Sickle Cell Disease is a genetic blood disorder characterized by mutated hemoglobin that causes red blood cells to become “sickle” shaped. These red blood cells stick together and hinder the blood flow and oxygen from reaching all parts of the body. It can create blockage of small blood vessels resulting in pain and organ damaging complications. Regular medical checkups and ongoing management are crucial to prevent further complications.

Causes of Sickle Cell Disease
- Sickle cell disease is caused by defect in gene and it is passed down from parents to children.
- The mutations in the beta globin genes affect the structure of hemoglobin molecule (also called as Hemoglobin S.), causing it to form abnormal "sickle" shapes.
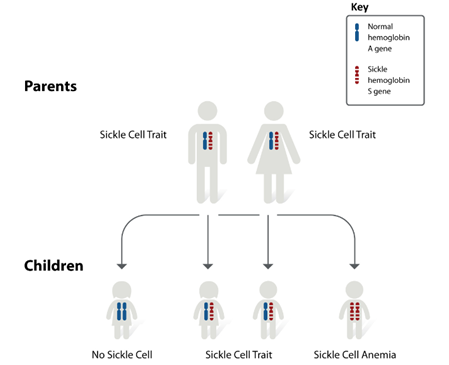
Figure 2 – How sickle cell disease is inherited?
- A child will be born with sickle cell disease only if two genes are inherited – one from mother and one from father. A child who inherits just one gene is “carrier” of the disease and can pass on disease if has child with another carrier.
- There is a 1 in 4, or a 25% chance of having a child with sickle cell disease if parents are carrier of sickle cell disease.
- A blood test is used to identify whether a person has sickle cell trait or they can carry a sickle cell child in future.
Changed
19/Jun/2024
Condition

















