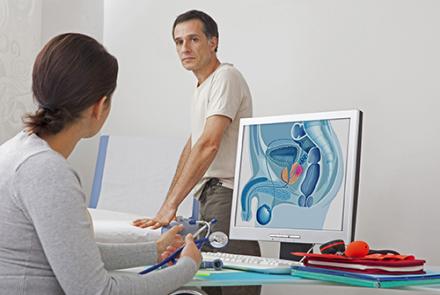
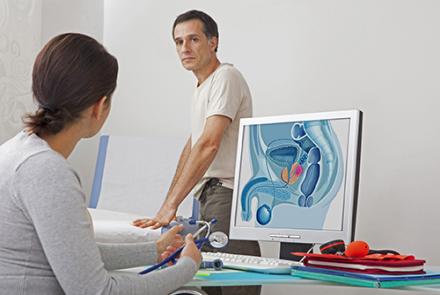
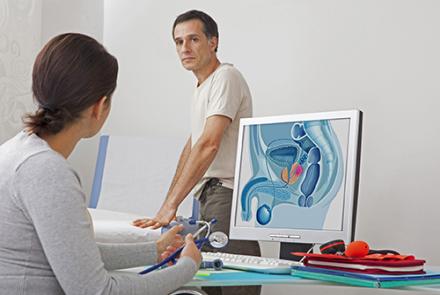
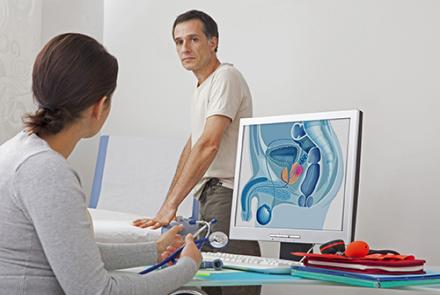
Stages of prostate cancer
There are 4 stages of Prostate Cancer
In stage I-Cancer is found in the prostate only
In stage II-Cancer is more advanced than in stage I, but has not spread outside the prostate.
In stage III-Cancer has spread beyond the outer layer of the prostate and may have spread to the seminal vesicles. In stage IV- Cancer has spread beyond the seminal vesicles to nearby tissue or organs, such as the rectum, bladder or pelvic wall or cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes; or has spread to distant parts of the body, which may include lymph nodes or bones.
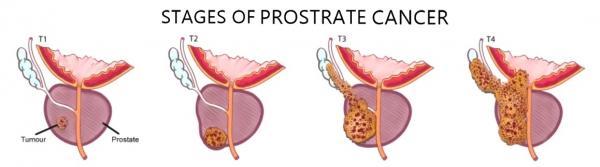
The above illustration shows the different stages of cancer. Prostrate cancer is categorised as Stage 1, 2, 3 and 4.
The type of cancer depends on the cell from it originates. The most common type of cancer is the Adenocarcinoma. Other types which are usually rare include Small cell carcinoma, Transitional cell carcinoma, Neuroendocrine tumours and squamous cell. Even rare types include sarcoma and lymphoma of the prostrate.
Reference:
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/prostate-cancer/about/what-is-prostate-cancer.html