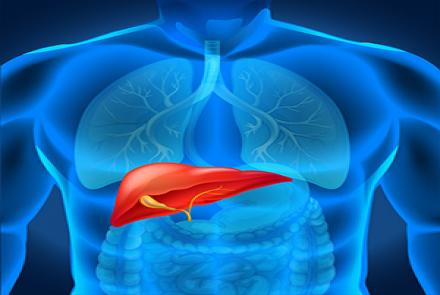
Chronic hepatitis is a disorder or inflammation of the liver that lasts at least 6 months. Common causes are hepatitis B and C viruses and certain drugs. Many people have no symptoms, but some have vague symptoms, such as a general feeling of illness, poor appetite, and fatigue.

Chronic hepatitis initially may not have any symptoms. But as the disease progresses there will be:
- Nonspecific symptoms such as generalized malaise, fever, poor appetite, fatigue, abdominal pain, weight loss, or anorexia.
- Muscle and joint pains.
- Hormonal imbalance leading to
- Hirsutism (abnormal hair growth).
- Gynaecomastia (swelling of the breast tissue in men).
- Testicular atrophy
- Loss of libido
- Absence of the menstrual cycle (amenorrhea)
- Peripheral edema (fluid accumulation in and around the ankle).
- Bleeding or hemorrhage especially from the Gastrointestinal system
- In advanced cases hepatic encephalopathy can cause confusion, disorientation, drowsiness etc..
- Abdominal distention.
- Itching all over the body.
Some signs to look out for include:
- Liver enlargement.
- Grey discoloration of the skin.
- Dilated veins or spider nevi on chest and upper body.
- Clubbing of fingers.
- Jaundice.
- Dupuytren’s contracture (flexed palm from hardened connective tissue)
- Xanthomas (fatty growths on skin)
- Palmar erythema (reddening of skin on palms and soles)
Changed
19/Jul/2017
Condition