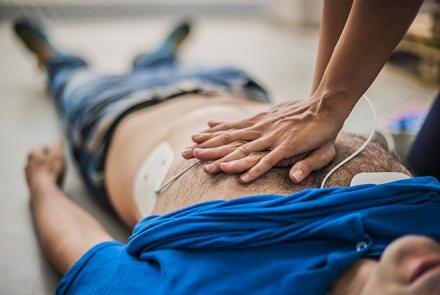
Have you been surprised to hear about fit and even young athletes having a cardiac arrest and even a sudden death? Can exercising be bad for you? Dr Shital Raval Patel unpacks the causes, risks, and the screening recommended.
We often read and hear about young, fit people and athletes having a sudden heart related incident and even succumbing to it while performing or working out and it is the most shocking news ever! It’s incomprehensible especially because we know them to be the fittest and healthiest of people. Sudden death occurs in 1 to 2 in 200,000 athletes annually and predominately strikes male athletes.
What causes this?
The most common reason is a genetic disorder called Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) followed by abnormal formation of coronary arteries.
It could also be happen due to a blow or injury to the chest causing cardiac concussion, especially seen in contact sports like American football, Ice Hockey, Karate, etc.
Also, it is now known that prolonged endurance type activities (marathons, triathlons, etc) can cause irreversible physiological changes to the heart and the cardiovascular system. This results in volume overload, when the chambers of the heart are carrying too large a volume of blood for it to function efficiently. This causes a transient reduction in the heart’s ability to pump sufficient blood to a muscular body. This is usually seen in athletes over months and years of training and body-building.
Although not all factors are currently known, it has been proven that excessive exercising leads to cardiac fatigue and all its complications. High-endurance training puts exceptional stress on our heart muscle. Although stressing a muscle usually makes it stronger, extremely high stress can have the opposite effect. Over-exercising has been linked to scarring of the heart muscle, which can lead to thickening or stiffening of the heart, or even structural changes in the heart. Endurance training leads to high levels of oxidative stress, inflammation and damage to your heart tissues, producing acute physiological responses that can trigger a cardiac arrest.
The other less common cause is a syndrome called Marfan’s, which is seen in taller and loose-jointed individuals.
Different types of cardiomyopathy
The main culprit here is Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), one of the most common causes of sudden death in athletes. In this condition, the heart muscle thickens, making it harder for blood to be pushed out of the heart. This type of cardiomyopathy is most often passed down through families. This condition may exist with no symptoms.
Other types of cardiomyopathy are:
Dilated cardiomyopathy, when the heart chambers enlarge and weaken the heart, causing less blood to be pumped out to the body. It can be brought about by many medical problems.
Restrictive cardiomyopathy, a cluster of disorders, where the heart muscle becomes stiff and the chambers are unable to fill with blood. The most common reasons are Amyloidosis and Cardiac Fibrosis (scarring of the heart) from an unknown cause.
Ischemic cardiomyopathy, a narrowing of the heart capillaries (arteries that supply the heart with blood). The heart is unable to pump blood because the walls become weak and thin.
Peripartum cardiomyopathy, seen commonly during the pregnancy months or in the first 5 months post-delivery.
Symptoms and signs of cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy usually has no symptoms and hence goes unnoticed. You could be exercising heavily and still remain unaware of it until it strikes. In some people, it can cause symptoms and signs listed below:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Fainting (syncope)
- Dizziness
- Palpitations (rapid heartbeat)
- Fatigue
- Heart murmur
Treatment options for Cardiomyopathy
The treatment is the same as for any Chronic Heart Failure patient. It is most important to treat the root cause of the condition if possible. Lifestyle changes are a huge part of treatment. Drugs may include Beta blockers, Cardiac glycosides, Angiotensin II receptor blockers, Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, diuretics, Aldosterone antagonists, vasodilators, Ionotropic agents, Antiarrhythmics, and/or Human B-type natriuretic peptide.
Surgical options may be Pacemaker implants, Cardiac resynchronization therapy (biventricular pacing), Ventricular restoration surgery, implantable defibrillators and heart transplants as the last resort.
What is the prognosis?
The outlook depends on the severity of the cardiac problems, the type and cause of the myopathy and the patient’s response to the therapy.
Can an athlete go back to his sport?
- An athlete can resume his sport after recovering from the initial cardiac failure and once treatment is initiated.
- He/she must however cut down on the exercising regimen.
- It is unlikely that he will be able to perform at his previous level.
- He/she must always warm up and rest after every workout to let the heart recover.
- The food plan must replace high protein diet with a more nutritious one including vegetables and fruits.
Preventive screening
The American Heart Association recommends that all high school and college athletes undergo a cardiovascular evaluation before athletic participation, performed preferably by a licensed physician. The screening should be repeated every 2 years and should include:
- Personal history of exertional chest pain, shortness of breath, heart murmur, systemic hypertension, severe fatigue, or exertional syncope (fainting)
- Family history of heart disease or sudden death in any relative
- Physical evaluation for murmurs, femoral pulses, Marfan syndrome and brachial artery blood pressure
- Parental verification of history