Today is World Kidney Day and the theme this year is ‘Kidney Disease & Children – Act Early to Prevent it’. We spoke to Dr Pankaj Deshpande, pediatric nephrologist, to apprise us about kidney disorders in children and how they can be alleviated.
What are some of the common kidney diseases/disorders in children? How does it affect them?
There are many kidney illnesses in children and that actually evokes surprise in a lot of people as they are quite unaware that kidney ailments can exist in children also. Some of the common conditions are enumerated below;
Nephrotic syndrome: This is a condition where the kidneys leak a lot of protein and hence cause swelling all over the body due to water leaking out of the blood vessels. While most children with nephrotic syndrome in the age group of 1 year to 10 years will do well in the long term especially if they respond to steroids, there is a fair portion who will have long term problems with kidney function and hence kidney failure, commonly in children who do not show a response to steroids.
Nephritis: In this condition, children show presence of blood in the urine along with swelling and high blood pressure. While some varieties may be benign (post infectious) others will need prompt treatment after evaluation, failing which kidney failure may ensue.
Tubular disorders: In these conditions, the kidneys ‘leak’ out all the good things that are supposed to be retained behind in the body. Consequently, the children pass a lot of urine, are constantly thirsty and do not grow well. While recognition and treatment of the conditions will result in improvement in most children, in other children there is progression to kidney failure. These are inherited disorders
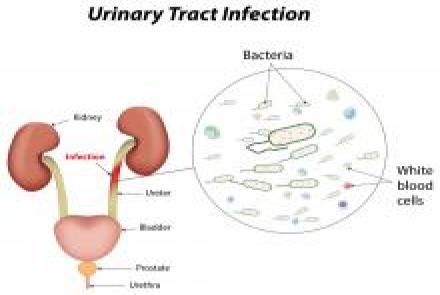
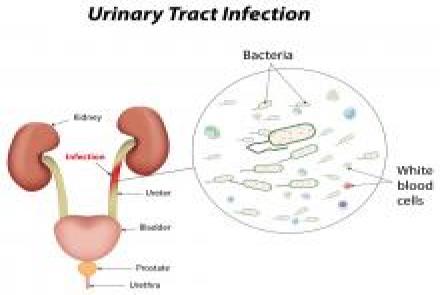
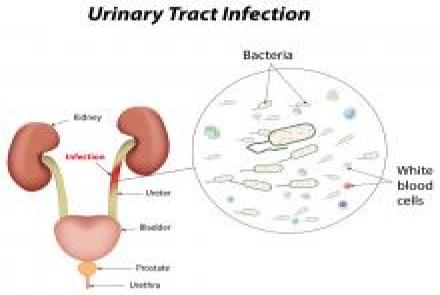
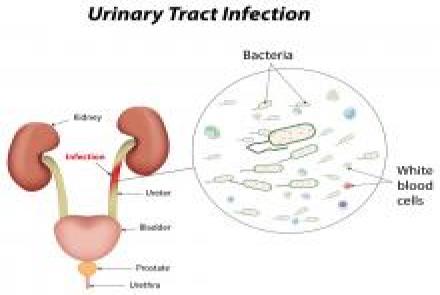
Urine infections: Common in children and repeated urine infections can damage the kidneys. However the flip side is that many children undergo unnecessary antibiotic therapy for urine infections when they exhibit some symptoms but do not actually have a urine infection
Acute kidney failure: This can occur due to many reasons like shock, severe infections etc. While most children will recover, some with underlying severe cause may recover only partially or not at all.
Related story: I had a Kidney Transplant
Renal dysplasia: Unfortunately this is a very underdiagnosed condition especially as the children do not have any symptoms till they reach kidney failure. As the kidneys are not formed adequately at birth, they are unable to provide adequate renal function. This happens more commonly when the body is growing rapidly as in puberty. Hence when they are small they do not show any symptoms and unless a high index of suspicion is kept, most of these children will present as adults needing dialysis
Thus there are many conditions in children, some inherited, some due to inadequate development and others acquired that will lead to kidney ailments, especially chronic kidney disease in the long term.
What causes kidney disease in children?
As mentioned above, some are inherited, some are due to inadequate development, some are secondary to infections and others are acquired.
What are the predominant symptoms of a kidney disease that can alert parents? How can parents actively participate in the child’s care?
There are some symptoms that the parents should be aware of that might indicate a kidney problem. It starts right in the beginning!
- Inadequate fluid around the baby on the ultrasound scan done during pregnancy means that the kidney function should be looked at after the birth of the child…even though the child may look completely normal. Remember, there are no symptoms in dysplasia till very late. Enquire with the attending pediatrician as to what tests need to be done. In most cases, it is a simple blood and urine test and in some an ultrasound scan may be needed.
- Baby or Child passing too much urine or too little urine
- Child straining to pass urine, especially boys
- Persistent wetting in the daytime in children above 3 to 4 years of age
- Swelling, however minimal or even if only on the eyes
- Red urine or blood in the urine
- Poor growth despite all the usual advice regarding feeding etc
These are some of the common things that parents can be alert about and seek an expert opinion from the pediatrician
Should children with kidney disease do sports? Or should there be any other restrictions for them?
Of course children should do sports and all kinds of sports. In very rare cases where the kidneys are very, very large like in Polycystic kidney disease are contact sports avoided. In fact, the aim of every Pediatric nephrologist is to ensure that their patient leads as normal a life as possible!
Could you list out some golden rules to keep the kidneys healthy?
Some simple things can go a long way in keeping the kidneys healthy
- In pregnancy scans, ensure the fluid around the baby is normal
- Ensure the baby/child drinks adequate fluids in the day (Most children will need at least a litre of fluid intake every day)
- Avoid stimulant drinks like tea, coffee or fizzy drinks
- Ensure children void urine at least 6 to 7 times every day
- Also play a game and tell them to make sure they sing a song in the bathroom while ‘peeing’ or count from 1 to 20 and then pee again! Very often children rush out of the toilet as they are unwilling to miss even a minute of the fun outside!! This causes incomplete emptying of the bladder and problems for the child
- Ensure that the child is not constipated by giving a high fibre diet, fluids, fruits and vegetables
- Don’t disregard any symptoms like swelling of the eyes, blood in the urine even if the child looks completely normal
- If the child is waking up every night to drink water or cry for water, seek attention of your doctor
- Ensure good physical activity and do not allow obesity to set in
Compared to other illnesses among children, what % does kidney disease account for in India?
Asian population is more prone to developing kidney disease and in children also, though numbers are not available it forms a fair percentage of the illnesses. For e.g, about 2 to 6 % children suffer from a urine infection at some point in young age. In conditions like Renal dysplasia, the words of Shakespeare hold true. ‘The child is the father of man.’ Inability to pick these children up in childhood and initiate treatment results in these children presenting as adults to Nephrologists needing dialysis.

Dr Pankaj Deshpande is a consultant pediatric nephrologist at Hinduja Hospital, Mumbai.