What is the treatment of heart failure
Various medications are utilized to manage symptoms, improve heart function, and slow disease progression.
- Medications to regulate water loss - diuretics reduce the congestion and relieve the symptoms of breathlessness. They play a crucial role in managing fluid retention in heart failure. Furosemide and hydrochlorothiazide are commonly prescribed.
- Oxygen therapy or use of ventilation therapy (non-invasive ventilation or invasive ventilator support based on the severity of the heart failure).
- Blood pressure stabilizing medications are usually needed to reduce the blood pressure if the BP is high or vice versa increase the blood pressure if low.
- Drugs used in heart failure management depend on the clinical situation and they include:
- ACE inhibitors: These medications work by inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme, which plays a role in regulating blood pressure. They relax blood vessels, reduce fluid buildup, and decrease the workload on the heart. Enalapril and lisinopril are commonly prescribed drugs.
- Angiotensin receptor blockers: These drugs block the action of angiotensin II, a hormone that narrows blood vessels, leading to relaxation and reducing blood pressure. Commonly prescribed drugs are losartan and valsartan.
- Angiotensin Receptor Blocker - Neprilysin Inhibitors ARNIs, combination of ARB and Neprilysin enzyme help reduce strain on the heart and improve symptoms of heart failure.
- Beta blocker – Beta blocker blocks the effect of adrenaline on the heart and reduce heart rate and blood pressure. It improves heart function; Metoprolol is commonly prescribed drug.
- Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs): These drugs help in reduction of fluid buildup and improve heart function. They block the action of aldosterone which promotes fluid retention. Spironolactone and eplerenone like drugs are commonly prescribed.
- Digoxin – It strengthen the force of heart contractions and can improve symptoms of heart failure. It can also help regulate heart rate in certain cases.
The most important part of treatment is treating the cause of heart failure. For example, if the heart failure is due to a heart attack or myocardial infarction, then revascularization of the heart muscle should be done expediently. If the heart valves are causing heart failure, the valve leakage or obstruction should be relieved as soon as possible.
What are the most common cardiac devices used for treatment?
Device Therapy Options:
Automated Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (AICD) - This device can be implanted in the heart which detects the fast heart beats and can deliver a lifesaving shock when appropriate to prevent sudden cardiac death. Patients with ejection fraction less than 35% are prone to heart arrhythmias and sudden death).
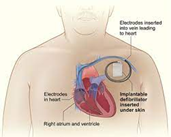
Image sourced from https://www.heartfoundation.org.au/bundles/support/automated-implantabl…
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) - In patients suffering from recurrent heart failure, where heart pumping is weak and the right and left side of the heart pump are out of sync, a special pacemaker called Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) can be implanted to improve the synchrony of the heart and relieve the patient’s symptoms.
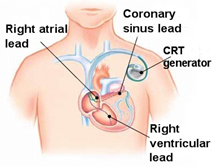
Image sourced from https://www.washingtonhra.com/pacemakers-icds/cardiac-resynchronization…
Left Ventricular Assist Devices (LVADs) -In patients with end stage heart failure, special mechanical pumps can be used to stabilize the patient and improve their blood pressure, circulation and organ perfusion. These are called LVAD – Left Ventricular Assist Devices/ Artificial hearts which are surgically implanted in the heart and can mechanically pump blood to the whole body. This type of pump can be a bridge to a heart transplant or in select patients, be ‘destination therapy’ or final therapy for end stage heart failure.
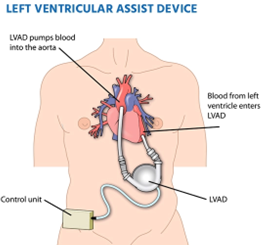
Image sourced from https://www.medicoverhospitals.in/procedures/lvad-Implantation/
Ultrafiltration – It is a method of mechanical fluid removal. It is used in acute heart failure which involves the extracorporeal removal of plasma water and solutes from the blood using semipermeable membrane.
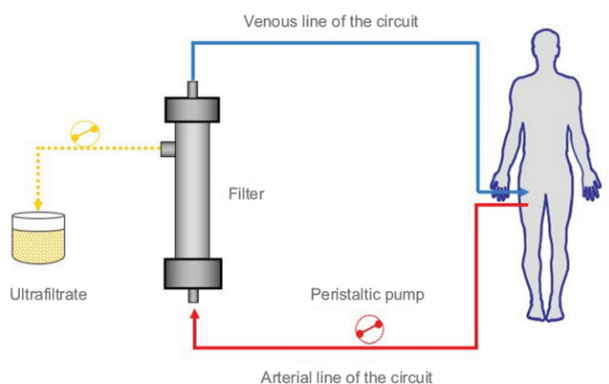
Image sourced from https://www.dovepress.com/extracorporeal-ultrafiltration-for-acute-hear…
Surgical Therapy Options:
Surgery may be required in certain cases of heart failure.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) – This is a surgical procedure that bypasses obstructed coronary arteries with grafts (e.g., saphenous vein, internal mammary artery) to restore blood flow to ischemic myocardial tissue and improve cardiac function.
Valve Repair or Replacement – Mitral valve repair or aortic valve replacement, may be performed treat valvular dysfunction, reduce regurgitation and improve hemodynamics in patients with heart failure.
Heart Transplant - In severe cases, when all other therapies have failed, a heart transplant may be considered. It involves replacing the diseased heart with a healthy heart from a donor. Before the transplant, the patient undergoes thorough evaluation to assess their overall health and suitability for the procedure.