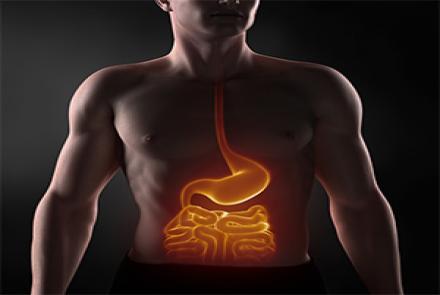
There is no cure for celiac disease. The only treatment is gluten-free diet which does not contain wheat, rye, barley and their derivatives. Gluten is found in biscuits, bakery items, saucesbread, pasta, breakfast cereals, snacks and other processed foods. Don’t forget to read food labels and see for gluten free alternatives.
The disease severity will be varying depending on the patient’s immune response. Some patients can ingest small amounts of gluten without developing symptoms, while others experience massive diarrhoea with only minute amounts of gluten.
Medication is not normally required, following a strict gluten free diet will greatly reduce the symptoms. Sometimes, the doctor may prescribe medications to manage the symptoms such as abdominal pain, vomiting or diarrhoea.
Consulting with a dietitian is important to get personalized nutrition plan and meal guidance to prevent malnutrition.
Regular monitoring and follow up with gastroenterologist for periodic tests is crucial.
Complications of Celiac Disease
If celiac disease is left untreated, it can cause these Complications:
- Weight loss and failure to grow
- Anxiety and depression
- Anaemia due to iron deficiency and folic acid deficiency
- Osteoporosis or Rickets
- Loss of tooth enamel
- Intussusception (one part of the intestine slides into an adjacent part)
- Rectal prolapse
- Lymphoma of intestine and probably cancer of oesophagus