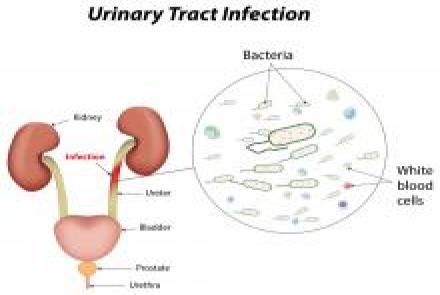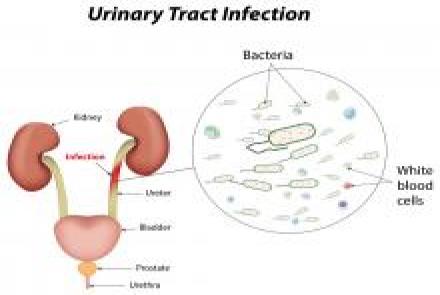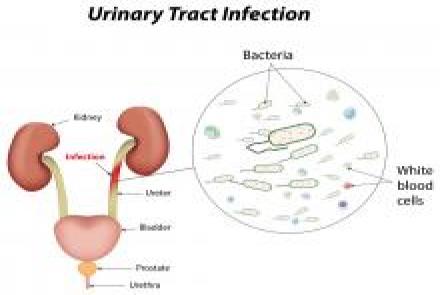
Types of UTI
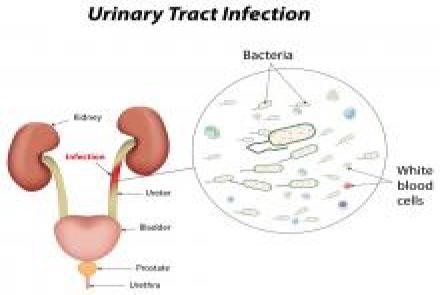
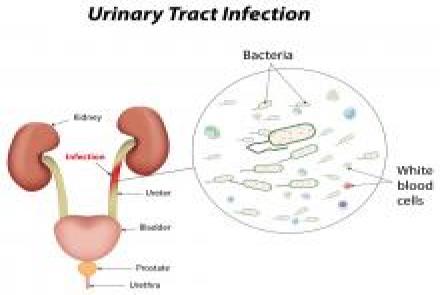
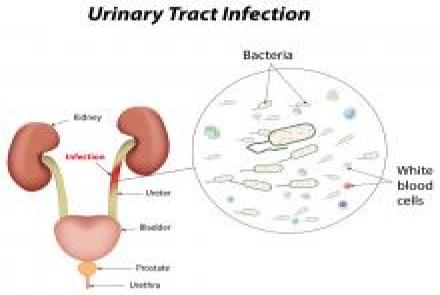
There are a number of different types of urinary tract infections. Urinary tract infections usually develop first in the lower urinary tract (urethra, bladder). If these infections are not treated, they may progress to the upper urinary tract (ureters, kidneys). Bladder infection (cystitis) is by far the most common UTI.
Infection of the urethra is called urethritis. Kidney infection (pyelonephritis) is a serious condition that requires urgent treatment. Pyelonephritis can lead to reduced kidney function and possibly even death in untreated, severe cases.
Complications of Urinary Tract Infection
Complications of UTI aren't common, but they can be serious. Complications usually only affect people with a pre-existing health condition, such as diabetes or a weakened immune system. You're also more likely to get complications from a UTI when you're pregnant, so it's important to tell a doctor if you are pregnant and have any of the symptoms of UTI. The complications of UTIs are discussed below.
Prostatitis
- Men experiencing recurrent UTIs are at risk of complications that affect the prostate, such as prostatitis. Prostatitis is inflammation (swelling) of the prostate gland, which can cause pain when urinating or ejaculating and general discomfort in the pelvic area.
- A four-week course of antibiotics can be used to treat prostatitis and the symptoms usually pass within two weeks.
Kidney infection
- A kidney infection (pyelonephritis) can happen when bacteria travel from the bladder to the kidneys. A kidney infection doesn't usually pose a serious threat to patient’s health if treated promptly. If a kidney infection is not treated, it can get worse and cause permanent kidney damage.
- The symptoms often appear quickly, often within a few hours. Patient may feel feverish, shivery, sick and have a pain in back or side.
Kidney failure
- Recurrent UTIs may sometimes cause kidney damage as well as kidney failure if not treated promptly. Most UTIs are not serious, but some infections can lead to serious problems. Chronic kidney infections, infections that recur or last a long time, can cause permanent damage. In most cases, UTIs can be treated successfully without causing kidney damage.
- UTIs caused by a kidney stone or (in men) an enlarged prostate gland can damage the kidneys if the problem is not corrected and the infection continues.
- Kidney failure is when the kidneys stop working properly. If a person has kidney failure (also known as renal failure), they may need to have artificial kidney treatment, called dialysis.
Blood poisoning (sepsis)
Blood poisoning (sepsis) is a rare but potentially fatal complication of kidney infection. It happens when bacteria spread from the kidneys into the blood stream. Once bacteria are in blood, the infection can spread to any part of the body, including the major organs.
Blood poisoning is a medical emergency that usually requires admission to a hospital intensive care unit (ICU) while antibiotics are used to fight the infection.
Chronic infections may result in urinary strictures, abscesses, fistulas, kidney stones, and, rarely, kidney damage or bladder cancer.
Permanent kidney damage from an acute or chronic kidney infection (pyelonephritis) due to an untreated UTI, especially in young children.
Increased risk of women delivering low birth weight or premature infants