While fever is a normal response to infection, fever during cancer treatment needs to be taken seriously since the body’s immunity is compromised. Read on to understand how cancer treatment impacts immune systems, fever.
Fever or pyrexia is a higher body temperature than normal. It may be due to an infection from bacteria, virus, fungus, parasite or even inflammation due to a disease or trauma. Fever is caused by substances called pyrogens. Contrary to what one may believe, fever is a good symptom, it means that the body’s immune system is working hard to fight an infection. Our brain has a part called the hypothalamus that acts as a thermostat to regulate the temperature when it becomes too high by dilating the peripheral blood vessels (in the limbs) and therefore one feels colder when one has a fever.
Normal body temperature: In older adults >65, the normal body temperature tends to be lower.
| Normal Body Temperature | In Fahrenheit | In Celsius |
| Average | 98.6°F | 37°C |
| Lower | 97°F | 36°C |
| Upper | 99°F | 37.2°C |
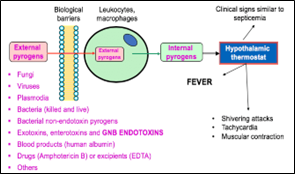
Source: http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/toxins10080331
Cancer, fever and immunity
Having cancer means overgrowth of cells of the body which leads to an invasion of organs in the body. It is caused by changes in the DNA. So, what makes it a menace? Fever in cancer can be because of an infection which can become life threatening really quickly because of low neutrophils (white blood cell) and immunity.
Cancer can lead to fever by these 3 mechanisms:
- By producing pyrogens and cytokines (both are fever causing substances).
- By leading to bacterial, viral or fungal infections that produce pyrogens. This could also be due to decreased immunity from the cancer itself which sometimes invades the bone marrow where the cells that fight infections are made or due to the various treatments offered for the cancer like anti-cancer medications, chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
- Having an impact on the hypothalamus.
Immunity is the body’s ability to fight infections and maybe of the 2 types:
- Innate immunity (present from birth): like the skin barrier, gut microbes that help prevent infection and aids digestion, urine flow that flushes the bacteria from the urinary tract etc. (biological barriers).
- Acquired immunity: acquired after infections when the body makes antibodies against the pathogen. It is also created artificially through vaccines.
Cells like white blood cells (leukocytes), B cells and T cells are the fighter cells that fight infections.
- White blood cells called neutrophils attack the pathogens and swallow them and kill them.
- B cells attack the pathogens by producing proteins called antibodies. They have memory and prevent future infections.
- T cells stimulate b cells to produce antibodies.
Many cancer treatments tend to reduce the neutrophil count. This is known as “neutropenia” and it affects the immunity, so the chances of infections increase along with an increase in the gravity of infection.
Note that there are some Cancers that present with fever as a symptom, these include:
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)
- Hodgkin lymphoma- sometimes may cause fever in cycles.
- Leukaemia
- Renal cell cancer
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Soft tissue sarcoma
- Adrenal gland tumours such as phaeochromocytomas
- Cancer of the hypothalamus like chordoid glioma
- Ovarian cancer
Cancers that usually don’t cause fever as a symptom:
- Breast cancer
- Lung cancer
- Bowel cancer
Fever during a cancer treatment:
- Most commonly caused by an infection due to lowered immunity and neutrophil count due to chemotherapy. Most commonly fungal infections.
- May sometimes be caused by inflammation.
- Some medications used for cancer treatment like gemcitabine, docetaxel, dacarbazine, and cyclophosphamide may also cause a fever.
Fever seen during remission:
- Most commonly caused by an infection due to lowered immunity.
- May sometimes be caused by inflammation.
When to visit or contact your oncologist when you have fever during a cancer treatment or remission:
- Temperature is 100.4’F or higher
- Fever with chills or shivering
- Dehydration (less urination, coated tongue, sunken eyes
- Cough or difficulty in breathing
- Excessive drowsiness
- Worsening symptoms or new symptoms adding on
- If your doctor has specifically told you to contact for certain cancers
What to do if you have a fever during treatment or remission:
- Measure your temperature every 3-4 hours and see a doctor if the temperature is >100.4’F
- Maintain good hydration
- Take rest
- Use acold cloth over your forehead, armpit and groin to bring down the temperature
- Avoid taking paracetamol or any fever medication without consulting your doctor
- Speak to your doctor about emergence of any new symptoms
- Eat a nutritious diet rich in proteins and antioxidants and vitamins
- Consume probiotics in food like yogurt
What steps to take to prevent fever in cancer:
- Wash your hands frequently. Hands are the quickest source of infection.
- Avoid coming in contact with people who have an active/acute illness (communicable/infectious disease).
- Avoid crowded areas with less ventilation as they become the source of airborne and droplet infections from people coughing and sneezing or contaminating surfaces.
- Avoid handling animal waste as that may be a potential cause of zoonotic (animal transmitted) diseases.
- Eat a well-balanced nutritious diet.
- Get adequate sleep.
- Indulge in activities that help reduce stress.
- Monitor your temperature regularly.
Tip: Ask your doctor when your white cell count is likely to be lowest as that is when you are most infection prone and need to be more cautious.
Post operative fever
In cancer patients, this can be of infectious or non-noninfectious origin.Infectious causes include preoperative and perioperative infections. Non Infectious causes include blood clots, inflammation, immunosuppressant medications and transfusion reactions. Fever can be acute (within first week of surgery) and subacute (within 2-4 weeks of surgery). They are due to infections like urinary infection, infection of the surgical site, pneumonia, IV line infections etc.
Bone Marrow Transplant fever
Fever is a common symptom that occurs after a bone marrow transplant due to an infection, chemotherapy, radiation or blood transfusion. Fever often occurs due to the lowered immunity from the radiotherapy and or chemotherapy before the transplant.
What to do if you have a fever after cancer surgery or a Bone Marrow transplant?
- Measure your temperature every 3-4 hours and see a doctor if the temperature is >100.4’F
- Maintain good hydration
- Take rest
- Use a cold cloth over your forehead, armpit and groin to bring down the temperature
- Avoid taking paracetamol or any fever medication without consulting your doctor
- Speak to your doctor about emergence of any new symptoms
What to expect for the diagnosis of cause of fever post operatively or after a bone marrow transplant?
- The doctor will take a history of your symptoms followed by a thorough physical examination, including inspection of the IV line and surgical site. This may be followed by some lab tests like:
- A urine test
- Echocardiogram
- Blood Test for sugar, liver function, complete blood count, inflammatory markers like ESR/CRP
- Fluid cultures
- Chest Xray/Ultrasound/CT scan
- Venous Doppler to check for Deep vein thrombosis
Word of caution:
All the information provided in this document is generalized and based on common medical cases observation. Every human body is individual in its ability to fight infections or withstand them and reacts differently to any treatment based on age, genetics, health status etc. Therefore, it’s important to listen to your doctor’s advice and ask the right questions for which this information may be helpful as a guide.
References:
- Cancer research UK. “the immune system and cancer.” Cancer research UK, cruk, 20 june 2018, www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/what-is-cancer/body-systems-and-c….
- ---. “the immune system and cancer.” Cancer research UK, cruk, 20 june 2018, www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/what-is-cancer/body-systems-and-c….
- CDC. “watch out for fever.” Preventing infections in cancer patients, 2024, www.cdc.gov/cancer-preventing-infections/patients/fever.html. Accessed 4 sept. 2024.
- ---. “watch out for fever.” Preventing infections in cancer patients, 2024, www.cdc.gov/cancer-preventing-infections/patients/fever.html. Accessed 4 sept. 2024.
- “does cancer cause a fever?” Www.patientpower.info, 10 mar. 2023, www.patientpower.info/navigating-cancer/does-cancer-cause-a-fever.
- “fever — the rules change after a cancer diagnosis.” Roswell park comprehensive cancer center, 20 sept. 2023, www.roswellpark.org/cancertalk/202309/fever-rules-change-after-cancer-d….
- “fever and infections | cancer-related side effects.” Cancer.org, 2021, www.cancer.org/cancer/managing-cancer/side-effects/infections/fever.htm…. Accessed 4 sept. 2024.
- “the cancer itself | coping physically | cancer research UK.” Www.cancerresearchuk.org, www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/coping/physically/fever/causes/ca….
- “why must cancer patients take fevers seriously?” Www.cohamed.com, www.cohamed.com/blog/fever-in-cancer-patients.