Risk Factors of Obesity
- Genetics:
Single-gene (monogenic) obesity: Rare cases of obesity are caused by changes in a single gene, such as MC4R. Polygenic obesity: Most obesity is multifactorial, meaning it's caused by many genes working together. Genetic mutations: Abnormal changes in DNA sequence can also contribute to obesity.
Genes may be a significant contributor to one’s cause of obesity if they have most or all of the following characteristics:
- If one has been overweight for most of their lives.
- One or both parents/several other blood relatives are significantly overweight. If both parents have obesity, the likelihood of developing obesity is as high as 80%.
- Inability to lose weight even when one increases their physical activity and adheres to a low-calorie diet for several months.
- Family History:
People who have a higher BMI and have a family history of obesity may be at risk of developing obesity. Research suggests that about 35-40% of a child’s weight predisposition is inherited from their parents. In some cases of childhood obesity, the genetic impact may be as high as 55 to 60%.
- Dietary Habits:
The body has more energy than it can use when we consume more calories than we expend. When this occurs, the body saves any excess energy for later use in adipose tissues, or fat cells. If we regularly consume more calories than we burn, our body continuously creates new fat cells and enlarges the ones already there.
Eating excess junk food, drinking excess alcohol that has high calories, eating large portions of food, drinking sugary drinks (cold drinks, soda, energy drinks, fruit juice), and stress eating or eating in front of a screen/phone or TV.
- Lack of physical activity, mobility, and exercise:
Lack of physical activity, combined with long duration spent on screen time being sedentary (TV, computer, video game, mobile, etc.), puts one at an increased risk of being overweight and obese.
- High Stress:
Long- or short-term stress may affect the brain and trigger the body to increase production of some hormones like cortisol that control energy balances and hunger pangs. These hormone changes can give an exaggerated sense of hunger, thus contributing to unhealthy eating habits and storage of fat in the body.
- Poor Sleep:
Many research studies now reveal the relationship between poor sleep and being overweight or obese. Sleep deprivation can disrupt hormones related to hunger like leptin and ghrelin. Ghrelin is produced by cells in the gut, and its main role is to increase appetite, while leptin is produced in the small intestine and inhibits hunger and energy balance. Sleep deprivation can lead to hedonic hunger, which is a preference for energy-dense food items.
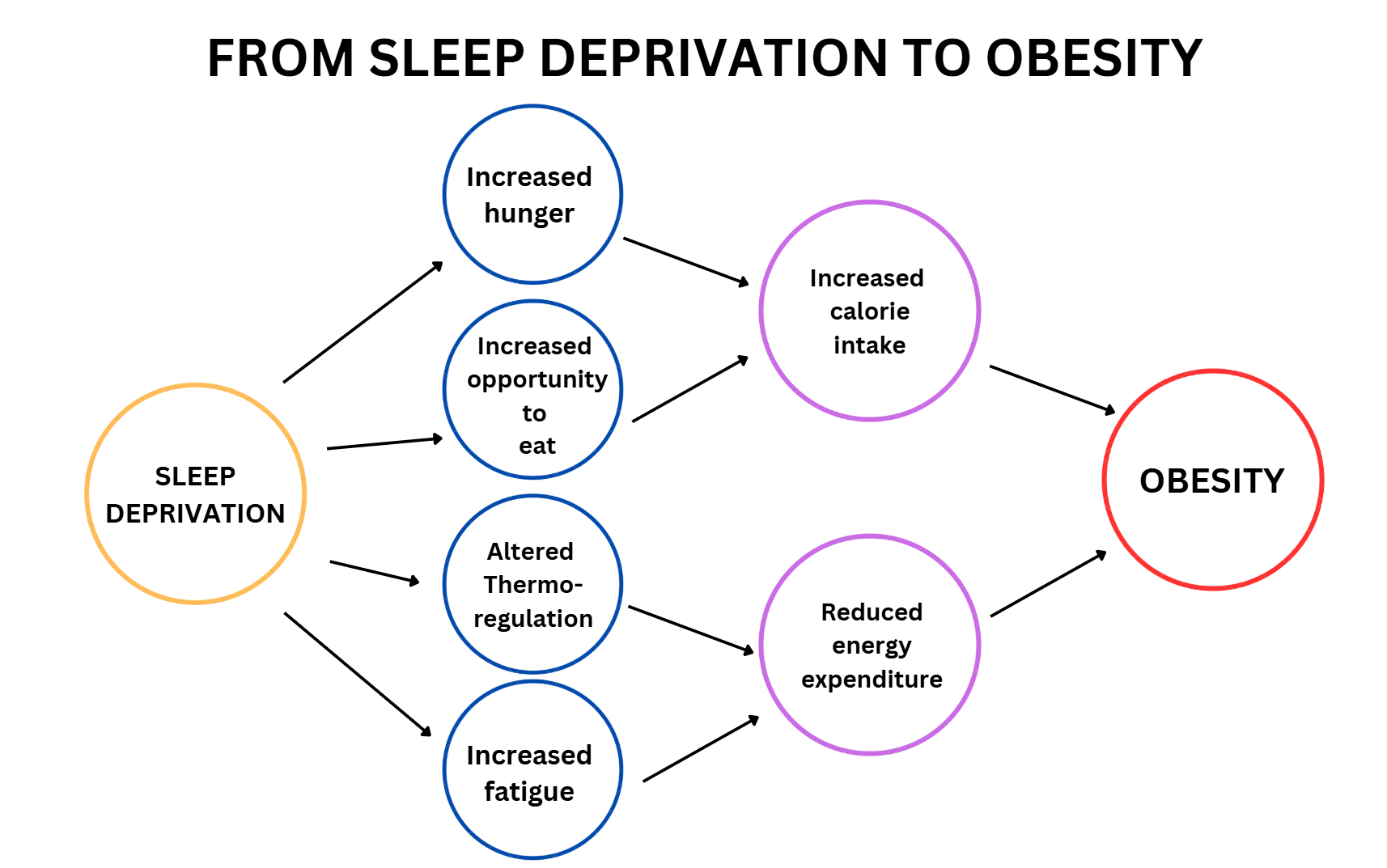
https://www.migrelief.com/from-sleep-deprivation-to-obesity/
- Smoking:
Smoking is associated with higher body weight, abdominal obesity, and insulin resistance. It can cause more fat to accumulate around the abdomen. It can also increase fat deposits around organs like the liver (visceral fat).
- Excess Alcohol Consumption:
Excess alcohol consumption is often associated with unhealthy eating habits, and the extra calories from alcohol also create room for being overweight and obesity.
- Environmental Factors:
Workspace environment: Jobs that demand long sedentary hours can add to the risk of obesity due to lack of physical activity.
The type of food available in the locality (restaurants/cafes/canteens) and the use of transport (how many people use cycles or walk) greatly influence the chances of obesity.
The level of air pollution indirectly influences chances of obesity, as in a more polluted place, people are less likely to exercise outdoors, walk, or cycle.