Parkinson’s disease can progressively become a debilitating condition that can affect daily functioning. Besides medications, there has been little progress in the treatment options. In recent years, a surgical therapy called Deep Stimulation of the brain has gained popularity as it seems to allow patients to manage certain symptoms. Lets take an in-depth look at what this procedure entails.
What is Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)?
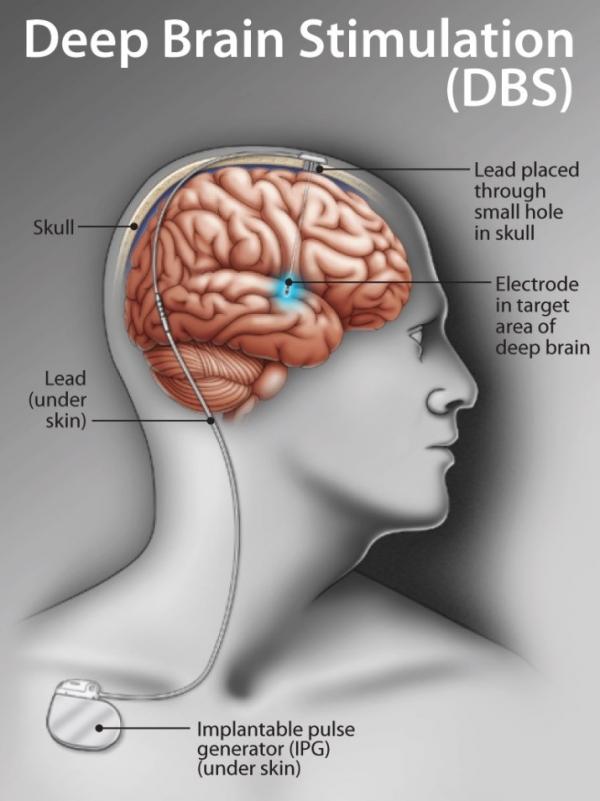
Deep Brain Stimulation or DBS is a surgical procedure to treat symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. 2 electrodes are inserted in specific areas of the brain to better control and prevent abnormal brain activity. In Parkinson’s, electrodes are commonly placed in the subthalamic nucleus (STN) or globus pallidus internus (GPi).
Tiny wires are connected to these electrodes to provide electrical impulses. These wires or leads are connected to a small neurostimulator (like a pacemaker) which is typically implanted below the collarbone. This device is then programmed to provide optimal symptom control.
Listen to the discussion on DBS with neurologists and persons with Parkinsons
DBS can be performed while the patient is awake or asleep (under MRI scan). Most neurologists prefer the patient to be awake unless it is very unsettling.
Besides Parkinson’s, DBS can be used to treat other movement & neurological disorders, epilepsy, essential tremors, dystonia etc. While DBS cannot completely resolve the symptoms, it can reduce them thereby improving the quality of life for patients. Consequently, medications will also be decreased but not completely stopped.
Why and when is DBS recommended?
The timing of surgery is very important. Not everyone is eligible for this procedure or may find it of benefit.
The criteria for patient selection includes:
- Persons with typical Parkinson’s disease
- Persons with Parkinson’s for at least 4 years
- Have motor symptoms that affect daily life
- Have increasingly “off’ periods when your medicine wears off before the next dose is due.
- Have troubling "on" periods when you have medication-induced dyskinesias (excessive wiggling of the torso, head, and/or limbs).
- Experience motor fluctuations despite medical therapy
- Have functionally disabling symptoms despite numerous adjustments to mediations
- Usually recommended under age of 70 but this is not an absolute cut-off. Young-onset patients are better candidates.
- Must not have any cognitive impairment (mild or moderate) as results will be much lesser.
Risks
The biggest and most fearful risk is of brain hemorrhage. This risk has reduced over time with new advances in imaging and surgical techniques. The second common risk is of infection, from the perioperative period but can occur at any point while the implant is present. The only solution is then to treat with antibiotics or ultimately remove the implant.
Choosing care team
Your neurologist will evaluate and recommend if you are eligible for DBS. A neurosurgeon who specialises in Motor disorders and DBS will be referred to for further pre-op evaluation. After the Neurosurgeon has implanted the leads and the neurostimulator, your Neurologist will program it after a few days. If there is a swelling at the site of the lesion, programming is delayed till the swelling settles, this may take weeks. The medication doses also come down in proportion to how well the programming is working.
Which DBS device to opt for?
Currently there are two brands available and used in India. Discuss with your doctor on which device may be most suitable for you based on price and function. All brands come with rechargeable or non-rechargeable batteries. Rechargeable devices can last upto 15 years while non-rechargeable ones last 3-5 years. In the latter devices, old battery can be replaced by the neurologist in an outpatient procedure.
Importance of setting up supportive care
Social support is important especially in the first 4 to 6 weeks. To a large extent, patients are able to manage their programming and battery themselves but it helps to have a carer around who is a little tech savvy and can handle the charging and minor adjustments for programming.
Choosing your device becomes very important esp for patients who are living alone. Recharging is a requirement of the device that must be done on time. If the patient is sick, or forgets then it can have drastic unwanted consequences. Hence, rechargeable devices are only for people who live with family members. For people living by themselves or in nursing or assisted care homes, nonchargeable devices are recommended.
What happens after surgery?
Surgery can be tiring so brace yourself for a lengthy procedure. Post surgery, programming starts at 3-4 days. Initially low currents are sent and patient is discharged after 7 days. At home, follow instruction on how to bathe, keep the incision clean & dry and how to operate the neurostimulator. Follow-up occurs after a month for any fine tuning. During this month, the Parkinson symptoms may be at the lowest but soon these surgical effects wean off and certain symptoms return. Hence optimisation of the programming is done after this period at 4-6 weeks. Subsequent follow-ups will be determined by your neurologist.
Managing life after DBS
DBS is expected to better the quality of life for patients and their care providers. Patients can expect improvement in the motor symptoms of the disease like tremor, slowness and stiffness. 70% to 90% improvement may be seen. Medication can be reduced by 50 to 60% but not discontinued completely since dopamine is still an essential component of treatment. Dyskinesias or involuntary movements also are expected to reduce by around 90%.
Other symptoms that may reduce are:
- Pain which can be very disabling during the ‘off’ times
- Sleep quality may also improve as nocturnal ‘off’ times reduce.
Note: Following symptoms will not improve after DBS
- Memory
- Gait
- Bladder control
- BP fluctuations
Certain activities like swimming have to be avoided after the surgery. Moods and behavioural changes may be seen. Apathy, compulsive behaviours, bipolar disorder and depression are some of the psychological changes that patients have reported. Doctors explain that these changes occur because medications are reduced post DBS, which normally keep the patient at a higher mood level. Reduction in dosage is likely to cause depression and low moods. Other reasons include resentment of the over-caring caregiver, loss of social support along the way, feelings of lack of meaning in life etc. now that DBS has provided physical independence. Some of these changes may be transient but you should alert your doctor and address them right away.
Remember that some of your earlier symptoms and dystonia or gait issues may return after a few years, since Parkinson’s is a progressive disease. Gait and balance are more challenging and can get worse.
References:
- Rachel Dolhun, MD. “ASK THE MD: Which DBS Device Is Right for Me?” The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research | Parkinson’s Disease, www.michaeljfox.org/news/ask-md-which-dbs-device-right-me. Accessed 17 Apr. 2024.
- Defepiadmin (2022) Deep Brain stimulation, The Defeating Epilepsy Foundation. Available at: https://www.defeatingepilepsy.org/treatment-for-epilepsy/deep-brain-sti… (Accessed: 15 April 2024).
- Deep Brain stimulation (2021) Johns Hopkins Medicine. Available at: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/de… (Accessed: 16 April 2024).