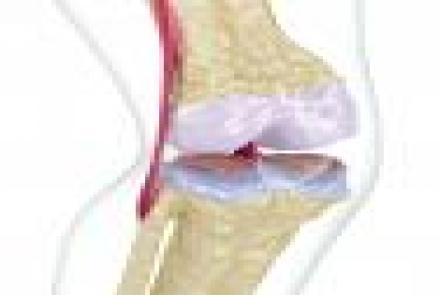
Even though knee replacement operations have become more commonplace these days, one needs to be aware of the do’s and dont’s after the operation.
When the severity of a condition is such that physiotherapy for knee pain and any other conversant treatment fails, knee replacement becomes binding. Recovering from knee replacement can be highly challenging especially during the initial days. Here is a comprehensive guide on post-operative care for knee replacement so that both you and your loved ones can oblige to the respective roles smoothly:
1. Start with the basics:
As Post-operative care for knee replacement begins at home, the foremost step is to prep up the basics. When we say prepping up the house, we mean:
- Sufficient lighting to avoid undesirable falls.
- Spare pillows for leg elevation as and when required.
- A bed that isn’t too high or low.
- Ice pack supply.
- Comfortable sleepwear.
- Essential toiletries and dressing items.
- Arrangement of phone near the bed for emergency calls.

2. Unsullied medication and wound care schedule:
Optimal post-operative care for knee replacement is based mainly on how the medication is administered and how professionally the wound is monitored.
- Create digital reminders for meting out timely medication.
- Renew subscriptions from your doctor at regular intervals.
- Check the operated area every day to ensure there is no visible inflammation or swelling in either of the legs or area around the knee.
- In case you are a working caretaker, outsource your responsibility to any at-home provider of post-operative nursing care services.

3. Backing on chores:
Any task that involves standing, stretching or bending will not be feasible for the patient thus mandating 24x7 surveillance.
Under any circumstance, do not let the patient perform:
- Household chores like cooking, cleaning, dusting etc.
- Personal hygiene regimes like bathing, dressing, and grooming.
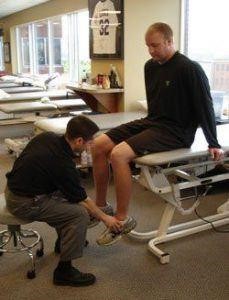
4. Push for rehab and exercises:
Adhering to a dedicated rehab plan is the key to rapid healing post knee replacement surgery. Exercising can be as mild as walking for 15-20 minutes twice a day or adopting a well-structured physiotherapy treatment.
The catch here is that exercising post knee replacement surgery is painful and this is where the role of loved ones comes in. Every time the patient complains about knee pain during exercise, it is essential to be their support system and motivate them by reminding how a little throbbing today will speed up their recovery process tomorrow!

5. Hire reliable nursing care services:
Executing post-operative care for knee replacement is not as easy as it sounds. It becomes highly demanding for the caretaker to differentiate their life from the patient’s thus making them feel frustrated by day end.
Let’s be honest; you don’t need to fulfill all responsibilities alone. The recovery from knee replacement surgery can take long, both emotionally and physically thus making at home nursing care services a sane choice.
Contributed by Healers at Home