There are number of treatments available to treat diabetes. Treatments are individualized based on factors such as age, overall health, and presence of other medical conditions.
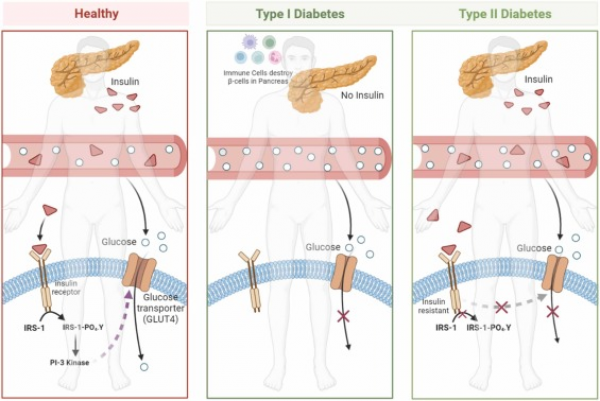
Image 1 - Type 1 vs Type 2 diabetes: Pancreas does not produce adequate insulin (Type 1 diabetes), or the body unable to use insulin appropriately (Type 2 diabetes) which results in impaired glucose metabolism
For Type 1 diabetes, insulin injection is prescribed whereas for Type 2 diabetes, insulin or medications are prescribed. Physical exercise and balanced diet also play important role in treatment.
Individuals with Type 1 diabetes will need insulin therapy throughout their life. There are many types of insulin:
- Short acting insulin – It is called regular insulin; this type starts working around 30 minutes after injection. It reaches peak effect at 90 to 120 minutes and lasts about 4 to 6 hours.
Examples – Actrapid, Humulin R - Rapid acting insulin – It starts working within 15 minutes. It reaches peak effect at 60 minutes and lasts about 4 hours. It is often used 15 to 20 minutes before meals.
Example – Insulin Lispro - Intermediate acting insulin- This type of insulin starts working in about 1to3 hours, reaches peak effect at 6 to 8 hours and lasts 12 to 24 hours.
Examples – NPH and lente - Long acting insulin – This type of insulin may provide coverage for as long as 14 to 40 hours.
Examples – Insulin glargine
These can be used in combination too as per individual needs.
Insulin delivery options
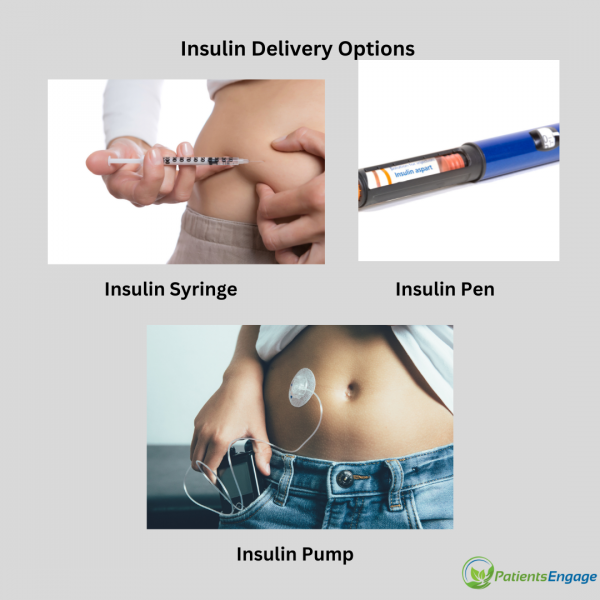
Image 2 – Insulin syringes and Insulin pen
Insulin is not administered through mouth as stomach enzymes break down insulin and prevent it from working. Insulin is administered through subcutaneous injections, Insulin pens and Insulin pumps.
Insulin syringes – These are specially designed syringes for administrating insulin injections. They have a thin, short needle that is specifically designed for subcutaneous injections, which means injecting insulin into the fatty tissue just beneath the skin. It is specifically calibrated for measuring small doses of insulin accurately.
Insulin pen are prefilled devices that allow easy and accurate dosing. Those are available in refillable and disposable varieties.
Insulin pump is a small device that delivers insulin continuously throughout the day as a healthy pancreas. An insulin pump is a device about the size of a cellphone that's worn on the outside of your body. A tube connects the reservoir of insulin to a catheter that's inserted under the skin of abdomen. It is programmed to dispense specific amounts of insulin automatically and when you eat. Insulin pumps require regular monitoring and maintenance, including checking blood sugar levels, changing infusion sets, and replacing the insulin cartridge.
Insulin should be stored at recommended temperature to maintain its effectiveness. It should be protected from heat, cold and direct sunlight.
Related Reading: Worried about Insulin Shots?
Medications used to treat Type 2 diabetes:
Metformin: A commonly prescribed oral medication that helps lower blood sugar levels by reducing glucose production in the liver and improving insulin sensitivity in the body.
Sulfonylureas: Oral medications that stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin, hence helping to lower blood sugar levels.
SGLT-2 inhibitors: Medications that work by blocking the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, leading to increased glucose excretion in the urine and lowered blood sugar levels.
Insulin: Injectable hormone used when blood sugar levels cannot be adequately controlled with oral medications alone. It can be short-acting, long-acting, or a combination of both. More information of insulin delivery options above.
GLP-1 agonists: Injectable medications that stimulate the release of insulin, suppress glucagon secretion, and slow gastric emptying, resulting in improved blood sugar control.
If blood sugar levels are not managed with oral medications, then insulin is prescribed for Type 2 diabetes.
Advanced mode of diabetes treatment includes Artificial pancreas, Connected CGM- Insulin pumps. There is also ongoing research for Nano medicine. Nano medicine is assisting emerging therapeutic methods opening a new path in diabetes cure, such as regenerative medicine, artificial organ, immunotherapy, gene therapy and stem cell therapy.
Updated February 2025
An Endocrinologist or Diabetologist should be consulted at least once every six months or as directed by your treating physician.