Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. Quick and fast intervention helps. Dr. Shital Patel recommends first aid tips for cardiac arrest.
Sudden cardiac arrest occurs when the heart stops beating suddenly commonly due to some electrical malfunction. The victim becomes unresponsive, unconscious with no signs of breathing or movement. Death can occur within minutes as blood stops flowing to the lungs, brain and other organs. This can be reversed with prompt emergency intervention.
Cardiac arrest is the growing cause of fatality in young and old. The first 60 minutes are considered the most crucial and draw the line between life and death. That's why its also called the Golden Hour.
Remember:
Cardiac Arrest is not the same as a Heart Attack
Cardiac Arrest is different from a Stroke
So if someone collapses in front of you, what do you do?
Here are some first-aid tips to aid the person till medical help can arrive on site:
- Check for danger to the person of any kind such as safety, hazards or injury due to the fall etc.
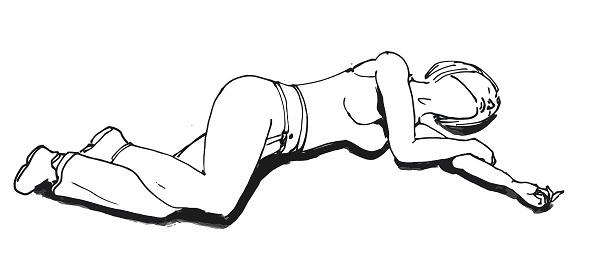
- Put the patient in a recovery position (see image below).
- Speak to them and see if they respond.
- If they respond, it means they are alive
- If there is little or no response, they are not conscious enough.
- Call emergency helpline number for medical help.
- Check to see if the airway is open. Put 2 fingers under the chin and other hand on the forehead; tilt the chin up so the tongue is not blocking the airway.
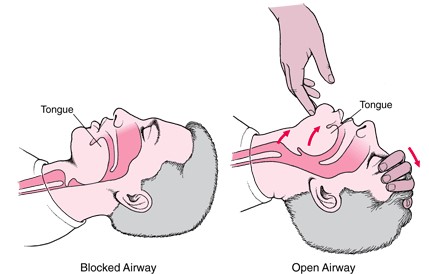
- Check for breathing by watching the chest, nostrils and listening.
- If person is breathing, open the mouth to ensure easy breathing.
-
The lower limbs should be elevated during CPR, this is key to get blood to the brain and heart.
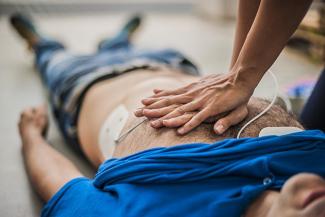
- If person is not breathing, start CPR*. CPR (Cardiopulmonary resuscitation) should be 2 compressions per second followed by 2 breaths. Continue CPR till person becomes responsive or breathing returns.
- If there is a Defibrillator (AED) nearby, attach it and follow the voice instructions.
*If you don’t know CPR, please do not attempt it, wait for medical help.
If you want to learn about CPR and AED basics, check out CPR Saves Lives to learn more.
















