Urinalyis or Urine Tests are often prescribed by doctors to detect certain conditions. Dr. Shital Raval explains what the results of a urine test mean, and the right way to collect a urine sample.
#KnowYourTest Series
What is urinalysis?
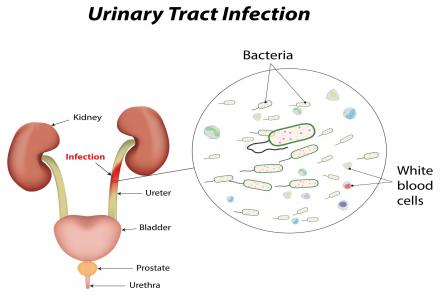
Urinalysis or Urine tests are a group of tests conducted on your urine that a doctor may prescribe. These tests are indicators of acute or chronic conditions or illnesses. It can also help detect insidious infections like urinary tract infections or UTIs, diabetes and organ malfunctions or organ failures in their early stages.
How is urine analyzed?
There are three ways to analyze the urine:
- Visual test
- Chemical/Dipstick test
- Microscopic test
What do the results mean?
1) In visual observation, the color, clarity and odor of the urine is checked. Normal fresh urine should be pale and almost clear. Darker yellow urine indicates that body is dehydrated and that the patient does not consume enough water. Note that yellow urine is also seen in people who have multivitamins and certain other medications. Red urine can be due to presence of blood or ingestion of red dye or foods such as beets, rhubarbs, blueberrie,s etc. Yellowish brown or greenish brown color can be a sign of bilirubin in the urine. The clarity of the urine is noted as clear, slightly cloudy, cloudy or turbid. If the urine is cloudy or frothy, it can indicate presence of mucus, sperm in men, urine crystals, blood cells or excess protein. Fresh urine would commonly have a mild odor, however if it has a fishy smell it may indicate a UTI. A “pear drop” or acetone-like smell may be indicative of ketones in the urine, suspecting Ketoacidosis in a diabetic patient. Here is a detailed colour chart that indicates what the colour of your urine may mean.

2) A chemical exam tests for about 9 substances that can provide clues about general health and presence of any illness. Ready test strips with test pads are available that can be dipped into the urine to check for presence of certain chemicals. The chemical reactions change the colours of the strip within seconds. The degree of colour change indicates whether a small or large amount of that substance is present. The most common chemical reactions tested for are:
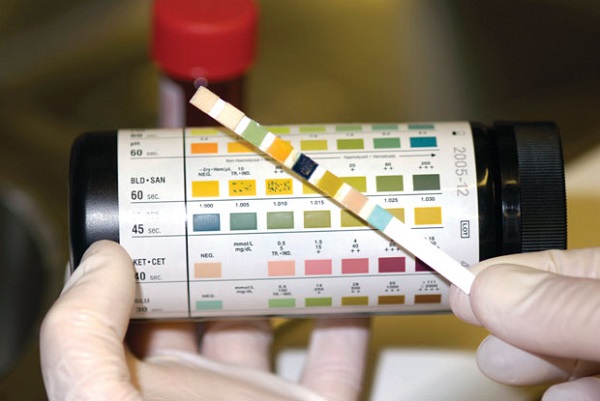
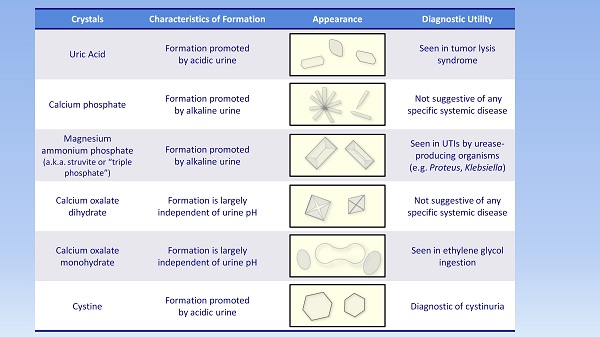
- Acidity (pH) shows the amount of acid or alkaline in the urine. Depending on the acid-base status of the body, the pH can range from 4 to 8. Normally urine pH is around 6. Alkaline urine may be due to an UTI or a diet rich in dairy & vegetables, whereas acidic urine is an indicator of high-protein diet or kidney stones (since it causes formation of crystals). Crystal can be further investigated under microscopy to detect exact cause and conformation of the crystals. Here is how crystals are analysed:
- Specific gravity (SG) measure the concentration of the urine and in turn shows how hydrated a person is. It normally falls between 1.001 to 1.035. If the urine is highly concentrated, it can indicate dehydration. If the urine is found to be very dilute, it can be due to high fluid intake, diabetes insipidus, high calcium levels, kidney diseases or low levels of anti-diuretic hormone.
- Protein molecules are normally too large to pass down into the urine. If there is protein present, also called proteinuria, it means there is damage to the kidney’s filtration system, or it is hypertension, diabetes or pre-eclampsia.
- Bilirubin is an indicator of broken red blood cells, which are not being removed by the liver, thus pointing towards liver disease, bile duct blockage, gall bladder stones etc.
- Nitrites are only present if bacteria are converting nitrate to nitrite. Thus it may indicate an underlying infection of the urinary tract.
- Glucose is usually a sign of diabetes, but also be seen in patients who are pregnant or on corticosteroids.
- Ketones are molecules that form when there is abnormal breakdown of fat usually from fasting, starving, prolonged vomiting or diarrhea, or those on a specific diet or with uncontrolled diabetes. In diabetic patients, high ketone levels can make the blood acidic and lead to a serious complication called Diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Leukocyte esterase is a test for presence of white blood cells or pus cells (also called pyuria) which are signs of an infection.
- Blood (also termed as hematuria) can be a sign of infection, kidney disease, kidney stones, prostate cancer, certain medications or even heavy exercise.
3) Microscopic examination looks at the urine under a microscope to identify and count all types of cells, crystals or any bacteria present. It is usually ordered if the vial or dipstick exam is found to be abnormal. It checks for five components:
- Red blood cells (RBCs) - a large number of RBCs can indicate presence of blood in the urine, this is called hematuria. Blood can come from the kidney, the ureter, the bladder or the urethra. Hematuria can be due to UTI, kidney infections, kidney stones, kidney inflammation called glomerulonephritis, enlarged prostate, prostate cancer, sickle cell anemia etc. Finding of RBCs is not uncommon but does require further investigation.
- White blood cells (WBCs) when seen in the blood can indicate an inflammation or infection in the urinary tract. If bacteria are also present, it is likely to be a UTI. Sometimes, WBCs can be seen due to contamination by vaginal secretions.
- Bacteria, yeast or parasites should not be normally seen if the urine is collected as “clean-catch” sample (see below). Microbes if seen are reported as few, moderate or many as seen under high power field. Bacteria can indicate a urinary tract infection (UTI), which if untreated can lead to kidney infection (pyelonephritis). Yeast is commonly seen in women who have a vaginal yeast infection. The parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, is indicative of a parasitic infection (usually in women) and is sent for Trichomonas testing for confirmation.
- Crystals. Non-specific crystals in small amounts, or if not tested freshly (within 1-2 hours, or kept in cold temperatures, or with low pH are considered normal. However, specific crystal formation is seen as a result of types of kidney stones. Certain antibiotics and anti-viral drugs also cause crystals to form in the urine.
- Epithelial cells are cells that line the bladder and urethra, and are seen in case of infection, inflammation and malignancies. They are reported as few, moderate or many as per low power field.
What are the different types of urine samples?
Different urine sample may be prescribed for a patient depending on symptoms and suspected illness. Here are the different test samples a doctor may ask for:
- 24 hour collection: urine is collected for 24 hours since the chemicals may change in the urine. This is commonly used to detect steroid use, white blood cells, electrolytes and osmolarity (solute/water ratio) of the urine.
- First morning sample: is mostly used for pregnancy testing by looking for Hcg levels.
- Fasting sample: is used to check for glucose levels.
- Midstream urine sample: is required for bacteria culture.
- Random sample: is used for most screening purposes.
- Catheter sample: is collected from a patient who has a catheter, suspected of having a UTI.
What is the correct way to collect a urine sample?
The right way to provide a urine sample is quite simple but not often known. It is known as the Clean-Catch method. This method makes sure that there is no contamination from normal bacteria which live on the skin or vaginal secretions. Patients should be instructed on how to do it.
For people unable to provide a sample this way (babies, hospitalized or comatose patients), a catheter is inserted to collect the urine. If you are menstruating, do inform your doctor. On average, a person produces 750 to 2000ml of urine in a day. For a urine sample, only 30-60 ml of urine is sufficient.
Here are the steps for midstream clean-catch urine sample collection:
- Wash the area around the urinary opening with either a cleansing wipe or water and a mild soap. For men, this means the tip of the penis and for women, the external labia should be spread and wiped front to back.
- Start to urinate and stop midstream.
- Collect about 30-60 ml, or fill the container till 3/4ths.
- Secure the lid of the container.
- Wash your hands and place the container in a bag to be handed over.
Images from the internet