
Bladder cancer is the 10th common cancer worldwide. In India it is often diagnosed late due to limited awareness of bladder cancer and its symptoms. Let us understand the symptoms of bladder cancer, the diagnostic tests, the treatment options and some commonly asked questions about bladder cancer treatment, prognosis and effect on quality of life.
What is bladder cancer?
Urinary bladder is a muscular organ situated in the pelvic cavity. Its primary function is to store urine produced by the kidneys. When the bladder is full, it sends signals to the brain for urination. Bladder cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the tissues of the urinary bladder. Typically, cancer begins in the cells lining the inside of the bladder.
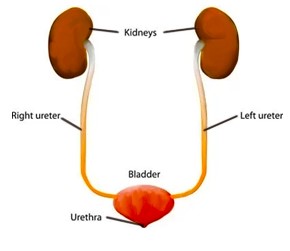
Image -1 Urinary system
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
There are various symptoms of bladder cancer, depending on its severity and stage. The most common symptom observed is painless passage of urine with blood, known as hematuria. Other symptoms may include frequent urination, pain or burning sensation during urination, back pain, and difficulty urinating. If the cancer has metastasized to distant body parts, additional symptoms such as abdominal pain or bone pains may arise. In advance stages, weight loss and fatigue can occur.
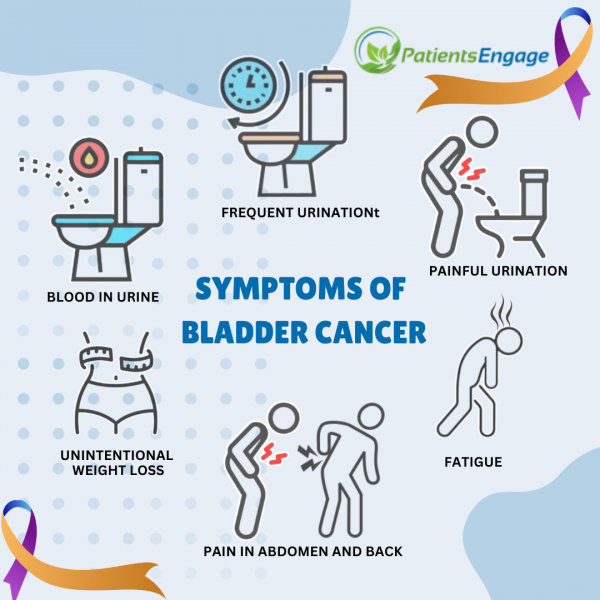
As symptoms of bladder cancer can resemble symptoms of urinary tract infections, diagnosis may be delayed. All hematuria is not a sign of bladder cancer, but must be brought to a doctor’s attention. Consulting a doctor is crucial, as based on the symptoms they can refer patient for tests.
How is bladder cancer diagnosed?
Initially doctor will examine the medical history, including the presence of any risk factors such as smoking or exposure to chemicals. The diagnosis of bladder cancer involves various tests:
- Urine cytology test – The urine sample is examined under a microscope to identify abnormal or cancer cells.
- Cystoscopy – It is done by passing an endoscope through the urethra into the bladder to examine any lumps or abnormal growth area in inner lining of the bladder.
- Biopsy – If suspicious areas are identified during cystoscopy, doctor may perform biopsy to collect samples for analysis.
- Various imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan and MRI are recommended to obtain more details on abnormalities and spread of tumor.
- Ultrasound helps identify tumors or other abnormalities in bladder.
- CT scan will provide detailed image of urinary tract including the bladder. It will also determine the size and location of the tumor.
A combination of these diagnostic tests help doctors to diagnose bladder cancer, determine the stage of the disease and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
What are the various types and stages of bladder cancer?
There are three types of urinary bladder cancer according to cell types observed under the microscope.
- Urothelial cancer – This is also known as transitional cell carcinoma. It accounts for the majority of bladder cancer cases.
- Squamous cell carcinoma – This is associated with parasitic infections like schistosomiasis, which are more prevalent in certain regions like Africa.
- Adenocarcinoma – This is less common type and relatively rare.
Stages of bladder cancer:
- Stage Tis – Known as tumour/carcinoma in situ. Cancerous cells are confined to the innermost lining of the bladder and have not penetrated the basement membrane.
- Stage T1 – Involves penetration of the cancer cells through the basement membrane into the connective tissue beneath the bladder lining.
- Stage T2 – Occurs when the cancer invades the muscular layer of the bladder.
- Stage T3 – The cancer extends beyond the bladder muscle, affecting surrounding structures such as prostate or seminal vesicles in men, and nearby tissues in women. Nearby lymph nodes also can be involved.
- Stage T4 – It is the most advanced stage of cancer, in which cancer has spread to distant parts of the body or to lymph nodes beyond a certain threshold. At this stage the cancer is considered incurable and palliative care is recommended.
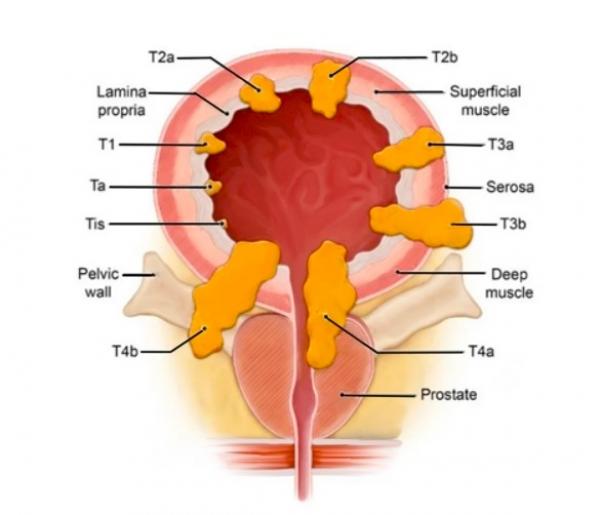
Image -2 Diagram illustrating the different T-stages of bladder cancer.
Early diagnosis is crucial to achieve better treatment outcomes, when cancer has not yet invaded the muscular layer of the bladder.
What are the various treatment options for bladder cancer?
The treatment of bladder cancer depends on the stage and the grade of malignancy. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy and immunotherapy.
Cancer grade indicates the rate of growth and abnormality of the cancer cells. Low grade bladder cancer cells resemble normal cells and spread slowly, whereas high grade bladder cancers grow rapidly and look different. For low-grade malignancies and localized disease, treatment typically involves transurethral resection of tumor followed by treatment with immunomodulators or chemotherapy agents.
High grade cancers typically have a worse prognosis and may require aggressive treatment. Taking into account, the invasion of cancer into muscles, involved lymph nodes, or metastasis of tumor to other organs, these patients will require multimodality treatment.
Radiation therapy can be used in curative treatment settings for organ preservation or as a palliative measure to relieve symptoms in cases of metastasized cancer, such as bone metastases causing pain.
Treatment plan is decided based on other factors also such as:
- Health and fitness levels as elderly patients may not be suitable for certain treatments. In such cases radiotherapy may be considered.
- Comorbidities may have limitations undergoing surgery or chemotherapy.
- Specific genetic mutations or biomarkers can guide targeted therapies. Specialized tests and molecular profiling are needed to identify these.
- Availability and affordability of treatments, especially for newer modalities like immunotherapy and targeted therapy. Cost is a deciding factor for many people
- Age related health issues like frailty is essential. In India, the median age of bladder cancer patients is relatively younger than in western countries.
- Careful consideration of patient’s specific circumstances and needs.
What are the main treatment approaches for any cancer?
There are three main treatment approaches in cancer care:
- Neoadjuvant treatment – It is given before the primary treatment, typically for surgery, with the aim of shrinking the tumor, making it easier to remove, and reducing the risk of micro-metastasis. This approach helps improve survival rates and decrease the likelihood of cancer recurrence. Recurrence is the development of entire new episode of cancer
- Adjuvant treatment – Administered after the primary treatment, to prevent cancer recurrence and improve survival rates.
- Palliative treatment – Focuses on improving the patient’s quality of life and managing symptoms, even if the disease can’t be cured. The primary aim is to enhance survival and overall well-being.
What are the newer treatment options for bladder cancer in India?
Newer treatment options are available with less side effects and improved efficacy.
- For non-muscle invasive bladder cancer, traditional treatment with BCG has been problematic. Newer chemotherapy drugs like docetaxel or gemcitabine offer more safety and tolerability.
- For muscle invasive bladder cancers, advancements in surgical techniques, particularly with bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder), have reduced post-operative mortality rates.
- The introduction of immunotherapy after chemotherapy and surgery has significantly improved disease control rates, compared to previous treatments.
- Innovations in bladder preservation techniques, such as combining radiotherapy with safer chemotherapy drugs, offer effective alternatives to radical surgery while preserving organ function.
- Molecular testing helps understand the disease and cellular structures to develop more effective treatments.
What are the side effects of the bladder cancer treatment and their management?
Cancer treatments including surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy can cause various short term and long-term side effects. Short-term side effects include lymphedema and sexual health issues. While long-term side effects include neuropathies, tumor development and cardiac problems, particularly due to radiation and chemotherapy.
- Structural changes resulting from surgeries, especially for muscle invasive bladder cancer can affect reproductive and sexual health. Patients may require psychological and emotional support to cope with these changes.
- Fertility is not directly impacted by surgery. However, radiation and chemotherapy can lead to infertility, making fertility preservation option important for younger patients before starting the treatment.
- Living with the stoma bag or urostomy bags may impact physical activities and body image perception.
- Metabolic abnormalities such as electrolyte imbalance and creatinine elevation may occur after bladder removal and reconstruction. Careful monitoring is necessary for managing this.
- Cystitis or inflammation of the bladder can occur after radiation therapy. Urinary symptoms such as urgency, frequency and discomfort may be experienced. Medications and supportive care is required to manage this side effect.
- Rectal complications also happen as radiation to the bladder area may affect the adjacent rectum, leading to inflammation of the rectum or bleeding from rectum. Symptomatic treatment is necessary.
- Nausea and vomiting can be experience after chemotherapy.
- Patient should take rest and maintain balanced diet to manage fatigue during the treatment.
- Hematologic effects – Chemotherapy can suppress bone marrow function, leading to anemia, low white blood cells counts (neutropenia), and low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia). Blood cell counts need to be monitored regularly, and supportive treatment such as blood transfusions or growth factor medications may be necessary to manage these effects.
- Hair loss, appetite changes, mouth sores, and neuropathy are common side effects of chemotherapy. Read more on managing chemotherapy side effects - https://www.patientsengage.com/conditions/managing-side-effects-chemoth…
Patients should communicate openly with their doctors about any side effects they experience to receive proper interventions and support.
What is the prognosis for bladder cancer?
The prognosis of bladder cancer varies depending on factors such as stage of the cancer, the type of cancer cells, and the individual’s overall health.
- Early detection is key for more favorable prognosis.
- Patient’s overall health plays a significant role in prognosis. Patients with underlying medical conditions or any health issues may face various challenges during the treatment.
- The response to the treatment can vary among individuals. Some patients may respond well to treatment and achieve long term remission, while others may experience recurrence.
- Continuing smoking and using smokeless tobacco after treatment can lead to recurrence.
- If treatment is not completed, relapse can occur. For advanced stages relapse rates are higher compared to stage I. Treatment should be initiated promptly in case of relapse.
Regular follow up with a specialist is crucial for assessing treatment response and detecting any sign of cancer recurrence.
What are the chances of bladder cancer recurrence or of a bladder cancer being a second cancer?
It depends on various factors such as tumor grade, stage and individual characteristics. Recurrence rates may range from 15 to 70% with superficial tumors having lower recurrence rates. Factors like infections or certain drug use may increase the risk of bladder cancer, though the incidence is relatively low. For patients with advanced stage cancer, it is crucial to remain hopeful as there are advancements in treatment options. With immunotherapy and maintenance treatments, survival rates have improved from about 9 months to over 2 years.
What precautions should be taken after bladder cancer treatment?
- Cessation of smoking is crucial as it can lead to recurrence.
- Diet and exercise play important roles in regaining health and reducing risk of recurrence.
- Balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains and adequate hydration is necessary.
- Maintaining weight through regular physical activities is important.
- There are generally no restrictions on physical activity unless the patient experiences significant fatigue.
- Patients can gradually get back to their routine exercises and physical activities over time.
- Precautions need to be taken to address potential risks for those who have undergone lymph node removal.
- Applying pressure bandages, elevating legs, continuing pelvic and leg exercises recommended post treatment under guidance of physiotherapist will help alleviate lower limb lymphedema.
- Stress management is crucial for overall well-being. Try relaxation techniques, hobbies, meditation or counselling.
- Do not hesitate to talk and seek help regarding any discomfort you experience esp in the genitourinary area. Attend follow up appointments on time.
By incorporating these precautions into daily life and staying vigilant about the potential signs, you can manage bladder cancer and improve quality of life post treatment.
What are the psychological and emotional support needs of bladder cancer survivors, and how can these needs be addressed?
Bladder cancer patients need emotional and psychological support even after completing treatment or entering into remission. Reproductive health issues are often not adequately addressed. Many patients, especially those who were sexually active before treatment, may experience concerns or changes in sexual desire and function following treatment. It is crucial for survivors to feel comfortable discussing these issues with healthcare providers or support groups to receive appropriate support and guidance.
Support groups play a vital role in providing psychosocial support for bladder cancer survivors. By discussing openly with other survivors, they can learn from their experiences and gain valuable insights into managing their concerns. No question is considered wrong, and seeking support can help alleviate anxieties and provide reassurance during the recovery process. Patients should consult their health care provider, and health care providers should also create a supportive environment for their patients. Addressing the emotional and psychological needs of patients is essential for their overall well-being.
What are the follow up protocols for bladder cancer patients?
The follow up protocol aims to ensure early detection of any recurrence or complications, monitor treatment outcomes and promote the quality of life of a patient. Consulting your treating doctor and going for follow ups is crucial part of the treatment.
- Regular physical examinations and blood tests may be scheduled for every two months to monitor overall health and detect any potential recurrence of cancer.
- Periodic imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRIs, may be performed to assess the status of the bladder and surrounding areas for signs of recurrence.
- Quarterly cystoscopies may be recommended for the first two years after intensive treatment to closely monitor the health of the bladder and rule out any recurrence.
- For patients who have undergone bladder replacement surgery with the formation of a stoma, regular monitoring of stoma health and addressing any complications is essential. Any issues related to their stoma should be communicated to their doctor during follow up visits.
- In cases where residual disease is present or to prevent recurrence, patients may be placed on maintenance therapy such as immunotherapy or chemotherapy. A strict follow up protocol is required in that case to monitor the treatment response and disease progression.
What are the complications associated with stoma bag? How can these be prevented?
- One common issue is the structural changes in the stoma, leading to prolapse or swelling, which can obstruct the urine or feces output.
- Continuous exposure to fluids can cause skin irritation, breakdown, and ulceration around the stoma site.
- The adhesive used to attach the bag can also cause erosion and inflammation during application and removal, increasing the risk of skin infections.
- Leakage may happen due to improper fitting of the bag or a defect in the bag.
- Many of these complications be prevented with proper care and attention.
- Maintaining good stoma hygiene, ensuring correct application of the bag, using proper skin barrier and seeking advice when required can help minimize these issues.
- Adjusting life with a stoma bag can be challenging psychologically, leading to anxiety, depression and self-consciousness.
- Connecting with the support group is also beneficial to get guidance from individuals living with stoma bag.
Read personal experience on managing stoma bag - https://www.patientsengage.com/personal-voices/managing-my-stoma-bag-co…
What factors contribute to patient attrition or not continuing cancer treatment in the Indian context?
Apart from financial concerns, several factors contribute to patient attrition during cancer treatment. Financial toxicity affects patients in India where patients have to pay out of pocket for the treatment. However, if patients see the broader picture and understand that treatment expenses contribute to longer survival and improved quality of life, the impact of financial concerns can be minimized.
Lack of awareness and understanding about the purpose of the treatment is a significant factor. Patients may feel that advanced stage cancer treatments are merely prolonging life for a short period without improving quality of life. This misconception can lead to sense of hopelessness and loss of control over life. There are misconceptions about treatment also such as getting bedridden after treatment or developing some other comorbidity after treatment.
It is important for patients to be aware about the reality, remain hopeful and understand that taking charge of their treatment can positively impact the treatment outcomes. Education, awareness and maintaining a sense of control are important in addressing patient attrition during treatment of any disease.
How to prevent bladder cancer?
- Quitting tobacco can greatly reduce your risk of developing cancer.
- If you have a family history of bladder cancer or other cancers, genetic predisposition may influence your risk. Early screening is recommended.
- Drinking an adequate amount of water can help dilute the concentration of harmful substances in the urine and reduce the risk of bladder cancer.
- Maintain a healthy diet and weight.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Minimize exposure to chemicals. If you work in industries involving chemicals such as aniline dyes, avoid direct contact with chemicals and inhaling chemical fumes whenever possible.
- Practice good hygiene habits to reduce urinary tract infections, which may be associated with bladder cancer. This includes practicing safe sex and proper genital hygiene.
- Seek prompt medical attention. Don’t ignore symptoms such as blood in the urine, urinary urgency or frequency, or pelvic pain. These could indicate bladder cancer or other health issues.
References
- PatientsEngage Bladder cancer webinar: https://www.youtube.com/live/xu1a2kByI-Y?si=O0zsjbPK02iozomS&t=19
- Know the symptoms of bladder cancer - https://www.youtube.com/live/d6uP-CLyW5U?si=lAEheiEyOElxSgby&t=9
- How Can We Prevent Bladder Cancer - https://www.youtube.com/live/oTne4HZ42rY?si=BkH9yb2w8MIGSwhZ
- Living well with bladder cancer - https://www.youtube.com/live/jRuMm7R8bLk?si=rlrM6VFbmiWHYTNP&t=8
- Navigating Treatment Choices For Bladder Cancer - https://www.youtube.com/live/V4ZPcVRUW04?si=EP8RzuiJ-lwgL5xU















