Stroke is one of the leading causes of disability and death worldwide. The good news is that stroke is treatable, and the patient has most chances of recovery when immediate treatment is given. Dr. PN Sylaja, Professor and Head of Neurology, In-Charge Comprehensive Stroke Program, SCTIMST Trivandrum, Kerala explains how to recognize signs of stroke and to be aware of the risk of stroke.
Introduction
Stroke is one of the leading causes of disability and death worldwide. In India itself, the incidence rates every year ranges from 105 to 152/100,000 people. The good news is that stroke is treatable, and the patient has most chances of recovery when immediate treatment is given. In order to be able to help a person having a stroke to timely reach hospital , it is important to be able to effectively recognise the warning signs and symptoms of Stroke. It is also important to understand if you are at a high risk of stroke.
Stroke Signs To Watch Out For
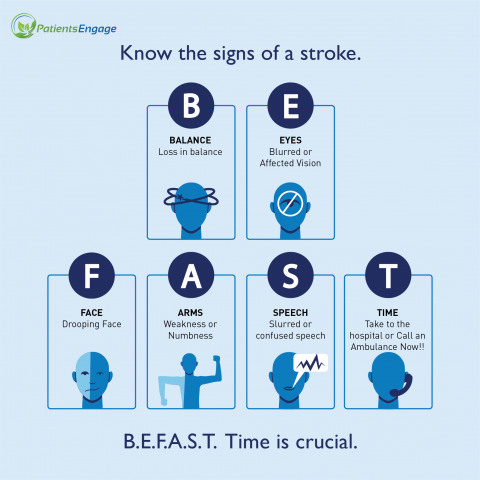
Use the acronym B.E.F.A.S.T. to spot a patient going through a Stroke attack:
B- Balance problems. Maybe be unable to walk or balance properly. There maybe be dizziness and/or lack of coordination
E- Eye troubles. Having vision problems in one or both eyes.
F- Facial drooping or palsy. This is often not easy to detect for a person who may not have seen the person in normal times. A simple test can be to ask the person to smile or raise their eyebrows and check if both sides look the same.
A- Arm weakness. This can be in both or just one arm. If the person is unable to lift or bend their arm or make a fist, this maybe a sign. Often you may find that the patient has dropped whatever they were carrying due to the sudden weakness.
S- Speech slurring. It may become difficult to speak as tongue may become weak or numb. Jaw muscle may not move, mouth may not open. Speech may become slow, incoherent or stuck.
T- Time for action. Call for an ambulance to take the patient to the nearest Stroke-ready hospital with a 24-hr CT scan facility. Do not wait for a doctor to arrive. If an ambulance is too far away, transport the patient in a car to the closest hospital. If you are transporting the patient, it would be wise to call the hospital ahead to alert them so they are prepared. Remember time is of essence and every minute counts.
Other Symptoms of Stroke
Beyond B.E.F.A.S.T, there are a few other signs and symptoms that you should watch out for. Remember that on their own, some of these symptoms may not be indicative of stroke but must be brought in for medical attention nonetheless, since stroke cannot be ruled out by observing the symptoms alone.
- Numbness. This could be sudden loss of feeling or weakness of arm, leg, face, hand. It may be one-sided.
- Confusion includes confusion, behavioural change, inability to understand others speaking etc.
- Severe headache. Sudden onset of a major headache with no known cause.
- Vertigo- Feeling of the room spinning around you.
- Nausea/Vomiting
Stroke diagnosis would require tests and scans that can be only be done only at a hospital setting. Mini-strokes are also called Transient Ischemic Attacks or TIAs and are self-limiting, i.e they resolve within 24 hours. We need to know that 15-20% of the patients with TIA if not treated will develop stroke in the next 3 months.
Fast Action
Time is critical after a stroke. The time window from presentation of a stroke symptom to receiving medical attention should be 4.5 hours. To ensure that a patient gets to the hospital within this time frame, it is important that people are aware of stroke symptoms, can recognise them and take action immediately. Delay in hospitalisation is known to increase the chances of disability and mortality.
|
Stroke is a Medical emergency, so act fast! |
Risk Factors of Stroke
Stroke can occur at any age. So, it doesn’t just affect the elderly. However, the chances of stroke do increase in a person who has certain risk factors.
Stroke is known to have multiple factors that can increase risk, but most of these factors can be treated and medically managed. For easy understanding, we divide the risk factors into modifiable and non-modifiable i.e. those can be changed and those that cannot be.
|
Modifiable Risk Factors |
Non-modifiable Risk Factors |
|
|
Reduction and management of modifiable risk factors can significantly decrease a person’s chances of getting a stroke. In those, who have the non-modifiable risk factors, it is imperative they pay attention to and control their modifiable risk factors. To find out what your risk is, try this simple scorecard to know your score and what you can do to reduce it.
|
Did you know that 90% of all strokes can be prevented? |
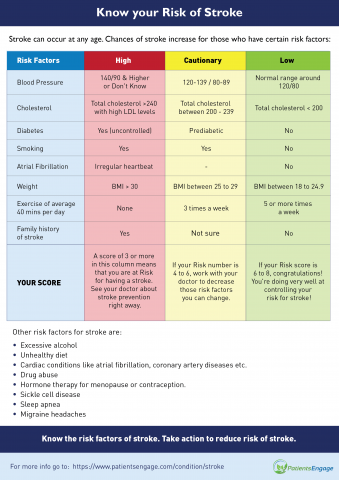
Risk Assessment (1 point each)
|
Risk Factors |
High Risk |
Caution |
Low Risk |
|
Blood Pressure |
> 140/90 or unknown |
120-139/80-89 |
<120/80 (normal) |
|
Atrial Fibrillation |
Irregular heartbeat |
I don’t know |
Regular heartbeat |
|
Smoking |
Smoker |
Trying to quit |
Nonsmoker |
|
Cholesterol (Total) |
>240 or unknown |
200-239 |
<200 |
|
Diabetes |
Yes |
Borderline |
No |
|
Exercise |
Couch potato (None) |
Some exercise |
Regular exercise |
|
Diet |
Overweight |
Slightly overweight |
Healthy weight |
|
Stroke in Family |
Yes |
Not sure |
No |
|
Your Score |
A score of 3 or more in this column means that you are at High Risk for having a stroke. See your doctors about stroke prevention right away |
A score of 4 to 6 in this column needs Caution. This is a good start, but work with your doctor to decrease those risk factors you can change |
If your score is 6 to 8 in this column, Congratulations! You’re doing very well at controlling your risk for stroke |
Issued as part of the public education series by Boehringer Ingelheim India and PatientsEngage
References:
- Brainin, M., & Heiss, W. (Eds.). (2014). Textbook of Stroke Medicine (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9781107239340
- Jones SP, Baqai K, Clegg A, Georgiou R, Harris C, Holland EJ, Kalkonde Y, et al. Stroke in India: A systematic review of the incidence, prevalence, and case fatality. Int J Stroke. 2021 Jul 2:17474930211027834. doi: 10.1177/17474930211027834.
- American Stroke Association (2021). Defeat stroke by acting FAST. Available at: https://www.stroke.org/en. Last accessed on 27th October 2021.
- Cure 4 Stroke Foundation (2014). Stroke risk scorecard. Available at: http://www.cure4stroke.org/2014/09/get-stroke-risk-score/. Last accessed on 27th October 2021.
- Howard G, McClure LA, Moy CS, Howard VJ, Judd SE, Yuan Y, et al. Self-Reported Stroke Risk Stratification: Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke Study. Stroke. 2017 Jul;48(7):1737-1743. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.016757.