Liver Cirrhosis is one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide. Dr. Ameet Mandot (DNB GastroEnterology) addresses commonly asked questions on Liver Cirrhosis.
1. What is Cirrhosis of Liver?
It is a chronic disease characterized by a structurally and functionally impaired liver. This includes loss of liver cells and scarring of the tissue.
2. What are the causes of Liver Cirrhosis?
Though routine understanding shows that alcohol consumption causes the Liver Cirrhosis, there are many more causes such as Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Autoimmune Hepatitis and Wilson’s disease. One of most emerging causes is Metabolic Dysfunction-associated liver disease (MASLD) or Metabolic dysfunction-associated Steatohepatitis (MASH). Few of the causes are seen to be common in family members, so family member screening should be considered for such inherit risk cases.
3. What are the signs and symptoms of Cirrhosis?
It varies from more specific symptoms like ascites (fluid build-up in the abdomen) , jaundice (yellow discoloration of the skin, eye, nails etc.) to vague non-specific ones like fatigue, pedal edema (swelling in the feet). Sometimes it may also be detected as part of work up for anemia or thrombocytopenia (low Hemoglobin or platelet count).
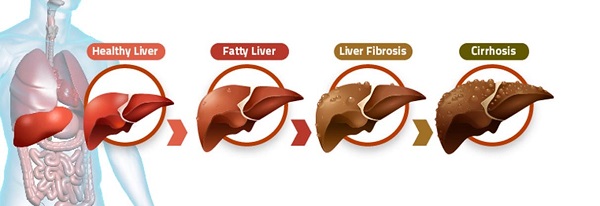
Fig: Stages of Cirrhosis
4. Which persons should be evaluated for Liver Cirrhosis?
Chronic alcoholics, obese patients with diabetes, family history of cirrhosis, unexplained long-term fatigue patients should all be assessed for liver damage.
What does MASLD mean for people with diabetes
5. What are the complications of Liver Cirrhosis?
Hematemesis (blood in vomit) and malena (black coloured stools), ascites (fluid in abdominal cavity), and Hepatic encephalopathy are common complications ultimately leading to death if left untreated. Small subset of patients may develop Hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer) over a long duration.
6. What are the tests required to detect liver cirrhosis?
To detect cirrhosis, ultrasound of the abdomen, liver function tests and complete blood count (CBC) are sufficient. Other important tests that can be useful are Fibroscan, MR elastography and ARFI scan.
- Fibroscan is a special ultrasound machine used for measuring scarring and fatty changes in the liver.
- MR elastography or MRE uses sound waves to measure the stiffness in cases of chronic liver disease.
- ARFI (Acoustic radiation force impulse) scan is also an ultrasound test often used with the Fibroscan to improve accuracy of liver fibrosis diagnosis.
Liver fibrosis is the buildup of scar tissue in the liver. These tests are accurate non-invasive tests to quantify the fibrosis in the liver and we know based on studies that the stage of fibrosis correlates with long term outcome of chronic liver disease. Hence these are useful modalities for evaluation of chronic liver disease
7. Is cirrhosis treatable? What are the current treatment options available?
Yes. If timely diagnosis is made then it can be treated and/or at least can be kept under control. Treatment options available and lifestyle changes include:
- Treating the underlying cause like antivirals for hepatitis B and C.
- Immunosuppressants for treating cases of autoimmune hepatitis.
- Vaccinate for the Hepatitis B virus, if tested and found to be negative.
- Abstinence from alcohol, a lifestyle modification for metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease (MASLD) (formerly called NAFLD) patients.
- Monitoring and treating complications of cirrhosis like GI bleed, ascites etc.
- Liver disease is known to cause changes in bowel movements and stool consistency, so avoid constipation. Eat a high fiber diet and exercise daily.
- Any types of long-lasting anesthetic drugs such as sedatives or painkillers (esp. NSAIDs) must not be used by patients of cirrhosis.
- Liver Transplant is the ultimate curative treatment for advanced cirrhosis of liver
8. What are measures to prevent development of Cirrhosis?
Some of the measures which have a huge impact on cirrhosis development and even progression are
- Cut down on/ stop alcohol intake
- Reduce weight
- Exercise
- Control Diabetes
- Hepatitis B vaccination.
9. How can Cirrhosis be detected earlier?
Do not ignore any non-specific symptoms. Seek prompt consultation and timely work up to detect and diagnose it early. Also be more alert if there is any family history of cirrhosis or any risk factors. Patient alertness is the key factor.

Dr. Ameet Mandot practices independently as a gastroenterologist and hepatologist at various reputed hospitals in Mumbai since 15 years.