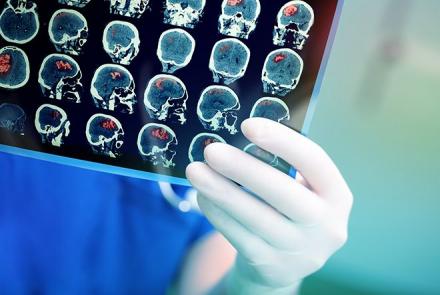
A stroke is caused by the interruption of the blood supply to the brain, usually because a blood vessel bursts or is blocked by a clot. This cuts off the supply of oxygen and nutrients, causing damage to the brain tissue.
The effects of a stroke depend on which part of the brain is injured and how severely it is affected. A very severe stroke can cause sudden death.

Different types of Stroke are:
Thrombotic stroke: This kind of stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is blocked by a blood clot in a blood vessel.
Embolic stroke: This is caused when a travelling particle like fat, air, cancer cells or clump of bacteria in the blood stream blocks a blood vessel in the brain.
Haemorrhagic stroke: This is caused by a breakage or rupture of a blood vessel in the brain leading to bleeding within the brain.
Silent stroke: This does not have any outward symptoms and the patients are typically unaware they have suffered a stroke. The patient may have slight memory problems or a little difficulty getting around. A doctor may be able to see signs of silent strokes without testing.
Changed
24/Oct/2021
Condition