Doctors advise diabetes patients to use a blood glucose meter or glucometer regularly in order to understand what alters blood glucose level, monitor the changes and learn to manage it more effectively.
A glucometer also known as a blood glucose meter is a small electronic device that measures the blood glucose levels. It is useful for all diabetic patients in monitoring and keeping track of their glucose readings. The American Diabetes Association recommends that patients with Type I test 3 or more times a day, pregnant women with gestational diabetes test 2 times a day and patients with Type II diabetes as recommended by their doctors. Thus it is an essential tool for all patients with diabetes (type I, type II and gestational).
A glucometer consists of roughly 4 parts:
- Meter that measures your blood glucose level
- Screen that displays your reading
- Lancet to prick and draw blood sample
- Test strips on which blood is smeared for the reading
Many types and brands of glucometers are available in the market with varying prices and functionality. Before buying one, make sure you consider all the factors listed below to choose the right glucometer for your needs.
- Ease of Use. The testing methodology although largely the same will vary slightly with each meter. Read the instructions on the box or speak to your Pharmacist about how easy it is to use before purchase. In addition, the result should be in a font that is simple to read and understand. Opt for a meter that doesn’t require calibration for every new batch of test strips.
- Pain. Sadly, there are no painless glucometers available. Inquire about how much sample size is required as this will determine the level of pain. A large sample means a larger lancet prick which means more pain. However, a bigger sample size usually means a better accuracy of your reading. Most glucometers require anywhere from 0.3 to 1.5 µl of blood. Pick one that requires lesser blood but also rates well for accuracy.
Tips to reduce finger prick pain
-Wipe finger with warm water & soap instead of alcohol
-Test on the side of the finger. Pads have more nerve endings
-Use a different finger for testing everyday
-Change the lancet after every use
-Use a finer needle lancet
-Make sure the lancet depth is not too deep
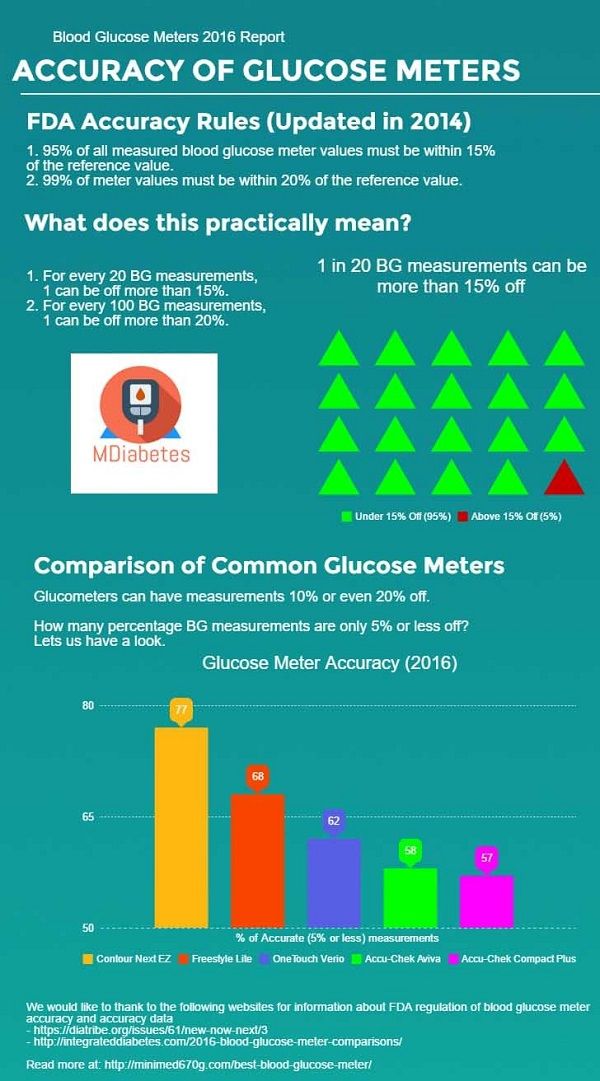
- Accuracy. This is an important feature to look out for. Most meters are allowed up to 20% range from the reading by the FDA. See the image below for a comparison of most common glucometers. Remember that price does not determine accuracy of a glucometer.
- Test speed. The speed with which the result comes can test one’s patience especially when you are doing frequent readings in a day.
- Maintenance. Ask if it is easy to clean? Is it affected by humidity or weather changes? Does it require calibration for every new strip?
- Price. In most cases, your insurance will not cover for cost of the glucometer or testing strips, so think about how much you are willing to spend. If your insurance does cover for it, find the list of the approved meters.
- Cost of strips. Testing strips are sold separately and can be pricey. So before purchasing any meter, always check prices of the strips as well. Always buy in bulk to save money. Also make sure they are easily available.
- Brand. Educate yourself about the various brands available. Some of the brands available in India are listed here (in no particular order):
- Size. If you carry your meter with you all day, you may want to choose a compact one. The elderly may prefer a larger model for easy grip.
- Memory. If you are good at keeping a written log of your your results after every reading, you may not require a device with high storage capacity. Many devices do have the ability to keep record of >100 test samples and you can even email these to your doctor or nurse.
- Special features.
- These may include Bluetooth or USB port for transferring of sample data to your computer or phone.
- Some even have bolus calculators for people on insulin shots.
- Some meters in addition allow blood samples to be taken from other sites (such as thigh, arm, hand, calf etc) besides finger.
- The visually impaired or those who have diabetic retinopathy should avail of the audio feature.
- Screens with black lights or large fonts are options.
- Colorful bright options are available for children which can even be connected to their game consoles.
- Teens & adolescents may prefer the sleeker pocket sized versions that hardly look like standard glucometers.
- Some meters also test the blood ketone levels.
















