Oral cancer refers to cancers of the head and neck. It includes cancer of the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, salivary glands, floor of the mouth, hard and soft palate, sinuses and pharynx. Brain cancer falls in a different category.

Oral cancer refers to cancers of the head and neck. It includes cancer of the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, salivary glands, floor of the mouth, hard and soft palate, sinuses and pharynx. Brain cancer falls in a different category. The leading causes of oral cancer are smoking and drinking too much alcohol.
Ninety per cent of oral cancers are squamous cell carcinoma of oral mucosal origin. Squamous cells line the lips and the oral cavity.
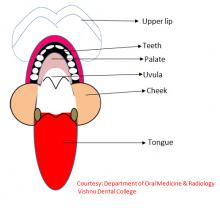
The oral cavity is bounded above and laterally by the upper jaw and lower jaw bones, teeth and gums; above by the palate; and below by the tongue. The oral cavity opens at the back into pharynx.
Changed
17/Jun/2025
Community
Condition















