
Ms. Malavika M. Nair and Ms. Aakriti Vig under the guidance of DEMCARES, SCARF India write about the stressors that lead to challenging behaviours of Dementia and how to handle them.
Dementia is recognized as a global health concern. It is estimated that nearly 47.5 million of the global population is diagnosed with dementia (WHO, 2017). It is a neurocognitive disorder, which is primarily prevalent in the elderly population. The symptoms include significant memory loss with impairments in other cognitive functions and behavioural manifestations. It has been found that certain characteristics of dementia, especially agitation and aggression can cause severe distress to the caregivers. The undesirable and distressing behavioural manifestations have been termed as ‘Challenging Behaviour’.
What is Challenging Behaviour?
It is important to understand that Challenging Behaviour is usually a maladaptive response towards an unmet need. An individual with dementia could feel unimportant, vulnerable or threatened if their needs are not perceived accurately. They could also feel unequipped and helpless because of their inability to effectively perceive and communicate their issues. This could lead to an undesirable behaviour and pose as a challenge to the caregivers.
The diverse dimensions of dementia are interconnected and complex. It is often difficult to accurately judge the current need of the individual and the stressor which has triggered the behaviour. These situations subsequently result in the caregiver undergoing tremendous amounts stress and negative emotions.
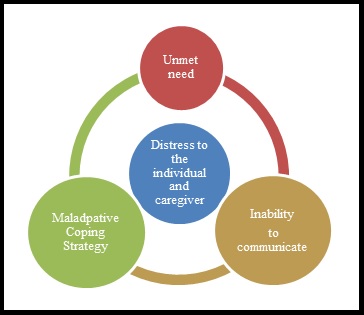
Stressors Leading to Challenging Behaviour:
It is important to identify the biological, psychological and social stressors leading to challenging behaviours that an individual with dementia may present with.
Biological Stressors: The presence of a physical health condition, ailment that might be causing significant distress to an individual like impaired vision, impaired hearing, cognitive deficits or the side effects of medication that the client has been prescribed or more commonly, pain.
Psychological Stressors: The individual’s knowledge and beliefs about his current state of functioning and how/she is coping with it plays an important role. It is important to assess the individuals personality and identify the presence of any co-morbid mental health condition like anxiety or depression that can have a significant impact on the clients overall wellbeing.
Social Stressors: The nature of the relationship the individual shares with the family and caregivers can influence ones behaviour. Absence of a supportive, caring relationship with the caregivers can cause significant stress for an individual. If the physical setting in which an individual stays is perceived as restricting their autonomy, uncomfortable or unsafe it can cause stress for an individual.
How to manage Challenging Behaviour?
It can be understood that the challenging behaviour exhibited by the individuals with dementia could be a cause of distress and frustration within their systems. The challenging behaviour is often a manifestation of an unmet need. However, a comprehensive list of interventions can be undertaken to effectively address these undesirable behavioural manifestations.
Person- Centered Approach: This approach is rooted in addressing the needs and providing care to every individual based on their unique capabilities and personality. It aims to understand the life story of the individual and enable them in meaningful ways focusing on their strengths.
Functional Assessments: A systematic chart is devised to identify the triggers (antecedents), which lead to a challenging behaviour and the subsequent responses to the behaviour. Through this assessment, one must also consider the emotions which accompanied the actions of the individual. This technique helps to reduce the perceived unpredictability of the individual’s behaviour and explore interventions that can be effective in reducing the trigger thereby preventing the challenging behaviour from emerging. This is usually lead by a health care professional like a psychologist or mental health nurse.
Clinical dimensions: The individual’s medication must be regularly reviewed in order to ensure the effectiveness and possible ill-effects. It is imperative to assure the individual’s physiological well-being through regular medical assessments as well. Furthermore, thorough checks must be made on possible sensory impairments to reduce the possibility of disorientation. Assessing and managing pain is also very crucial.
Psychological Dimension: The needs of the individuals must be assessed along with the characteristics of the challenging behaviour. A therapeutic intervention can be charted out accordingly. This may be done by putting in place strategies to reduce the unmet need for a more sustainable management of the challenging behaviour. Cognitive stimulation therapy is another means through which the individual can be engaged meaningfully and also improve their cognition and quality of life to some extent.
Related Reading: Coping with Difficult Dementia Behaviours
Enabling Environment: It is understood that a peaceful and relaxing environment can positively affect the mood and the subsequent behaviour of an individual with dementia. The spaces around them can be sensitized according to their needs and comfort. Assessing noise levels and temperature might be key in making the person feel comfortable. Adapting the environment to be simple and dementia-friendly (for example, by having signs to label toilets, bedroom, kitchen, etc.) can also reduce disorientation and increase autonomy.
Contributed by Ms. Malavika M. Nair and Ms. Aakriti Vig. Both of them are M.A. in Applied Psychology with specialization in counseling psychology at The Banyan Academy of leadership in mental health (TISS), Chennai, India
Download a detailed E-Book on handling Challenging Behaviours of Dementia brought to you by DEMCARES
If you have registered before, please make sure you are logged in.
Join our community on dementia here: https://www.patientsengage.com/communities/alzheimers-dementia

















