
Management of Interstitial Lung Disease includes active treatment of the underlying causes and supportive therapies like pulmonary rehabilitation and oxygen therapy.
Alongside management of the common comorbidities encountered in ILD is essential. Common conditions seen with ILD are:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)- The acid from the stomach regurgitates back into the esophagus which may cause a burning sensation in the chest. This acid can flow into the lungs and cause inflammation, which worsens ILD. It can also cause a constant cough due to irritation of the throat.
- Pulmonary hypertension (PH)- It is a type of high blood pressure that occurs in the blood vessels of the lungs. Echocardiography is used for diagnosis in patients with ILD.
- Lung cancer- Patients with ILD are at a higher risk of lung cancer. ILD patients having a history of smoking, chest pain, blood in sputum (hemoptysis) are screened for lung cancer using a CT scan.
- Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)- Screened in patients of ILD with obesity and history of daytime sleep, snoring and sleep disturbance using polysomnography (it is also known as sleep study during which the doctor records your various body functions like brain waves, oxygen levels, leg movements etc. while you sleep in a monitored environment)
- Venous thromboembolism (VTE)- Patients have history of worsening breathlessness, palpitations, swelling of lower limbs and are diagnosed using blood tests and imaging tests like duplex ultrasonography and Computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA).
- Depression and anxiety-The impaired quality of life and functional decline associated with ILD may often lead to anxiety and depression that may need the intervention of a psychologist and or psychiatrist.
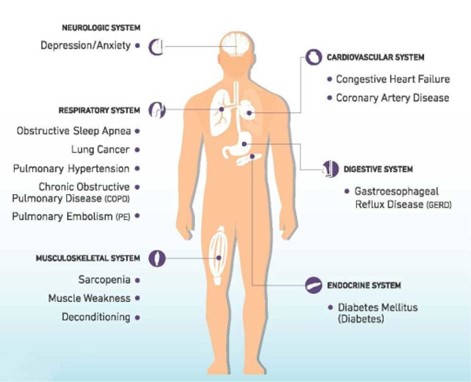
Image sourced from: https://foundation.chestnet.org/lung-health-a-z/interstitial-lung-disea…
Other issues which may be associated with ILD are:
- Congestive heart failure: It happens secondary to pulmonary hypertension when the right lower heart chamber (right ventricle) becomes enlarged due to congestion.
- Coronary artery disease: Due to poor lung function and related oxygen supply the risk for coronary artery disease increases and sometimes may be secondary to related connective tissue disorders that lead to ILD.
- Diabetes Mellitus: This is often secondary to the treatment with steroids for autoimmune causes of ILD.
- Sarcopenia and muscle weakness- It is a condition in which there is progressive and systematic loss of skeletal muscle mass along with a decline in the function and quality of muscle. It happens mostly secondary to the connective tissue causes of ILD. ILD also causes deconditioning of the muscles where they lose their tone due to lack of oxygen and mass.
Palliative care - It is a form of specialized medical care that focuses on improving quality of life during the course of a severe illness. It is provided in addition to disease-focused, life-extending treatment. It usually involves a team of a physician, a nurse, a social worker and a chaplain. The goal is to provide symptomatic relief for both physical and emotional symptoms, such as pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, poor appetite, constipation, nausea, anxiety, and depression. It also helps with assistance with decision-making and advance care planning.

















