Who should have a Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery and what are the alternatives available? Dr Shital Raval suggests factors to help you make a decision.
Let us evaluate the various options available and the factors to consider.
Arthroplasty
Total hip replacement surgery is also known as Total Hip Arthroplasty while a knee replacement surgery is called Knee Arthroplasty (can be partial or total).
Both are common and effective procedures for hip and knee arthritis.
These are elective…

Many people often confuse osteoporosis with osteoarthritis, commonly known as arthritis. The terms may be used interchangeably quite often; however, they are not even distant cousins. Let us understand the differences and how each of these needs to be managed.
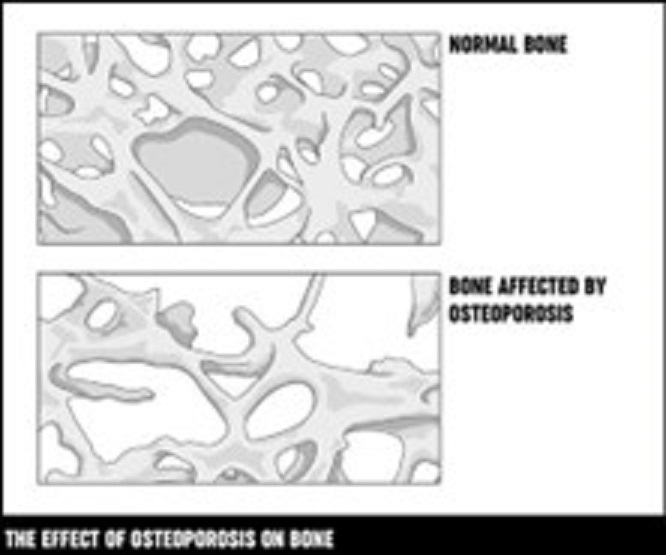
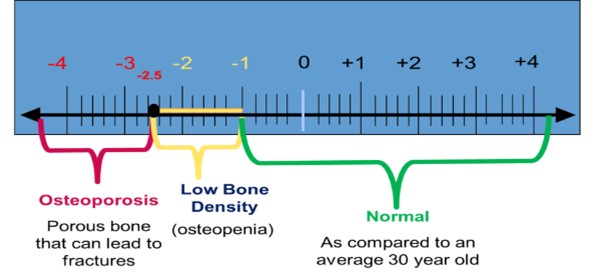
Osteoporosis occurs when the bones in our body lose mineral density and become thin and brittle. They cannot bear normal weight and thus break easily.
Osteoarthritis is a disease of wear and tear of not just the bone but the surrounding cartilage that leads to joint pain and limits movement.
|
OSTEOARTHRITIS(OA) |
OSTEOPOROSIS | |
|
WHAT IT MEANS |
Degeneration/wear and tear of joint and surrounding cartilage | Loss in bone mass |
|
WHAT IT DOES |
Causes joint pain and limits movement and function of joints | Causes bone loss and fractures |
|
CAUSES |
Modifiable factors:
Non-Modifiable factors:
Research has shown that muscle weakness can contribute to osteoarthritis and muscle wasting is a common occurrence. |
|
|
SYMPTOMS and SIGNS |
|
|
|
HOW IS IT DETECTED? |
|
|
|
PREVENTION & SCREENING: |
Prevention tips:
Screening for early identification of osteoarthritis
|
Can be primarily prevented by:
|
THERAPIES FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS
- Medical Therapy: Pain relief medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or intraarticular steroid injections
- Physical Therapy: A therapist can assist with exercises to strengthen your joints and improve your mobility.
- Occupational therapy: Helps you adapt your work environment or habits to manage the effects of arthritis.
- Orthotics: Like braces, splints, or shoe inserts to help relieve stress and pressure on the damaged joints.
- Joint surgery: A joint replacement to replace the damaged joints.
THERAPIES FOR OSTEOPOROSIS
- Medications:
- Bisphosphonates are the most widely prescribed oral medications and can be taken only when prescribed the doctor.
- Sometimes, injectable medication called Denosumab is also given as per the doctor’s advice.
- Bone Building Medications:
- Hormonal Therapy
Citation:
- Professional, C. C. M. (n.d.). Osteoporosis. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4443-osteoporosis
- The National Council on Aging. (n.d.). https://www.ncoa.org/article/osteoarthritis-vs-osteoporosis-what-are-th…
- Osteoarthritis Action Alliance. (2022, August 4). Resources - Osteoarthritis Action Alliance. https://oaaction.unc.edu/resource-library/" https://oaaction.unc.edu/resource-library/
- Strickland, S. (2023). American Bone Health | Osteoporosis Education and Awareness. American Bone Health. http://www.americanbonehealth.org/
- Website, N. (2022, October 14). Causes. nhs.uk. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/osteoporosis/causes/
- LeBoff, M. S., Greenspan, S. L., Insogna, K., Lewiecki, E. M., Saag, K. G., Singer, A., & Siris, E. S. (2022). The clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis International, 33(10), 2049–2102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-021-05900-y
- Osteoporosis. (n.d.). National Institute on Aging. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/osteoporosis#keep
- Migliore, A., Алексеева, Л. И., Avasthi, S., Bannuru, R. R., Chevalier, X., Conrozier, T., Crimaldi, S., De Campos, G. C., Dıraçoğlu, D., Gigliucci, G., Herrero‐Beaumont, G., Iolascon, G., Ionescu, R., Jerosch, J., Laíns, J., Maheu, E., Makri, S., Мартусевич, Н. А., Matucci‐Cerinic, M., . . . Tarantino, U. (2023). Early Osteoarthritis Questionnaire (EOAQ): a tool to assess knee osteoarthritis at initial stage. Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease, 15, 1759720X2211316. https://doi.org/10.1177/1759720x221131604
- American Bone Health. (2022, January 28). Understanding Bone Density Results - Your T-score & Z-score Explained. American Bone Health. https://americanbonehealth.org/bone-density/understanding-the-bone-dens…
Changed
07/Dec/2023
Condition