Fatigue, often confused with mere weakness, is now recognized as one of the most common symptoms of cancer itself as well as a side-effect of the treatment that a patient goes through. Often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed, it leads to a distress and affects daily living of the cancer patient. So how does one recognize it and what do we do about it. Sarika Mahajan, senior Physiotherapist with Tata Memorial Hospital helps us unpack this unvalued symptom for both patients and their care providers.
What does the term cancer fatigue mean? Is it different from fatigue in healthy people?
|
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) 2014 Guideline has defined “Cancer Related Fatigue (CRF) as a distressing, persistent, subjective sense of physical, emotional, and/or cognitive tiredness or exhaustion related to cancer or cancer treatment that is not proportional to recent activity and that significantly interferes with usual functioning”.
|
It simply means a feeling of extreme physical, emotional and mental tiredness, exhaustion or lack of energy. Caused by the disease itself or related to side effects of treatment, it is more pronounced with the advancement of disease or in the terminal stages of disease. It is one of the most distressing symptoms which can last for months or years following treatment completion and affects daily functioning in survivors causing harm to their quality of life. Normal fatigue or tiredness usually lasts for a short period of time and a person may feel completely normal with some rest, sleep and relaxation whereas CRF usually does not go away, unless the cause is treated.
What are the signs and symptoms of fatigue?
A person suffering from CRF may feel constant tiredness, lethargy, limited motivation, increased weakness, impatience, irritation, anxiety, nervousness, depression, sleepiness, decreased concentration, memory issues, social isolation.
Why is fatigue not easily diagnosed?
Fatigue is a subjective experience and cannot be measured. As a patient, you should report any symptoms of fatigue to your physician. It goes mostly underreported, as patients are unaware and tend to overlook how fatigue negatively affects their quality of life (QOL). There are many scales which are developed for assessing fatigue and multiple other symptoms but those are not freely available nor are they translated in Indian languages. Hence, it is important to identify and treat all physical, psychological and mental problems along with the disease.
When should a patient seek or be referred for a PT consult?
The cancer medical team will assess all patients at the baseline (beginning of treatment), every follow-up (active treatment) and during survivorship. As CRF is multifactorial, the cause needs to be ruled out by taking detailed history e.g. time of onset, aggravating and relieving factors, duration of fatigue etc. If as a patient, your fatigue is not relieved with adequate amount of rest and sleep, you should notify your doctor and see a physiotherapist.
What are the common causes of fatigue in cancer patients?
CRF is multifactorial in origin, relating to the effect of the tumor and anti-cancer treatments, as well as co-morbid conditions. Physiological factors that may cause fatigue include anemia, cancer therapy, cachexia and tumor burden. Psychological factors like anxiety, depression, difficulty sleeping have also shown to play an important role.
Is there a grading system for the fatigue levels? How do you assess the patients?
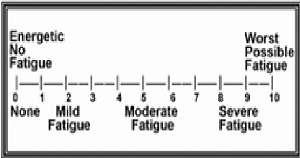
The best method for assessing fatigue is by self-reporting or by rating the fatigue on a numerical rating scale of 0 to 10, where 0 indicates no fatigue, 1-3 score denotes mild fatigue, 4-6 score denotes moderate fatigue and 7-10 score denotes severe fatigue.
What role does physiotherapy play in relieving fatigue?
Recent review of literature supports referring patients to physical therapy as a beneficial treatment intervention for cancer-related fatigue as it is an effective and efficient way to improve patient’s symptoms and positively improve the quality of life.
What exercises do you prescribe? Please explain the exercise and benefits of each.
Physiotherapists perceive CRF as a common problem, with management being based mainly on using and recommending exercise and teaching energy conservation techniques. Exercises are tailored to the patient’s needs to maximize its benefits in a variety of cancer populations, across all stages of the disease trajectory. Physiotherapists recommend the type, intensity, timing and mode of exercise based on the health status, disease trajectory, previous and/or current treatment, current fitness level and past/present exercise participation and preference in order to be safe and effective. Physical activity in the form of aerobic exercises, resistance exercises has proved to be effective, also improving psychological factors and quality of life.
For Moderate/Mild Fatigue - Start with low to moderate intensity exercise intervention and slowly increase its frequency, intensity and duration over a period of weeks. Moderate - intensity continuous exercise are more frequently advised and high-intensity continuous aerobic exercise use is rarely recommended.
For Severe Fatigue - Start with low-impact exercise, such as walking, bed and chair-based exercises, flexibility and stretching and an exercise bicycle. Comfortable or symptom limited low- intensity exercises and low to moderate aerobic interval training were commonly recommended.
Aerobic exercises
|
Aerobic exercises are defined as “the rhythmical contraction and relaxation of large muscle groups over a prolonged time for rehabilitation of cancer patients affected by the problem of energy loss”.
|
It is any type of workout that increases both heart rate and breathing; also referred to as Cardiovascular exercises.
Resistance exercises
It involves muscle contraction against resistance leading to improvement in muscular function and bone density. Resistance can be achieved by using dumbbells, or even bodyweight, resistance bands and weight machines. Low resistance training is proven to be safe, decreasing side effects, and improves QOL when performed during and following cancer treatment.
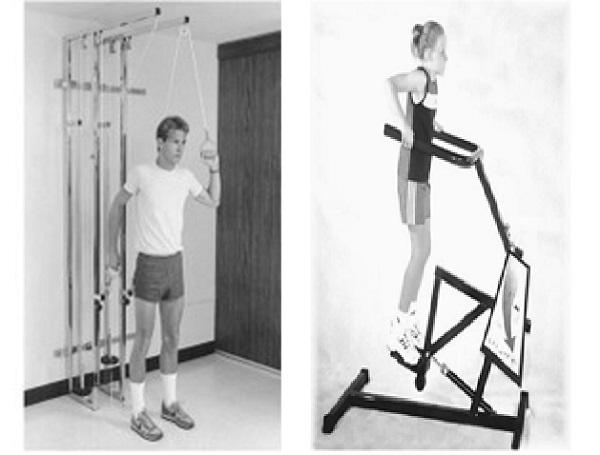

Source : Therapeutic exercise by Kisner and Colby 6th edition
|
Cancer patients can exercise from time of diagnosis till treatment end. Simplest of all is walking as it needs no prior testing or assessment. It is advised to walk at their own pace which can be gradually increased. Walk under supervision of a physiotherapist if there is a risk of injury or fall due to neuropathy or muscular weakness. It is recommended to maintain physical activity by doing moderate intensity exercises for 150 mins/week or 30 mins/day along with resistance exercises 2-3 times/week.
|
How do you determine the time duration of each exercise?
Based on the patient’s performance status (fatigue status, cardio respiratory function, disease status, type of cancer) and numerical rating scale (0-10 score), the physical therapist will make an individualized exercise plan (type, duration, frequency and time of exercise).
When is the best time of the day to do these exercises?
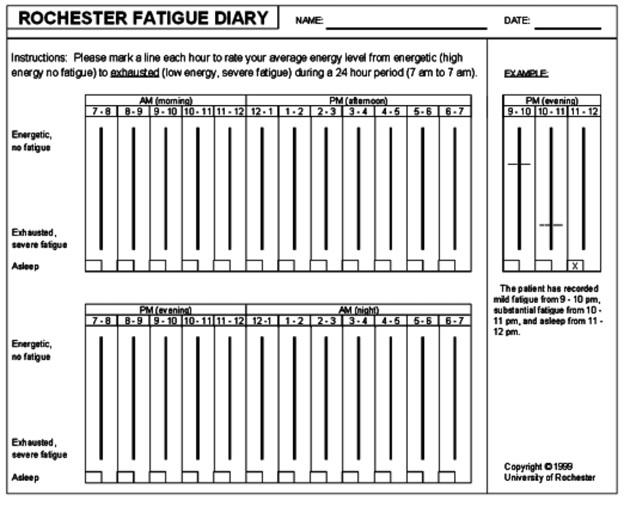
Identifying the patient's energy level by means of a diary helps the patient and therapist to find out their variation in energy throughout the day. A fatigue dairy can help to identify the time at which the patient has maximum energy and activities, e.g., bathing, wearing clothes etc. which trigger the fatigue. Keeping these things in mind, exercise recommendations are made. The Rochester fatigue dairy (see image) is one such diary that consists of 24 vertical bars representing hours of the day. Upper end of each bar indicates no fatigue and the lower end indicates severe fatigue; the box at the bottom of the bar is to be ticked if the patient sleeps during those hours. This helps identify patients' sleep time and variation in fatigue through the day.
When and how much should a patient rest and sleep?
Though sleeping at all times is not recommended, it has also proven beneficial to reduce cancer fatigue. If sleep is frequently interrupted, anxiety and depression is affecting sleep it is important to look into it. Pain, nausea, vomiting, breathless and some medications can also affect sleep.
If patients are too sleepy during the day, it could be due to poor sleep at night. Naps are recommended for no more than 30 mins. Consult the treating physician if there is no improvement in sleep.
Is massage suggested. If so, what type of massage?
Massage is of different types: Swedish massage therapy, light touch massage, deep touch. Massage stimulates the skin which helps to release the happiness hormone i.e., endorphin, which helps people relax. In addition, it improves circulation which in turn reduces inflammation, muscle soreness, reduces anxiety and depression. Swedish massage has proven to be beneficial for reducing fatigue in two studies conducted on breast cancer patients.
In your opinion, what are the common challenges/issues faced by patients with cancer fatigue?
Common challenges/issues faced by patients with CRF are inability to perform activities of daily living, social interaction, mood swings, memory lapses, along with monetary and job issues. Medically, they may face a spectrum of problems such as cardiac/endocrine/pulmonary/ renal dysfunction, anemia, arthritis, neuromuscular complications, pain, infections, and nutritional deficiencies.
Any advice for patients and their care providers? Devices or apps that are useful, daily routine tips, etc?
For patients - Asking for help is from friends and family members to prepare meals, clean the house, or run errands is advisable. Return to normal activity as soon as possible during and following treatment. Some exercise is better than none. Start slowly and progressively increase. Strive to achieve the recommended levels of exercise. See a medical professional if any questions or concerns arise. See a physiotherapist working in oncology for assistance with exercise testing, prescription and monitoring.
As a caregiver try not to encourage the patient to rest more, in fact they have to be pushed to maintain self-care, routine activity (as was before the diagnosis of cancer). Help the patient set up a routine for activities during the day.
Devices or Apps - There are significant advancements in fatigue monitoring with innovative technology in the past decade. These technologies determine fatigue related impairment by measurement of brain activity (electroencephalogram), behavioral symptom capture (eye behavior, gaze direction etc.), and heart rate variability.
App-based technologies and devices are currently not available in India and they have not been used nor tested (especially devices) on patients with Cancer related fatigue, hence cannot be recommended.
References:
Bower J. E. (2014). Cancer-related fatigue--mechanisms, risk factors, and treatments. Nature reviews. Clinical oncology, 11(10), 597–609. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.127
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (2003). Cancer-related fatigue. Clinical practice guidelines in oncology. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network : JNCCN, 1(3), 308–331. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2003.0029
Pattanshetty, Renu & Chopde, Ceona. (2016). Role of Physiotherapy in Cancer-Related Fatigue in Cancer Survivors - A Narrative Review. Journal of Novel Physiotherapy and Physical Rehabilitation. 10.17352/2455-5487.000032.
Donnelly, C. M., Lowe-Strong, A., Rankin, J. P., Campbell, A., Allen, J. M., & Gracey, J. H. (2010). Physiotherapy management of cancer-related fatigue: a survey of UK current practice. Supportive care in cancer: official journal of the Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer, 18(7), 817–825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-009-0715-2
Kuehn, M., Wypyrsczyk, L., Stoessel, S., Neu, M. A., Ploch, L., Dreismickenbecker, E., Simon, P., et al. (2023). Physical Activity as a Treatment for Cancer-Related Fatigue in Children, Adolescents and Young Adults: A Systematic Review. Children, 10(3), 572. MDPI AG. Retrieved from http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/children10030572
Kinkead, B., Schettler, P. J., Larson, E. R., Carroll, D., Sharenko, M., Nettles, J., Edwards, S. A., Miller, A. H., Torres, M. A., Dunlop, B. W., Rakofsky, J. J., & Rapaport, M. H. (2018). Massage therapy decreases cancer-related fatigue: Results from a randomized early phase trial. Cancer, 124(3), 546–554. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.31064
Fisher, M. I., Cohn, J. C., Harrington, S. E., Lee, J. Q., & Malone, D. (2022). Screening and Assessment of Cancer-Related Fatigue: A Clinical Practice Guideline for Health Care Providers. Physical therapy, 102(9), pzac120. https://doi.org/10.1093/ptj/pzac120
Lewandowska, A., Rudzki, G., Lewandowski, T., & Rudzki, S. (2020). The Problems and Needs of Patients Diagnosed with Cancer and Their Caregivers. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010087
Schwid, S. R., Covington, M., Segal, B. M., & Goodman, A. D. (2002). Fatigue in multiple sclerosis: current understanding and future directions. Journal of rehabilitation research and development, 39(2), 211–224.
Bower, J. E., Bak, K., Berger, A., Breitbart, W., Escalante, C. P., Ganz, P. A., Schnipper, H. H., Lacchetti, C., Ligibel, J. A., Lyman, G. H., Ogaily, M. S., Pirl, W. F., Jacobsen, P. B., & American Society of Clinical Oncology (2014). Screening, assessment, and management of fatigue in adult survivors of cancer: an American Society of Clinical oncology clinical practice guideline adaptation. Journal of clinical oncology :official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, 32(17), 1840–1850. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.53.4495

Sarika Mahajan, senior Physiotherapist with Tata Memorial Hospital