Fever is a common symptom. It is usually a symptom that the body is fighting an infection. However there are times, it should be taken seriously. Here the PatientsEngage team helps you understand the types and causes of fever and when to see a doctor.
All of us have experienced a fever sometime in our lives. Fever is actually a good symptom as it indicates that our body is fighting an infection in our body. Our average normal body temperature is 98.6° Fahrenheit or 37° Celsius. The baseline body temperature may vary by 1^∘ F/-17.2ºC or more and it fluctuates through the day. It is usually lower in the morning and higher in the evening. It is higher during the ovulation phase of the menstrual cycle in females and when you are exercising. A fever is when the body temperature is above 100.4°F/38ºC in adults and in children, higher than 99.5°F/37.5ºC (taken orally), 99°F/37.2ºC (taken under the arm), or 100.4°F/38ºC (taken rectally).
Types of Fever
Based on the fluctuation of temperature:
- Intermittent fever is when the fever fluctuates between normal body temperature and higher temperature than normal through the day.
- Remittent fever means that the fever fluctuates >1^∘ C) throughout the day but never touches the baseline normal temperature.
- Hectic fever is when the temperatures has major fluctuations throughout the day, with a difference of at least〖2.5〗^∘ F/-16.3ºC between the lowest and highest temperature of the day. A remittent or intermittent fever can also be considered hectic.
- Continuous (or sustained) fever is when the body temperature stays elevated throughout the day with little fluctuation (<1^∘ C).
- Relapsing fever - This type is an intermittent fever that spikes again after days or weeks of having a normal body temperature.
Read here about the connection between cancer and fever: https://www.patientsengage.com/conditions/fever-and-cancer
Based on the duration:
- Acute fever has a sudden onset and is a short-term increase in body temperature. It lasts for a few days, typically up to 7 days like in viral upper respiratory tract infection.
- Subacute fever is a persistent, low-grade fever that lasts longer than an acute fever, typically up to 14 days as seen in typhoid.
- Chronic fever lasts for an extended period, often more than 2 weeks as in tuberculosis, cancer, HIV etc.
Based on grades
- Low grade fever is when the temperature is slightly above normal, typically between 99.1°F/37.2ºF and 100.4°F/38ºC and is often a sign of a mild illness or activation of the immune system.
- High grade fever is when the temperature is between 102.4°F/39.1ºC and 105.8°F/41ºC and is often a sign that the body is fighting a significant infection. Some viral infections may cause high fever too.
How to measure fever?
Use a digital thermometer. Place the thermometer in the mouth, armpit, or rectum for a reading. Never measure fever with your hand. Hand cannot accurately quantify the body's precise temperature change, unlike a thermometer, and is easily influenced by the temperature of the surrounding environment or the person's own hand temperature.
Rectal is the most accurate, especially for babies less than a year, while underarm is the least accurate but a safe and convenient method. Oral method is the most used for older children and adults.
- Oral is best for children older than 5 years and adults. Place the thermometer tip under the tongue and close the mouth, breathing through the nose. Wait for the beep, then read the temperature.
- Underarm or Axillary is the best easiest for all ages but is the least accurate. Ensure the armpit is dry. Place the thermometer's tip in the armpit, making sure that it’s touching the skin. Press the arm firmly against the side of the chest to hold it in place. wait for the reading.
- Rectal is best for infants and small children, as it is the most accurate method. Place the thermometer tip in the anal area and hold till it beeps. This method is often recommended for children under 3 months old and is the most accurate for children up to 5 years old.
- No-touch thermometers can measure temperature through either the ear or forehead using infrared technology. For the forehead hold the thermometer perpendicular to the centre of the forehead, between the eyebrows and maintain the distance of about 1-5 cm from the skin. Do not touch the skin. Make sure that the forehead is clean, dry, and not blocked by hair, headbands, or hats. For the ear, remove the probe cover and insert the probe into the external ear canal. In both cases press the button to take the reading, which is instantaneous.
Differences between the methods: A rectal temperature reading will be around 1°F (0.6°C) higher than an oral temperature. An underarm temperature will be around 1°F (0.6°C) lower than an oral temperature.
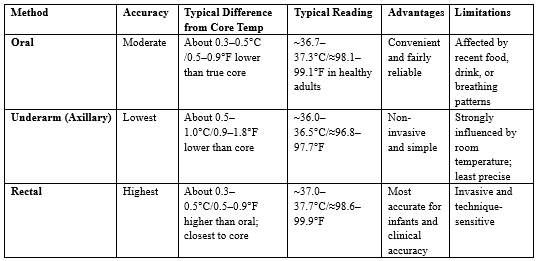
| Method | Accuracy | Typical Difference from Core Temp | Typical Reading | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral | Moderate | About 0.3–0.5°C (0.5–0.9°F) lower than true core | ~36.7–37.3°C (~98.1–99.1°F) |
Convenient and fairly reliable | Affected by recent food, drink, or breathing patterns |
| Underarm (Axillary) | Lowest | About 0.5–1.0°C (0.9–1.8°F) lower than core | ~36.0–36.5°C (~96.8–97.7°F) |
Non-invasive and simple | Strongly influenced by room temperature; least precise |
| Rectal | Highest | About 0.3–0.5°C (0.5–0.9°F) higher than oral; closest to core | ~37.0–37.7°C (~98.6–99.9°F) |
Most accurate for infants and clinical accuracy | Invasive and technique-sensitive |
Symptoms associated with fever
- Chills or shivering
- Back pain or pain behind the eyes
- Sweating
- Headaches
- Body aches
- Fatigue
- Feeling dehydrated and or dizzy
- Loss of appetite
- Flushed complexion/hot skin.
What is a febrile seizure? Some children have a side effect of fever known as febrile seizures. Febrile seizures are caused by a rapid increase in body temperature, typically due to a viral or bacterial infection, and a child's developing brain reacting to the high fever. This happens in 2% to 4% of children under the age of five years. Some seizures may cause involuntary jerking movements and when this happens as with any fits/seizures, lay your child on their side, protect their head with something soft and do not put anything in their mouth. Seek medical help.
Causes of fever
A fever occurs because the immune system is fighting a viral, bacterial, or some other type of infection (usually the ear, throat, skin, kidney, or bladder). Other issues that affect the immune system may also cause fever:
- Vaccination
- Autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
- Inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatic fever
- Neurological issues like brain injury
- Certain cancers like Hodgkin lymphoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Acute leukaemia, Chronic leukaemia, Renal cell carcinoma, Liver cancer (especially with metastasis), Bone sarcoma
Pancreatic cancer. Read more about cancer and fever here - Medications like some antibiotics (Penicillin, cephalosporins, and sulfa drugs), drugs used for seizures like phenytoin, drugs used for heart conditions (procainamide, clonidine), diuretics etc.
Read here about the connection between cancer and fever: https://www.patientsengage.com/conditions/fever-and-cancer
Home remedies to try for a fever
- Most people get better with rest, fluids, and fever-reducing medications (paracetamol and ibuprofen).
- When you have a fever, wear light clothing to help your body cool down. You may use a light blanket if you have chills but avoid heavy blankets or layering clothes as that traps heat and does not allow the temperature to come down.
- Keep the person in a well-ventilated room, with low fan speed or comfortable A/C temp (around 24-26ºC)
- Sponge the body with cool (not cold) water for temporary relief. Avoid cold baths, as they can cause shivering and trap heat.
- One may apply cooling gel patches on the forehead. They offer surface cooling and a soothing sensation, though they don’t change core temperature.
- Nutrition matters. Mild, easy foods—soups, broths, porridge—support energy without taxing digestion.
When to see a doctor
One should see a doctor if a person has a fever plus any of these symptoms.
- sunburn
- chest pain
- rapid or shallow breathing
- shortness of breath or breathlessness
- cough with thick yellowish/greenish phlegm or blood.
- bluish/greyish discoloration around the lips or fingers
- a severe headache
- intolerance to light
- a severe or worsening rash
- neck stiffness
- confusion
- excessive drowsiness
- loss of consciousness
- signs of severe dehydration like dry coated mouth and tongue, decreased urination.
- seizures or fits
- temperature >=104°F/38ºC that does not reduce with paracetamol or ibuprofen
- fever lasting > 5 days.
- Persistent low-grade fever should not be ignored either
For babies, watch out for:
- any fever in babies less than 12 weeks old
- sunken eyes, a soft spot on top of a baby’s head, or no tears when crying.
- rash or purple spots that do not fade when pressed along with fever.
- persistent temperature above 104^∘ F/40^∘ C
- fever with no apparent reason, like a cold or flu.
- child appears very inactive/floppy and or is unusually sleepy or irritable.
- seizure or fits.
- fast and or shallow breathing
Fever in elderly:
Fever in older adults needs a bit more vigilance because their immune responses can be muted, and even a mild temperature rise may signal something significant. Keep an eye on subtle changes. Older adults sometimes show infection through confusion, lethargy, poor appetite, or weakness rather than a dramatic temperature spike. A rise of even 1–1.5°C above their usual baseline matters. Hydration is essential. Dehydration sets in quickly with age and can worsen fever. Small, frequent sips of water or oral rehydration solutions work better than large gulps. For the elderly we need to mindful, Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is typically the safest option, but dosing must match kidney and liver status. Anything more complex should be handled by a doctor, fever lasting more than 24–48 hours, or fever paired with confusion, chest pain, difficulty breathing, severe dehydration, or very low energy, calls for medical evaluation. The key with older adults is to pair temperature monitoring with awareness of behaviour and cognition, since these often shift before the thermometer does.
What to expect at the doctor’s office
The doctor will measure temperature of the patient and other vitals like blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation. They will take a detailed history of any associated symptoms to look for any indication of an infection. This may be followed by blood tests (Complete blood count, inflammatory markers (CRP/ESR), Malarial Ag, Typhi Dot, Dengue serology, liver function test, urine test, blood culture etc).
If any suspicion of infection is there then additional tests/imaging like chest Xray (for suspected lung infections), otoscopy (suspected ear infections), swab from throat or skin lesions for culture may be sent.
How to prevent fever
As discussed above, fever happens when one acquires an infection. So, to prevent fever one must prevent infections which can be done by:
- wash your hands regularly with soap and water or use a hand sanitizer.
- avoid touching the face with unwashed hands.
- clean and disinfect surfaces in your house like door handles etc. regularly.
- avoid close contact with people who are sick.
- stay updated with your vaccinations.
References
- Brazier, Yvette. “Fever: What You Need to Know.” Medicalnewstoday.com, Medical News Today, 5 May 2020, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/168266#summary.
- Cleveland Clinic. “Fever: Symptoms, Causes, Care & Treatment.” Cleveland Clinic, 31 May 2023, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/10880-fever.
- “Fever: Symptoms & Causes.” NewYork-Presbyterian, www.nyp.org/primary-care/fever.
- Mayo Clinic. “Fever - Symptoms and Causes.” Mayo Clinic, 2022, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/fever/symptoms-causes/syc-203527….