
Colorectal cancer is the 4th most common cause of deaths related to cancer worldwide. Lynch syndrome or HNPCC is one of most common genetic causes of Colon cancer. Here are a few questions to better understand Lynch syndrome and how we can screen for it.
1. What is the Lynch syndrome? Which genes are involved?
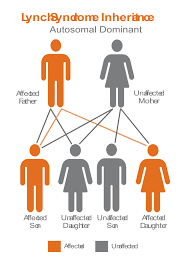
Lynch Syndrome is also known as hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer or HNPCC. It has a genetic disposition, hence the term hereditary and is known to be associated or the causative factor for various cancers including endometrial (second most common), ovarian, stomach, small intestine, hepatobiliary tract, upper urinary tract, skin and brain. It is an autosomal dominant genetic condition, which means that the gene defect can be passed down to the child even if only one parent has the mutated gene. Just one copy of the mutated gene is sufficient to develop cancer. Gene mutation is the permanent alteration in the DNA sequence that makes up a gene. Individuals who are carriers of such a mutated gene have a higher than normal chance of developing colorectal and the various cancers mentioned above, often at a young age. The early age onset, sporadic occurrence and right-sided colon lesions are discovered to be characteristic to Lynch syndrome. [Image result for lynch syndrome]
Genes currently known to be susceptible for Lynch syndrome include MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, and EPCAM.
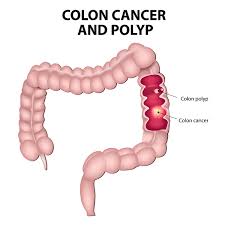
2. What are signs and symptoms of Lynch syndrome?
It is recommended that one watch out for any signs and symptoms of colon and endometrial cancer. People with Lynch syndrome have the following risk factors:
- Personal history of multiple gastrointestinal polyposis.
- History of colon or gastrointestinal cancer at a younger age, especially before age of 50 years.
- Personal history of any of the following cancers: endometrial cancer, ovarian cancer, kidney cancer, stomach cancer, small intestine cancer, liver cancer, sweat gland cancer (sebaceous carcinoma), skin or brain.
- Family history of colon or endometrial cancer under the age of 50.
- 1 or more 1st or 2nd degree relative with colorectal or Lynch syndrome associated cancers.
- 2 or more 1st or 2nd degree relative with colorectal or Lynch syndrome associated cancers.
3. How common is the Lynch syndrome in India?
There are several inherited syndromes that can lead to increased risk of colon cancer, of which Lynch syndrome is the most common.
Statistics says that approximately 3 out of every 100 colon cancers are due by Lynch syndrome. In India, the annual incidence rate of Colon cancer is 4.4 per 100,000 in men and 3.9 per 100,000 in women. Approximately 5% of all colon cancers are attributed to genetic predisposition of Lynch syndrome.
4. Does Lynch syndrome affect every generation?
Yes. It does not skip generations. Both sexes can have Lynch syndrome and it may pass to any of their children.
5. How can a mother prevent passing on the gene to her child? How does preimplantation genetic diagnosis work for Lynch syndrome?
Mother can prevent passing unwanted genes to her child by doing preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD). Preimplantation genetic diagnosis is the procedure used to identify any genetic defects in an embryo. Embryos are usually made via the in vitro fertilization (IVF), tested at day 5 and only the desired embryos free of genetic problems are implanted into the uterus. Since the procedure is carried out before implantation, a couple has the choice of whether they want to start the pregnancy or not.
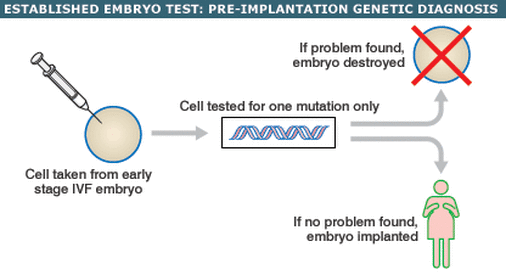
PGS or preimplantation genetic screening, is a procedure where all the embryos (produced by IVF) are checked for genetic diseases, so that the best embryo is then selected.
6. How is Lynch syndrome diagnosed?
After the tumor has been found via physical examination and colonoscopy, Lynch syndrome can be confirmed via tumor tissue testing from a biopsy. This is carried out for any individual who is suspected of having Lynch syndrome.
The two tumor tissue tests available are:
- Microsatellite instability (MSI) test where a dye is used to check for missing proteins.
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC) test determines instability in the DNA sequence.
Genetic testing of blood samples is commonly done to check for heritable mutations. Molecular genetic testing is necessary to confirm diagnosis of Lynch syndrome.
7. When and when should one start screening for it?
Families with Lynch syndrome and family members tested positive for gene mutation and those who have not been tested, should start colonoscopy screening during their early 20s, or 2 to 5 years younger than the youngest person in the family with a diagnosis (whichever is earlier).
- Colonoscopy should be done every 1 or 2 years. If there are any polyps present, they can be detected and removed. This helps find any early cancers too. People known to carry one of the gene mutations may also be given the choice of having surgery to remove most of the colon as a prophylactic measure.
- Women are also recommended to inform their Gynecologist and get a transvaginal ultrasound or endometrial biopsy done every year after the age of 30.
8. If a person has been detected with the HPNCC genes, what preventive/ prophylactic measures are offered to the person?
- Subtotal colectomy with ileorectal anastomosis (i.e. removal of subtotal colon and to join with rectum) and after that there is surveillance for rectum.
- Or total colectomy with permanent ileostomy (removal of entire large colon and small bowel is put outside abdominal wall to pass stool and flatus permanently). This operation may be considered for prophylaxis in selected mismatch repair (MMR) gene mutation carriers.
- Women may choose to have a hysterectomy (removal of the womb) or oophorectomy (removal of the ovaries). Such measures are recommended only after women have completed their families and do not prefer regular screening.
9. How much does genetic testing cost?
Testing of MLH1 is around 30,000/ rupees in India. If you have Lynch syndrome, each of your children have a 50% chance of acquiring the mutated gene. Children over the age of 18 can undergo genetic testing.
10. Can Lynch syndrome also cause Breast cancer?
The estimates of an increased risk of breast cancer in Lynch syndrome is relatively small compared with the increased risks observed for colorectal and endometrial cancers.
It has a risk of around 12%.
11. What is the prognosis for Lynch syndrome-associated cancers?
Prognosis for Lynch Syndrome is,
- Ten-year survival was 87% after any cancer.
- 91% if the first cancer was colorectal.
- 98% if endometrial and 89% if ovarian cancer..
References:
- Indian Council of Medical Research http://www.icmr.nic.in/guide/cancer/Colorectal/
- https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/lynch-syndrome
- MedIndia, network for Health. https://www.medindia.net/patientinfo/lynch-syndrome.htm
- American Pregnancy Association. www.americanpregnancy.org
















