
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common type of heart disease, also known as ischemic heart disease or coronary heart disease. Urbanization has increased sedentary behavior, unhealthy diet, and smoking, all significant risk factors for CAD. Read this to learn about Coronary Artery Disease and what you can do to manage this.
What is CAD or coronary artery disease?
Coronary artery disease is the most common heart problem. It is also known as ischemic heart disease or coronary heart disease. It occurs when the arteries carrying blood to the heart get blocked. This is due to accumulation of plaque which is a combination of fat, cholesterol, and other substances. This can restrict the blood flow to the heart causing a heart attack. It is often called a “silent killer” because it doesn’t usually cause any symptoms for many years until a heart attack suddenly happens.
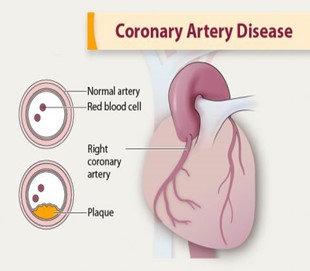
Image 1 – plaque buildup and narrowing of artery in coronary artery disease
What is the incidence in India? Why is it such a growing concern?
According to a World Health Organization (WHO) survey, 24.8% of annual deaths in India are because of cardiovascular diseases, and the main cause is CAD. It has created a big worry because people are living sedentary lives, eating unhealthy food and smoking due to adopting western ways living in the cities. These things are all big reasons why CAD is becoming more common. Early detection, timely treatment and regular monitoring is crucial for any disease, but many people don’t have access to preventive services or know about it. While people are living better lives due to improved health care services, chronic conditions like CAD is also increasing.
What are the possible causes? Who is most at risk?
Atherosclerosis is the main cause of CAD, where plaque builds up in arteries. It narrows arteries, resulting in impaired blood flow to the heart. This can lead to angina, or in severe cases, heart attack. Other risk factors include,
- High cholesterol - High LDL (low density lipoprotein), known as “bad cholesterol”, can induce plaque formation in arteries.
- Hypertension, Diabetes and smoking all lead to damage of the blood vessels supplying the heart.
- Obesity & sedentary lifestyle lead to high blood pressure, high cholesterol and diabetes, increasing the risk of CAD.
- Stress and family history also play an important role.
What are the types of coronary artery diseases?
There are 3 main types of CAD:
- Obstructive CAD – In obstructive CAD, the coronary arteries become narrow due to plaque buildup and blood flow is impaired. If this condition is not treated on time can cause a heart attack.
- Non-Obstructive CAD – This happens when coronary artery and its inner lining is damaged. Chest pain or shortness of breath can be experienced in this condition.
- Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection (SCAD) – When there is a tear in the artery wall, it results in reduced blood flow to the heart. Symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath or heart attack can happen. Extreme physical or mental stress, pregnancy, and abnormalities in the arteries can induce this condition.
What signs and symptoms of CAD should one look out for ?
Signs and symptoms of CAD can vary based on the severity of the condition. Each individual can experience different symptoms such as,
- Chest pain – Tightness or discomfort in chest. This pain usually occurs on the middle or left side of the chest, might radiate to shoulders, arms and neck. It often happens after physical exercise or stress and goes away after a few minutes.
- Palpitations – Fast heartbeats and fluttering during exercise, anxiety or stress.
- Shortness of breath and difficulty in breathing after normal activities.
- Excessive sweating without chest pain. Along with sweating, women may often experience nausea.
- Fatigue and dizziness- Persistent tiredness and dizziness experienced with normal physical activity.
What is the diagnostic process for CAD?
Regular checkups and monitoring are very important for early diagnosis of heart disease, as there are no symptoms observed in CAD before a heart attack often. Experts suggest that children and adolescents who are overweight or have a family history should get their self-checked for heart disease.
Diagnosis of CAD includes:
- Examination of blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, and respiratory rate.
- Pulse examination – Checking radial, carotid, femoral, and tibial arteries for swelling.
- Blood tests
- Lipid profile – For measurement of cholesterol and triglyceride to assess cardiovascular risk.
- Cardiac enzymes (e.g., troponin, creatinine kinase)– It measures enzymes released into the bloodstream during a heart attack.
- Assessment of blood sugar levels, especially in people with diabetes.
- Uric acid test – Elevated levels of uric acid are associated with CAD development.
- C-reactive protein – It examines inflammation in the body.
- ECG – It is used to check the heart’s electrical activity to detect any abnormality.
- Angiography – It is an invasive procedure that uses contrast dye and x-rays to visualize coronary arteries and identify blockages or narrowing.
- Cardiac MRI – It provides detailed images of the heart and blood vessels to assess damage due to CAD.
- Coronary calcium scoring –It is used to detect coronary artery calcification which is an important marker of Atherosclerosis. It is done through a CT scan and is quantified using scoring system.
- A score of zero - No calcium is seen in the heart and low chances of developing a heart attack.
- A score of 100 to 300 – Moderate plaque deposit which is associated with high risk of a heart attack over the next 3 to 5 years.
- A score > 300 – There is a high risk of a heart attack.
- Exercise stress test – This test checks your heart rate while you walk on a treadmill to examine how well your heart works under stress.
To understand cardiac tests in more details, read this: https://www.patientsengage.com/conditions/understanding-maze-cardiac-tests
Is it difficult to detect? Why are the symptoms often ignored or misconstrued as a mild issue?
Yes, detecting CAD is difficult as its symptoms may vary person to person. In people with diabetes, it may not show any symptom until a heart attack. While fatigue and shortness of breath can lead to other diagnosis instead of being diagnosed for heart problems. Lack of awareness about early symptoms and not knowing one’s family history can worsen the outcome. It is crucial to know about early symptoms and visit the doctor quickly for check-up. Raising awareness about the common signs helps in receiving timely treatment.
What treatment options are available (medical and surgical)?
Treatment of CAD depends on its severity and patient’s condition.
Medications for CAD:
- Anti platelet agent such as aspirin is prescribed to prevent blood clot formation and plaque rupture into the arteries.
- Statins are used to lower cholesterol levels.
- Beta blockers are used to reduce heart rate and blood pressure. bisoprolol and metoprolol are the most commonly prescribed beta blockers.
- To improve blood flow and widen blood vessels, calcium channel blockers are used. They allow blood vessels to relax and open by blocking calcium entry into arteries. The most commonly used are the longer-acting forms of diltiazem and verapamil, amlodipine, or felodipine.
- ACE inhibitors such as enalapril, lisinopril, ramipril are used to control the blood pressure.
- For immediate relief of chest pain (angina) nitroglyceride is given sublingually.
Medical Procedures for CAD
-
Coronary angioplasty – In this procedure, a balloon is used to open the blocked arteries. There are two types: plain balloon angioplasty and stent placement.
As shown in image 2, a catheter with a deflated balloon at its tip is guided to the site of the blockage. The balloon is inflated to compress the plaque and widen the artery, restoring blood flow. Sometimes as per the patient’s heart condition, a stent (a small mesh tube) is inserted into the artery to keep it open and prevent narrowing after the balloon is deflated and removed.
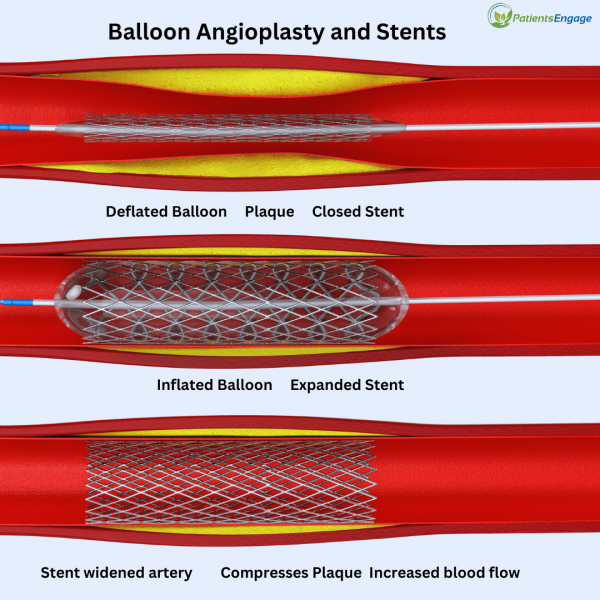
Image 2 – Angioplasty procedure - Thrombectomy – It removes blood clots from the coronary arteries to restore blood flow.
- Enhanced External Counter pulsation (EECP) - It is typically used to reduce chest pain that is not relieved by any medication. It increases blood flow to the heart using inflatable cuffs on the legs as shown in the image.
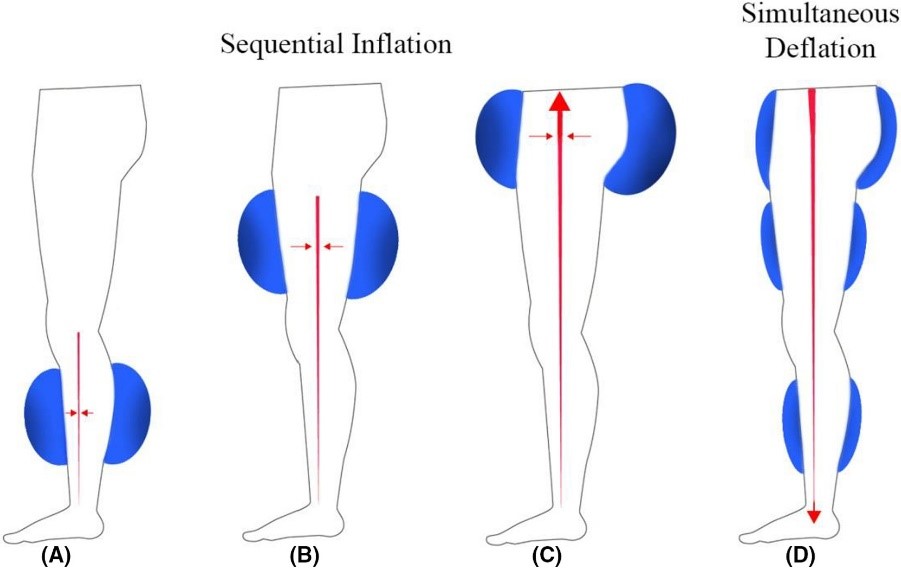
Image 3 – EECP procedure
Surgical Treatment for CAD
-
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG):
It is recommended when medicines and angioplasty is not enough. It bypasses blocked arteries using blood vessels from elsewhere in the body to create new route for blood flow to the heart muscle. Read about a personal experience of CABG at https://www.patientsengage.com/personal-voices/lucky-escape-heart-attack-trauma
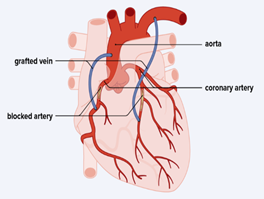
Image – 4 Process of coronary artery bypass
- Trans Myocardial Laser Revascularization (TMR): It improves blood flow to the heart by creating new channels directly into the myocardium using a laser. It will bypass the blocked coronary arteries and improve oxygen supply to the heart. It is recommended when traditional treatment don’t work.
How can Coronary Artery Disease be managed ?
You can follow the below mentioned tips for the management of CAD.
- Ensuring you take your regular medications and go for regular checkups.
- Following a heart-healthy diet by including more vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and whole grains. Inclusion of fiber-rich food in diet.
- Foods that are high in fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants to be preferred in the diet.
- Control saturated fats, sugar and salt in your diet.
- Quitting smoking and alcohol will improve your overall health.
- Joining cardiac rehabilitation programme is helpful for supervised exercise and overall fitness.
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercises, muscle strengthening exercises or aerobic exercises per week. It is best to do under trainer’s guidance as over exertion can be harmful.
- Brisk walking, cycling, swimming or dancing can be done to improve heart health. Always consult with a doctor before choosing any exercise, as per your heart condition.
- Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or mindfulness.
- Always be open for discussion with your counselor or support group people to address the emotional and social challenges.
What should one do to prevent their chances of getting CAD?
Lifestyle changes play a very important role in preventing the chances of CAD.
- Adopt a heart healthy diet by eating food that are rich in protein, fiber, antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids while low in saturated fats, cholesterol, sugar and sodium.
- Stopping smoking and alcohol is crucial for better heart health.
- Regular monitoring of blood pressure and blood sugar is very important. Keep regular track of it to maintain normal levels.
- Try to get a full medical checkup done bi-annually.
- A normal body BMI is 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m2. Eating well and exercising help keeps your weight healthy and reduces the risk of heart disease.
- Regular physical activity is key to better heart health.
- Mediation, art therapy, yoga and pet therapy can be helpful to relax your mind or relieve anxiety.
- Spending time with your loved ones and doing what you like plays a vital role in reducing stress.
- Keeping your eye on risk factors, making necessary lifestyle changes and seeing your doctor regularly is an essential part of preventing chances of getting CAD.
Dr. Lavleen Gaur and Dr. Shital Patel
References:
- Image1-https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/coronary_ad.htm
- https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/coronary_ad.htm
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16898-coronary-artery-di…
- https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lansea/article/PIIS2772-3682(23)0001…
- https://journals.lww.com/indjem/fulltext/2023/03000/prevalence_of_coron…
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/magazines/panache/world-heart-day-…
- https://bmccardiovascdisord.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12872-0…
- https://www.advocatehealth.com/health-services/advocate-heart-institute…
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/coronary-heart-disease/diagnosis
- https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medica…
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3587668/
- https://www.medtronic.com/us-en/patients/treatments-therapies/heart-sur…
- Image 3 EECP - https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jcpt.13330
- Image 4 - CABG image - https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322443#procedure
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronary-artery-disease/…










