Most of us are familiar with the term Gout without being aware of its full implications. This FAQ briefs us about all that we need to know about the condition and how we can tackle it, should we be affected.
1. What is Gout?
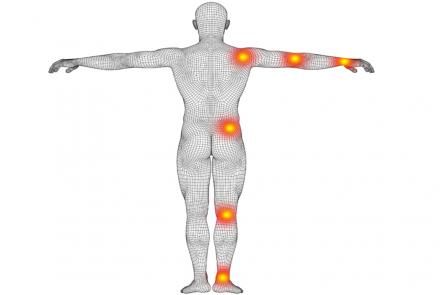
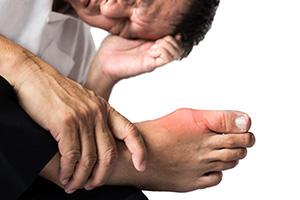
Gout is a kind of arthritis where uric acid gets deposited in the joints and soft tissues. This, in turn, causes inflammation with redness, swelling, heat, pain and stiffness in the affected joint. Since the foot has numerous joints, the big toe is primarily affected by Gout. However, Gout can affect other joints as well such as the fingers, ankles, elbows, knees etc. Uric acid crystals can even lead to formation of hard deposits termed tophi. Tophi causes daily pain, pressure and damage to the joint and cartilage -- this is called Chronic Tophaceous Gout.
2. What is Uric acid?
Uric acid is a chemical that is released when organic compounds called purines are broken down. Purines are found in food products like anchovies, liver, mackerel etc. Normally uric acid in blood is processed by the kidneys and excreted via urine. Increase in uric acid production may cause accumulation of uric acid in the blood and kidneys. Such a condition is called Hyperuricemia. Consequently, these uric acid crystals can lead to kidney stones or Gout. The crystals build up in the joints gradually over years. When there is over-spilling of the crystals from the joints, they fall out into the joint synovium and cause inflammation.
3. What is Pseudogout?
This is a type of arthritis that often gets confused with Gout. This is because it also is accompanied by sudden joint pain, swelling and redness. However, the cause is the calcium phosphate crystals and not uric acid crystals.
4. Common causes of Gout?
- Genetics is the most common cause. Genes may also play a role in inefficient flushing of urate from the kidneys.
- Being overweight or obese causes increased production of uric acid and a higher risk or hyperuricemia.
- Conditions such as diabetes, high cholesterol, chronic kidney disease, hypertension, chronic blood disorders etc can hamper proper kidney functioning and excretion of uric acid.
- Excessive alcohol intake because it interferes with removal of uric acid from blood.
- High purine food intake.
- Exposure to lead.
- Renal insufficiency which causes Secondary Gout may stem from:
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypertension
- Conditions that cause high cell turnover such as Psoriasis, haemolytic anemia, cancer etc.
- Deficiency or lack of uric acid enzyme control as seen in Kelley-Seegmiller syndrome and Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
5. Who is at risk for Gout?
- Family history of Gout.
- It is more common in adults (between age 30-50) and rarely seen in children.
- Men are at a larger risk than women. Risk for women increases after menopause.
- Overweight people
- African-Americans are twice at risk than other races.
- Triggers such as an injury, infection, therapy (such as Chemo etc) or surgery ( such as organ transplants etc)
- People who take certain medications (Refer to Question 7 below)
6. Is gout hereditary?
Gout is known to have a familial cause, which means that children with parents who have Gout have a higher risk of getting it.
7. Can any medication increase the risk of Gout?
Several drugs are known to increase the risk for Hyperurecimia and Gout:
- Thaizide diuretics which are common treatments for hypertension cause low secretion of uric acid via urine.
- Vitamin B3 or niacin or nicotinic acid.
- Levodopa, a medication used for Parkinson’s disease treatment.
- Cyclosporine, which is an immunosuppressant drug, commonly seen in organ transplant patients.
- Aspirin and other salicylate-containing drugs.
8. What are the signs and symptoms of Gout?
- Intense joint pain at night time
- Inflammation (warmth, swelling, tenderness & redness) at the joint
- Attack on only one joint, often the toe, ankle or knee
- Blood or urine test showing hyperurecimia
- Uric acid crystals detected in synovial joint fluid.
9. What are the treatment options for gout?
There are two aspects of Gout treatment: addressing an acute attack and preventing further attacks.
Acute Gout attack usually peaks in 36 hours and subsides in about 7 to 10 days. Treatment should include:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) for pain relief.
- Take any medication that you have been prescribed for Gout such as colchicine (taken orally) or corticosteroid (taken orally or injected into the inflamed joint).
- Elevate the affected joint, ideally above heart level and to avoid weight bearing.
- Apply ice packs (for 20 mins) to reduce swelling and warmth.
- Rest the joint and avoid too much movement.
10 Diet Tips to Prevent Gout Attack
Preventing further attacks aims at reducing uric acid levels in the body! These medications can only be taken after an attack is over because they can, in fact, prolong or aggravate an attack. Your doctor may decide to prescribe these medications along with NSAIDS or colchicine for a few months after an attack to prevent future attacks.
- Allopurinol is a once a day tablet that helps bring down the production of uric acid. It is important that it is started only when the uric acid levels are low or else it can cause an attack.
- Febuxostat is also taken once daily and functions like Allopurinol. It is recommended if Allopurinol is not suitable.
- Lesinurad is used in combination with Allopurinol or Febuxostat in people where the single treatment drug has failed to work.
- Probenecid helps eliminate uric acid faster from kidneys.
- Peglioticase is used when all standard medications have been unsuccessful. It is given via IV infusion every 2 weeks.
10. Does one need to take medications for Gout for a lifetime?
This would depend on the severity and the type of Gout that each person suffers from. Some people may need medications only during a Gout attack. However, many people experience Gout attacks once medications are stopped or reduced. For such patients, life long treatment may be essential.
11. Can essential oils help treat Gout?
Certain oils contain gamma-linoleic acid (GLA) which can help alleviate arthritis pain. Such oils include evening primrose, borage and black current oil. Also, do a skin patch first to make sure you are not allergic to any of these oils.
12. Can Gout be controlled?
Certain lifestyle changes may help control attacks and reduce chances of future attacks:
- Take medications on time daily and as instructed.
- Do regular follow-ups with your doctor.
- Daily exercises
- Lose excessive weight.
- Diet changes: avoid purine rich foods and alcohol
*Avoid weight loss programmes that focus on low carbohydrate diet. When carbohydrate intake is low, body burns fat and forms ketones. Excess ketone formation can in turn increase uric acid levels.
13. How can diet change help? What diet needs to be followed?
- Best to avoid all food items high in purines such as anchovies, liver, brains, beef kidneys, game meats, gravies, dried beans and peas, asparagus, herring, mackerel, mushrooms, sardines, scallops, sweetbreads.
- Drink a lot of water as it may help flush out excess uric acid from the system.
- All alcoholic drinks should be stopped. Alcohol is known to increase uric acids levels in blood.
- Avoid sugary food and beverages.
- Focus on food like low fat dairy products, skimmed milk, whole grain food, plant oils, coffee and fruits (not too sweet).
- Vitamin C supplements are also known to be helpful in reducing Gout.