumor cannot be assessed
T0
No evidence of primary tumor
Tis
Carcinoma in situ (preinvasive carcinoma)
T1
I
Cervical carcinoma confined to the cervix (disregard extension to the corpus)
T1a
IA
Invasive carcinoma diagnosed only by microscopy; stromal invasion with a maximum depth of 5.0 mm measured from the base of the epithelium and a horizontal spread of 7.0 mm or less; vascular space involvement, venous or lymphatic, does not affect classification
T1a1
IA1
Measured stromal invasion ≤ 3.0 mm in depth and ≤ 7.0 mm in horizontal spread
T1a2
IA2
Measured stromal invasion > 3.0 mm and ≤ 5.0 mm with a horizontal spread ≤ 7.0 mm
T1b
IB
Clinically visible lesion confined to the cervix or microscopic lesion greater than T1a/IA2
T1b1
IB1
Clinically visible lesion ≤ 4.0 cm in greatest dimension
T1b2
IB2
Clinically visible lesion > 4.0 cm in greatest dimension
T2
II
Cervical carcinoma invades beyond uterus but not to pelvic wall or to lower third of vagina
T2a
IIA
Tumor without parametrial invasion
T2a1
IIA1
Clinically visible lesion ≤ 4.0 cm in greatest dimension
T2a2
IIA2
Clinically visible lesion > 4.0 cm in greatest dimension
T2b
IIB
Tumor with parametrial invasion
T3
III
Tumor extends to pelvic wall and/or involves lower third of vagina and/or causes hydronephrosis or nonfunctional kidney
T3a
IIIA
Tumor involves lower third of vagina, no extension to pelvic wall
T3b
IIIB
Tumor extends to pelvic wall and/or causes hydronephrosis or nonfunctional kidney
T4
IV
Tumor invades mucosa of bladder or rectum and/or extends beyond true pelvis (bullous edema is not sufficient to classify a tumor as T4)
T4a
IVA
Tumor invades mucosa of bladder or rectum (bullous edema is not sufficient to classify a tumor as T4)
T4b
IVB
Tumor extends beyond true pelvis
Regional lymph nodes (N)
NX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
N1
Regional lymph node metastasis
Distant metastasis (M)
M0
No distant metastasis
M1
Distant metastasis (including peritoneal spread; involvement of supraclavicular, mediastinal, or para-aortic lymph nodes; and lung, liver, or bone)
Primary tumor (T)
TNM
FIGO
Surgical-Pathologic Findings
Categories
Stages
TX
Primary tumor cannot be assessed
T0
No evidence of primary tumor
Tis
Carcinoma in situ (preinvasive carcinoma)
T1
I
Cervical carcinoma confined to the cervix (disregard extension to the corpus)
T1a
IA
Invasive carcinoma diagnosed only by microscopy; stromal invasion with a maximum depth of 5.0 mm measured from the base of the epithelium and a horizontal spread of 7.0 mm or less; vascular space involvement, venous or lymphatic, does not affect classification
T1a1
IA1
Measured stromal invasion = 3.0 mm in depth and = 7.0 mm in horizontal spread
T1a2
IA2
Measured stromal invasion > 3.0 mm and = 5.0 mm with a horizontal spread = 7.0 mm
T1b
IB
Clinically visible lesion confined to the cervix or microscopic lesion greater than T1a/IA2
T1b1
IB1
Clinically visible lesion = 4.0 cm in greatest dimension
T1b2
IB2
Clinically visible lesion > 4.0 cm in greatest dimension
T2
II
Cervical carcinoma invades beyond uterus but not to pelvic wall or to lower third of vagina
T2a
IIA
Tumor without parametrial invasion
T2a1
IIA1
Clinically visible lesion = 4.0 cm in greatest dimension
T2a2
IIA2
Clinically visible lesion > 4.0 cm in greatest dimension
T2b
IIB
Tumor with parametrial invasion
T3
III
Tumor extends to pelvic wall and/or involves lower third of vagina and/or causes hydronephrosis or nonfunctional kidney
T3a
IIIA
Tumor involves lower third of vagina, no extension to pelvic wall
T3b
IIIB
Tumor extends to pelvic wall and/or causes hydronephrosis or nonfunctional kidney
T4
IV
Tumor invades mucosa of bladder or rectum and/or extends beyond true pelvis (bullous edema is not sufficient to classify a tumor as T4)
T4a
IVA
Tumor invades mucosa of bladder or rectum (bullous edema is not sufficient to classify a tumor as T4)
T4b
IVB
Tumor extends beyond true pelvis
Regional lymph nodes (N)
NX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
N1
Regional lymph node metastasis
Distant metastasis (M)
M0
No distant metastasis
M1
Distant metastasis (including peritoneal spread; involvement of supraclavicular, mediastinal, or para-aortic lymph nodes; and lung, liver, or bone)
Another way to classify cancer is by stage grouping. Cancer staging generally runs from stage 0, which is pre-cancerous or non-invasive, to stage 4, in which the cancer has spread throughout a significant part of the body.
Stage 0
The carcinoma is confined to the surface layer (cells lining) of the cervix. Also called carcinoma in situ (CIS).
Stage I
The carcinoma has grown deeper into the cervix, but has not spread beyond it.
The cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes nor distant sites.
Stage 1 is sub-divided as follows:
IA: Invasive carcinoma that can be diagnosed only by microscopy, with deepest invasion <5 mm and the largest extension <7 mm
IA-1: Measured stromal invasion of <3.0 mm in depth and extension of <7.0 mm
IA-2: Measured stromal invasion of >3.0 mm and not >5.0 mm with an extension of not >7.0 mm
IB: Clinically visible lesions limited to the cervix uteri or pre-clinical cancers greater than stage IA
IB-1: Clinically visible lesion <4.0 cm in greatest dimension
IB-2: Clinically visible lesion >4.0 cm in greatest dimension
Stage II
Cervical carcinoma invades beyond the uterus, but not to the pelvic wall or to the lower third of the vagina
IIA: Without parametrial invasion
IIA-1: Clinically visible lesion <4.0 cm in greatest dimension
IIA-2: Clinically visible lesion >4.0 cm in greatest dimension
IIB: With obvious parametrial invasion
Stage III
The tumour extends to the pelvic wall and/or involves lower third of the vagina and/or causes hydronephrosis or non-functioning kidney
IIIA: Tumour involves lower third of the vagina, with no extension to the pelvic wall
IIIB: Extension to the pelvic wall and/or hydronephrosis or non-functioning kidney
Stage IV:
This is the most advanced stage of cervical cancer. The cancer has spread to nearby organs or other parts of the body.
Stage IVA: The cancer has spread to the bladder or rectum. It has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant sites.
Stage IVB: The cancer has spread to distant organs beyond the pelvic area, such as the lungs or liver.





