Do cardiac tests like CAT Scan, Angiogram, MRI and Thallium Scan confuse you? What does each of them tell the Cardiologist? Dr. Shital Raval decodes this complex maze of tests so you can understand the purpose of each of these cardiac tests and why they have been prescribed.
When it comes to the matters of the heart, you can never be too careful. Your doctor will assess your symptoms, ask about your medical and family history and perform a physical examination before prescribing any cardiac tests. The tests you will be prescribed by your Cardiologist will depend on your symptoms and suspected heart condition. As a first line of testing or routine testing, most patients are asked to undergo:
- Blood tests can provide information on blood cells, minerals and hemoglobin.
- Chest X-ray helps check on the general size and structures of the heart & lung.
- Electrocardiogram or ECG is the live recording of the electrical activity of the heart.
- Stress Test aims to check how the heart functions when forced to work harder & faster.
- Blood pressure monitoring is measurement of BP over 24 hours.
- Echocardiogram is the ultrasound of the heart.
- Colour Doppler is to check for speed & direction of blood flow in the blood vessels.
If any of these tests are found to give abnormal or uncertain results, you will be asked to do further testing.
The second line of tests includes:
I. Holter monitoring
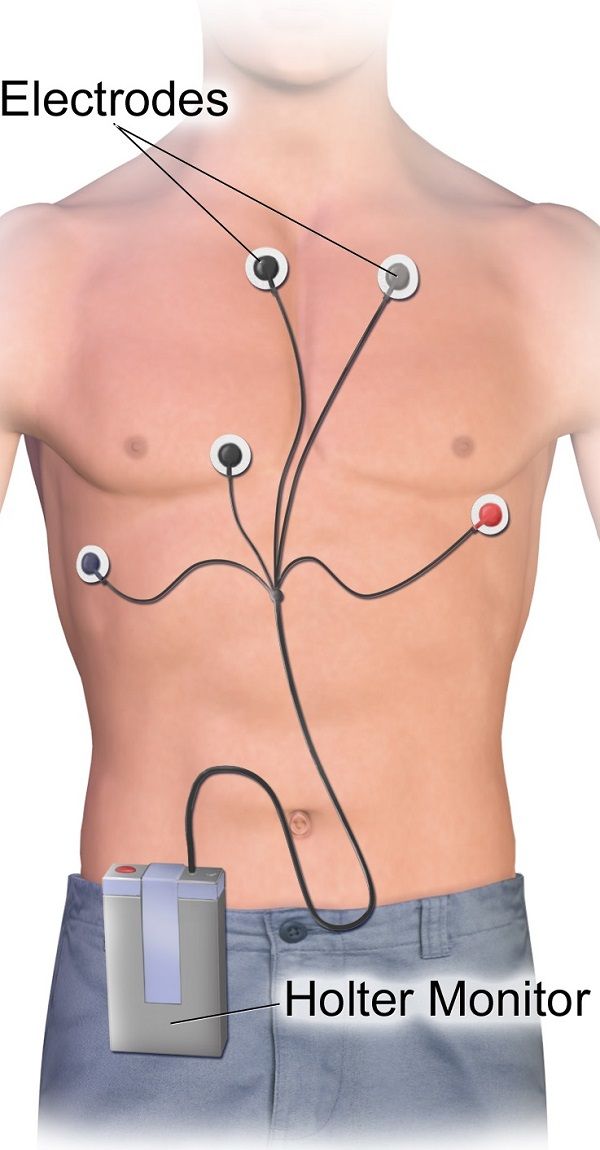
A holter monitor is a portable battery operated device that continuously records a person’s electrical activity (rate and rhythm). It is used to detect irregularities or arrhythmias in the heart rhythm that a routine ECG is unable to provide.
Your doctor may ask you to be fitted with a holter monitor for 24 to 48 hours, so that he can check for any abnormalities in your reading. It is attached to around the chest or shoulder via a strap. Tiny leads are connected to electrodes that are stuck onto the skin of the chest. These leads transmit the electrical activity and record this data. The monitor is to be worn day and night for the hours indicated, and a log of any cardiac symptoms along with time and activity is to be recorded. The data is then scanned by a technician and interpreted by the Cardiologist.
II. Thallium Scan
Also known as the Myocardial perfusion scan, it is used to see how well blood flows to the heart. A thallium dye, which is a radioactive substance, is inserted into a vein and a scan takes images to follow how well blood is reaching the heart muscle. It can also be done when the doctor wants to check on the coronary blood supply when the heart is made to work faster or harder. This is done by injecting a stimulant drug or making the patient exercise. It is an alternative test done when the patient is unable to undergo an exercise test or when specific information is required that a treadmill test cannot provide.
III. Electrophysiology Studies or EPS
EPS is the study of the electrical conduction of the heart. Patients who complain of palpitations, unexplained fainting or abnormal heart rhythms are recommended this test. It is done to detect the causes of abnormal heart rhythms (brady or tachycardias), and also to check if medications are effective in controlling these arrhythmias.
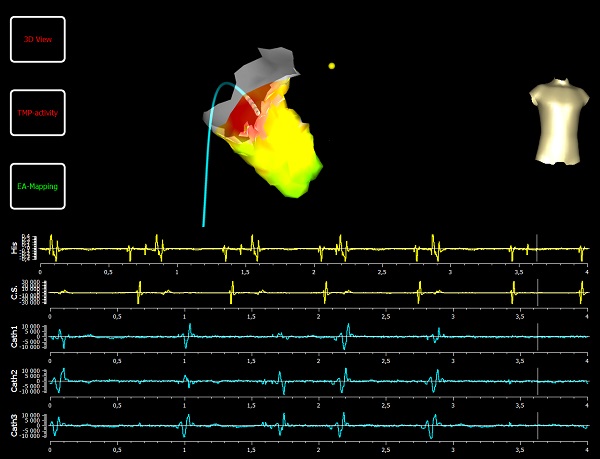
This is a minor invasive test that requires a day or two stay at the hospital. Specific leads (inserted through the groin) are placed within the heart to record all electrical conduction by the heart. It can generate a 3D mapping of the heart and its chambers. If any abnormality is found, radiofrequency energy can be used to ablate/remove the culprit area.
IV. Cardiac Catheterization
An angiogram or a cardiac catheterization is an invasive test that allows the doctor to see the blood flow and pressure in the body’s blood vessels and in the heart. It helps see how well the heart is functioning and if there is any disease of the heart muscle, valves or the coronary arteries (arteries that supply the heart).
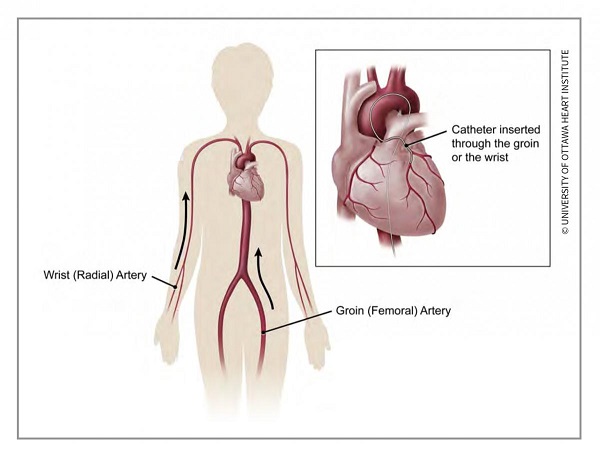
A thin tube called the catheter is inserted via a transparent sheath into an artery or vein of the groin, neck or arm. With the aid of special imaging called Fluoroscopy (much like an X-ray movie), the catheter is guided all the way to the heart. A contrast dye can be injected at the time of catheterization to further view the blood vessels via X-ray imaging. This is called a Coronary Angiogram or Angiography and is the standard test for identification of any blockages in the coronary arteries (also called Coronary artery disease or CAD).
In case of any blockage found, stents can be inserted at the same time or at another scheduled time to open up the narrowed/obstructed arteries in a procedure called Angioplasty. During this procedure, samples of the blood and heart tissue can also be taken to measure oxygen content and view cells under a microscope respectively. In specialized hospitals, procedure such as intra-vascular ultrasound (IVUS) and fractional flow reserve can also be performed during cardiac catheterization to capture in depth images of the blood vessel walls.
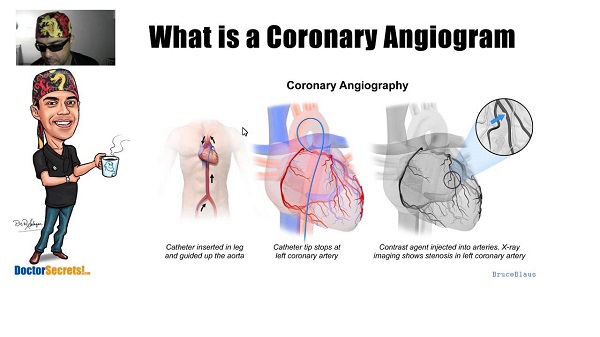
The procedure usually takes about 40-50 minutes with additional prep and recovery time (~2-5 hours in total). A patient is given a sedative but is awake during the procedure. It is a minimally invasive procedure and a local anesthetic is given at the site of the catheter insertion. The patient is attached to an ECG monitor to record the electrical activity of the heart during the procedure. Blood pressure, heart rate and oxygen levels are also monitored throughout. Once the procedure is done, the catheter is pulled out and the blood vessel is sealed with collagen, sutures or just pressure. The patient is advised to lie down and will have his vitals monitored for some time before discharge.
V. Computed Tomography of the Heart
It is often called the coronary CT angiography, Multislice CT Angiogram or MSCT, CT, cardiac CT, coronary CTA or cardiac CAT scan. The scan is done when the doctor needs to:
- Check for calcium build-up in coronary arteries or valves
- Assess the pulmonary veins after Atrial fibrillation
- Check for aortic aneurysm
- Pericardial disease
- Proper functioning of the heart valves
- Monitor result of a bypass surgery
- Pre-operative planning before any invasive cardiac surgery/procedure
The test takes about 15-20 minutes along with prep time. A contract dye (usually iodine) is injected into the patient's vein in the arm to procure better images. If you are allergic to any dye, inform your doctor before the scan. Patients with kidney or liver disease, or kidney failure are more susceptible to develop a serious reaction to such dyes. A beta blocker may be given to slow down the beating heart in certain cases. The CT scanner is a long table with a circular tunnel that a patient slides down. The circular scanner rotates around the patient taking multiple cross-sectional images of the heart. An EKG is attached to the patient during the scan to monitor the heart activity. The patient must lie still for the length of the test and may be told to hold his breath at times. After the scan, patients can go home immediately. If they have been injected with the dye, the doctor may ask them to stay back for an hour to monitor any reactions to the dye. Drinking plenty of water for the following 24 hours helps flush the dye out.
VI. MRI of Heart
Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI is an imaging test that unlike an X-ray uses magnetic and radiofrequency waves to produce accurate photos of the internal body structures. An MRI of the heart can be used to:
- Diagnose aortic tear, bulging or aneurysm.
- Check damage to heart muscle esp. post angina or a heart attack or if pericarditis is suspected
- Check the blood flow to the heart and detect any blockages.
- Detect heart failure, heart enlargement (cardiomyopathy) or heart tumors.
- Check success of surgical repairs esp. in congenital heart cases.
- MRI of the pelvis and leg is done to detect peripheral artery disease.
- MRI of the brain is used to diagnose stroke.
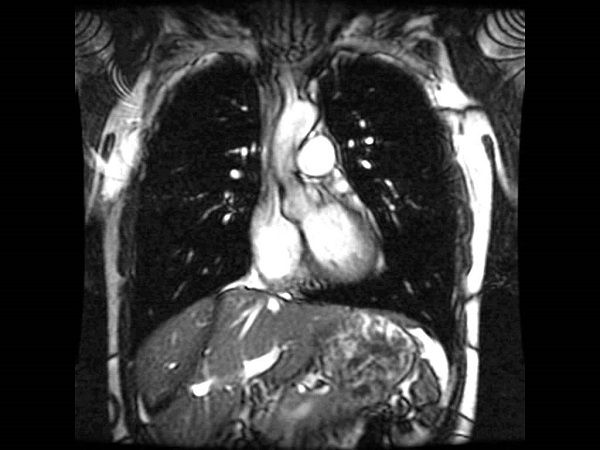
For most patients, MRI is a safe and painless option. However, it is not advised for anyone who has a non-MRI safe metal device. These include:
- Pacemakers
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillators
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs)
- Drug infusion pumps implanted in the body
- Dental implants
- Aneurysm clips
- Cochlear (inner ear) implants
- Any other metallic fragments or implants in the body
The MRI machine is a long table with a circular tunnel that a patient slides into. The circular scanner rotates around the patient taking multiple cross-sectional and 3D images of the heart. The machine can be quite noisy so patients are provided with ear plug or earphones where music is played. An EKG is attached to the patient during the scan to monitor the heart activity. The test takes about 50-60 minutes along with prep time. A contract dye (usually iodine) is injected into the patient's vein in the arm to procure clearer images. If you are allergic to any dye, inform your doctor before the scan. Patients with kidney or liver disease, or kidney failure are more susceptible to develop a serious reaction to such dyes. A beta blocker may be given to slow down the beating heart in certain cases. The patient must lie still for the length of the test and may be told to hold his breath at times. Patients, who are unable to lie still such as babies and children, are given sedative medicine before the scan. For patients who are claustrophobic, an anti-anxiety pill may be given.
References:
American heart Association. http://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack/diagnosing-a-heart-attack/cardiac-catheterization
Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/16832-cardiac-catheterization
Stanford Healthcare. https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-tests/c/cardiac-catheterization/types.html
Secondscount by The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions. http://www.secondscount.org/tests/test-detail-2/holter-monitor-2#.W6Sk82gzaUk