It is quite usual for us to experience headaches at some point in our lives as a child or adult. It is of the most common prevailing symptoms that hampers our daily life and is one of the most common causes of abuse of pain killers around the world. This article focuses on types and causes of headaches, when to be concerned about it, and when to visit a healthcare professional.
Headache is one of the most common causes of pain in the body around the world. Headaches are mostly caused by irritation or inflammation of the brain, blood vessels, nerves or membranes of ear, nose, and throat.
Headaches are classified based on the cause.
Causes of headaches may be primary or secondary.
A) Primary Headaches
Primary headaches are of four types. They are not linked to other medical conditions.
- Cluster headaches.
- Migraine.
- New daily persistent headaches (NDPH).
- Tension headaches.
B) Secondary Headaches
Secondary headaches are related to some underlying medical conditions, like:
- Issues related to the blood vessels supplying the brain.
- Head injury.
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
- Infection.
- Medication overuse.
- Sinus congestion.
- Trauma.
- Tumor.
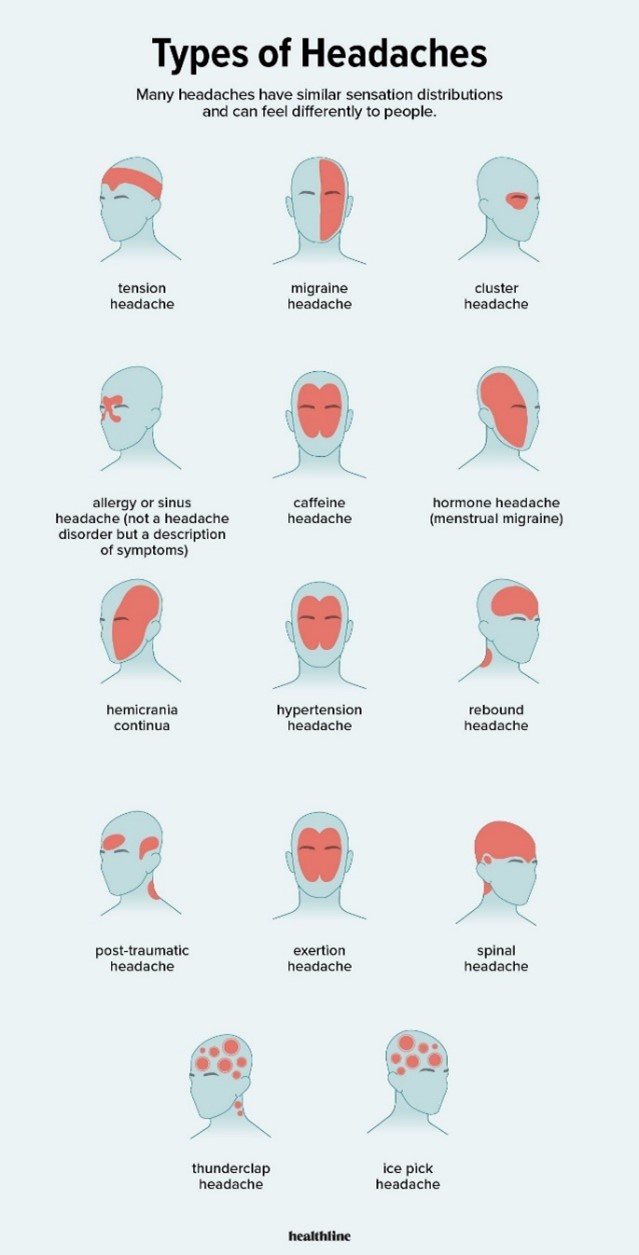 https://www.healthline.com/health/headache/types-of-headaches
https://www.healthline.com/health/headache/types-of-headaches
Heredity Association of Headaches
Some headaches like migraines do have a familial origin. According to studies, children are four times more likely to get migraines if their parents have a history of migraine.
Environmental Triggers of Headaches:
Sometimes our environment may also be the cause of headaches and may go unnoticed as a potential cause for the pain.
- Food items like caffeine, alcohol, fermented foods, chocolate, and cheese.
- Exposure to allergens.
- Secondhand smoke.
- Strong odors (perfumes or any odor at home like strong incense sticks, mosquito repellant sprays, strong perfumes etc.).
- Air pollution- Many subcomponent pollutants are associated with occurrence of headache disorders, including migraine like PM (particulate matter), NO2, SO2 etc.
- Weather changes like high humidity and high temperature may trigger a headache. Pressure changes that cause weather changes are likely to trigger chemical and electrical changes in the brain which may irritate nerves, leading to a headache.
Exercise Triggered Headaches:
After exercise or a workout, the related strenuous physical activity, dehydration, and low blood sugar can cause headaches.
Hormones and Headaches:
- Menstrual headache: Usually occurs when the estrogen levels begin to drop in the cycle.
- Perimenopausal and Menopausal headache: This may occur due to fluctuations in the hormonal levels.
- Dehydration and Headaches
Identifying Different Headaches:
- Tension headaches: they are the most common type of primary headaches and have the following characteristics:
- Consistent pain without throbbing.
- Mild to moderate pain.
- Pain occurs on both sides of the head/cranium (bilateral).
- Responsive to over-the-counter treatment.
- They tend to worsen during certain activities like bending over or walking upstairs.
- Migraines
They are the second most common type of primary headaches. The associated characteristics of this type of headache are:
- Moderate to severe pain.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Pounding or throbbing pain.
- Headaches may extend from four hours to three days.
- Sensitivity to light, noise, or odors.
- Issues with gut like loose stools or abdominal pain.
- Cluster headaches
They are the most severe type of primary headache. They tend to appear as clusters, commonly during spring or autumn seasons during the change. During a cluster phase, which could span two weeks to three months, they happen one to several times per day. The headaches may disappear entirely (go into remission) for months or years only to reappear later.
- Pain of high intensity often feels like a burning or stabbing sensation.
- Located behind either eyes or in the peri-orbital region and does not change sides.
- Throbbing or constant.
- New daily persistent headaches
They are of sudden onset and usually continue or last for more than three months. They usually affect those who previously did not experience frequent headaches.
- Constant and persistent pain without easing up.
- Located on both sides of the head.
- Not responsive to over-the-counter pain medications like paracetamol or ibuprofen.
- Sinus headaches
They are caused by an infection of the sinuses that leads to inflammation and congestion. Migraines are often confused with sinus headaches.
- Unpleasant taste in mouth.
- Deep, constant pain in your cheekbones and forehead.
- Facial swelling.
- Feeling of fullness in the ears.
- Fever.
- Pain that worsens on sudden movement of the head or on straining.
- Discharge of mucus from the nose.
- TMJ headaches
The jaw and cheeks are lined with TMJ (Temporo-mandibular joint) muscles, which may occasionally experience pain and even cause headaches. A headache can result from strained jaw muscles, such as those caused by grinding your teeth, which can also cause discomfort in other TMJ muscles, the cheekbones, and the sides and top of the head.
- Tight facial or jaw muscles
- Jaw or facial pain.
- A “clicking” noise in the jaw.
- Restricted movement of the jaw
- Changes in the way the top and bottom teeth fit together which may appear as changes in the way one bites things.
- Medication overuse headaches (MOH)
They are also known as rebound headaches. The most common cause is frequent use of pain killers for headaches which tends to increase the frequency of headaches. Signs of MOH include:
- Headaches that are increasing in frequency.
- More days with headaches than without.
- Pain that worsens in the morning.
- Headaches in children
Most kids have had a headache by the time they get to higher grades in school. Studies suggest that in about 20% of kids, tension headaches and migraines are a reoccurring problem. Causes may be the same as mentioned above. Triggers for headaches in children are:
- Some foods items may trigger headaches (additives and preservatives like Monosodium glutamate (MSG) contained in Doritos and Ramen noodles, aged cheese, caffeine in chocolates etc.)
- Changes in sleep habits.
- Environmental/external factors (pollution, strong odors, excessive screen time, exposure to secondhand smoke, loud noises, or bright lights etc.).
- Stress or conflicts.
- Dehydration
Headache Symptoms That Require Urgent Medical Attention:
One should see the doctor if the headaches are increasing in frequency, interfere with daily activities, if home remedies fail or is continuous for more than a day.
Here are a few red flags that require one to seek immediate medical attention, failing which there could be serious outcomes.
- A sudden, new onset, severe headache like a thunderclap headache as that may indicate a stroke
- Headaches accompanied by one or more neurological symptoms such as:
- Weakness
- Dizziness
- Sudden loss of balance or falling
- Numbness or tingling
- Paralysis
- Speech difficulties
- Mental confusion
- Seizures
- Personality changes/inappropriate behavior
- Changes in the vision such as blurred vision, double vision, or blind spots
- Headache accompanied with fever, breathlessness, stiffness in the neck, or rash
- Headache that causes one to wake from sleep at night
- Headaches with severe nausea and vomiting
- Headaches following any head injury or accident
- Experiencing a new kind of headache after age 55
Diagnosis Of Headaches
- Maintaining a headache diary with the following things to note:
- Character
- Frequency
- Duration
- Intensity
- Triggers
- Quantity of caffeine consumed in a day
- Stress level
- Sleep habits
- Work issues
- Single/Multiple types of headaches
- Aggravating and relieving factors
- Familial history of headaches
- What symptoms occur between headaches
- History of any treatment taken
- Physical and neurological examination
- Tests like CT/MRI if needed
Prevention Of Headaches
- Avoid headache triggers.
- Avoid medication overuse.
- Avoid smoking.
- Avoid oversleeping or sleep deprivation.
- Avoid skipping/delaying meals.
- Exercise regularly.
- Reduce stress.
- Reduce caffeine.
- Avoid food additives or naturally occurring substances, including nitrates in processed meats, MSG in fast food and Chinese food, tyramine found in certain aged cheeses and soy-based foods, and the artificial sweetener aspartame.
- Maintain good hydration.
- Get the right pillow.
Headaches, though common, should not be ignored if they’re recurrent or persistent as that may lead to abuse of pain killers and an insidious underlying cause may be masked. Headaches that have the associated red flag symptoms as discussed, should always be assessed by a doctor to help prevent an unwanted outcome.
Citations:
- “Apollohospitals.” Apollo Hospitals, 3 Oct. 2024, www.apollohospitals.com/diseases-and-conditions/headache. Accessed 29 Nov. 2024.
- Bay Biosciences. “Headache - Bay Biosciences, LLC.” Bay Biosciences, LLC., 28 Dec. 2020, baybiosciences.com/headache. Accessed 29 Nov. 2024.
- Cleveland Clinic. “Headaches: Types, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment.” Cleveland Clinic, 29 Aug. 2022, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9639-headaches.
- “Difference between Primary and Secondary Headaches: Types, Causes.” MedicineNet, www.medicinenet.com/difference_between_primary_and_secondary_headache/a….
- doctormmdev. “A Headache Is One of the Most Common Pain Conditions in the World. - Radiant Pain Relief Centres.” Radiant Pain Relief Centres, 13 Dec. 2021, www.radiantpainrelief.com/a-headache-is-one-of-the-most-common-pain-con…. Accessed 29 Nov. 2024.
- “Headache and Facial Pain | Neuro Care in New Jersey.” Holmdel Neuro Care, 11 Oct. 2021, www.holmdelneurocare.com/neuro-care-conditions/headache-and-facial-pain. Accessed 29 Nov. 2024.
- “Headaches & Migraines.” Blue Mountain Wellness -, 2 June 2021, bluemountainwellness.com/what-we-treat/tension-headaches. Accessed 29 Nov. 2024.
- Lubin, Edward. “Cluster Headaches: 2 Types, Causes, Symptoms & Pain Relief.” EMedicineHealth, 14 Oct. 2022, www.emedicinehealth.com/cluster_headache/article_em.htm. Accessed 29 Nov. 2024.
- Mayo Clinic. “Headache Causes.” Mayo Clinic, 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/headache/basics/causes/sym-20050800.
- “National Migraine and Headache Awareness Month | DRH Health.” DRH Health | Healthcare for Our Community, 16 June 2022, www.duncanregional.com/news/national-migraine-and-headache-awareness-mo…. Accessed 29 Nov. 2024.
- Parker, Hilary. “Physical Side Effects of Oversleeping.” WebMD, WebMD, 24 July 2008, www.webmd.com/sleep-disorders/physical-side-effects-oversleeping.
- Robblee, Jennifer, and Rashmi Halker Singh. “Headache in the Older Population: Causes, Diagnoses, and Treatments.” Current Pain and Headache Reports, vol. 24, no. 7, 29 May 2020, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-020-00866-8.
- Services, Department of Health & Human. “Headache.” Www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au, 30 June 2015, www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/headache.
- “TMJ Headache: Symptoms, Treatment, Causes, and One Side.” Healthline, 5 Mar. 2018, www.healthline.com/health/tmj-headache.
- Watson, Kathryn. “10 Types of Headaches and How to Treat Them.” Healthline, Healthline Media, 10 July 2017, www.healthline.com/health/headache/types-of-headaches"www.healthline.com/health/headache/types-of-headaches.
- Mehndiratta, ManMohan, et al. “Air Pollution and Headache Disorders.” Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology, vol. 0, no. 0, 2022, p. 0, https://doi.org/10.4103/aian.aian_1138_21. Accessed 22 Aug. 2022.
- NHS. “10 Headache Triggers.” Nhs.uk, 9 Apr. 2018, www.nhs.uk/conditions/headaches/10-headache-triggers/"www.nhs.uk/conditions/headaches/10-headache-triggers/.
- “Headaches and Hormones: What’s the Connection?” Mayo Clinic, 2024, mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/chronic-daily-headaches/in-depth/headaches/art-20046729. Accessed 10 Dec. 2024.