
Loud snoring is often a sign of a more serious condition known as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Here are all the facts on sleep apnea that you should know if you or your loved one snore. Including treatment options available.
What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
Obstructive Sleep Apnea or OSA is a medical condition in which breathing stops periodically during sleep in an involuntary process. These brief periods of no breathing are called apnea.
हिंदी में पढ़ें: खर्राटों को कब गंभीरता से लेना चाहिए
Apnea is caused by either partial or complete blockage of the airways during sleep. This occurs because the person’s throat muscles and tongue relax and fall back leading to air flow being blocked. This leads to reduced blood flow to the brain. When blood flow stops, the brain compels the body to wake up and start breathing again. The person may awaken briefly but usually don’t remember it. This can occur several times through the night causing poor sleep quality and daytime drowsiness.
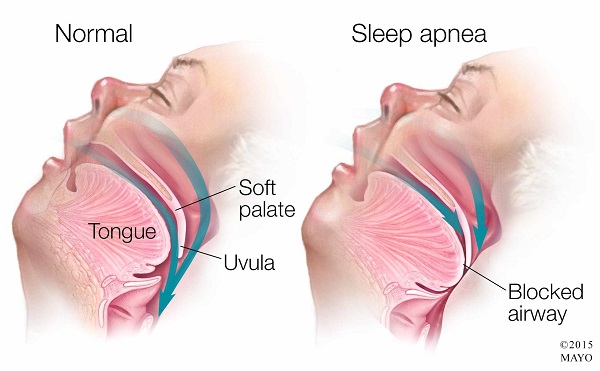
What are the types of Sleep Apnea?
There are three types of sleep apnea, Obstructive, Central and Mixed.
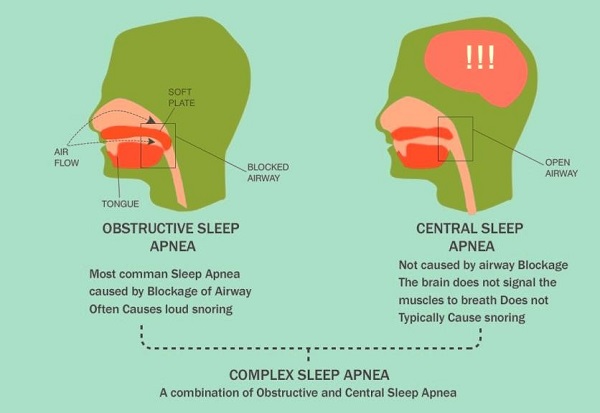
Obstructive sleep apnea is the most common one and is known to affect approximately 4% of men and 2% of women. OSA is caused by a mechanical problem that obstruct the airways. The OSA can be mild, moderate or severe depending on the number of episodes of wakeful interruptions per hour per night.
| Type of OSA | Number of episodes of interruptions per hour |
|---|---|
| Mild | 5 to 14 |
| Moderate | 15 to 30 |
| Severe | 30 or more |
In Central Sleep apnea, there may be no airway obstruction but the brain fails to signal the body to continue breathing. Such apneas are also temporary but originate in the central nervous system of the brain.
Mixed or Complex sleep apnea occur when a person experiences both Obstructive and Central sleep apnea at the same time. It is diagnosed only during an overnight sleep study.
Related Reading: How I fixed my Sleep Apnea Problem
What symptoms should you watch out for?
- Snoring that is often loud, regular and followed by periods of silence. Snoring is usually loudest when the person sleeps on his back and quiets down when the person lies on his side. This is the most obvious sign and is often noticed by the partner who shares the bed.
- Disrupted breathing noises such as gasping or choking due to the airway blockage.
- Daytime sleepiness from sleep deprivation. People may fall asleep during work, driving or while on the phone.
- Broken sleep due to breathing disruption and the body unable to reach REM and non-REM cycles.
- Morning headaches occur due to the low oxygen supply to the brain during the night.
- Dry or sore mouth/throat in the mornings.
- Decreased libido.
- Mental health symptoms such as irritability, grumpiness, forgetfulness, difficulty concentrating, short temper and even depression.
Who is at risk of developing OSA?
OSA can affect anyone but your chances increase if you have the following:
- Narrowed airways either an inherit feature or due to enlarged adenoids(tonsils).
- Frequent nasal congestion especially at night time that can obstruct breathing.
- Excess weight which leads to fatty tissue around the neck & throat area that restricts breathing. Remember thin people can also get OSA.
- High blood pressure or hypertension which is a common cause.
- Diabetes is also a major risk factor.
- Smoking habit that causes inflammation in the respiratory system and decreases quality of airflow.
- Chronic alcohol use causes thrदat muscles to relax and block airways during sleep.
- Asthma has been recently associated with OSA.
- Family history of sleep apnea.
- Male gender.
- Aging that causes weaker muscle tone in the throat muscles.
How is it diagnosed?
The first point of diagnosis is history of symptoms and physical examination of the mouth and throat area. The doctor will check to see if there is any enlargement of tonsil and adenoids or excess fatty tissue in the uvula, tongue and soft palate. If there is any doubt, your doctor will then refer you to a Sleep specialist for a sleep study where machines will record heart, lung, and brain activity while you sleep.
What are the treatment options?
Treatment will depend on severity of the condition and as recommended by your doctor. Here are the commonly prescribed options:
- Positive Airway Therapy (PAP) Therapy- includes Continuous, Automatic or Bilevel PAP.
- Oral devices such as Mandibular advancement devices and Tongue retaining mouthpieces.
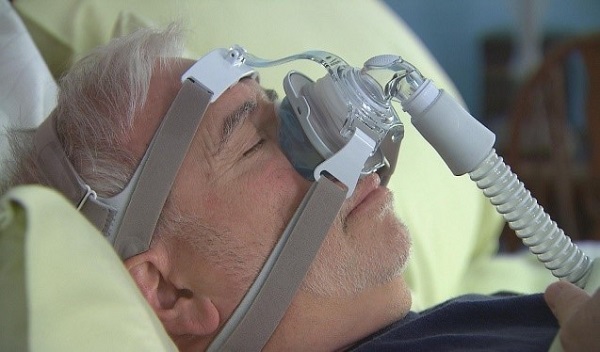
- Surgery that may be Tonsil removal, Nasal repair, Uvuloplatopharyngoplasty (removal of uvula and other soft tissue from the throat) or Maxillomandibular advancement (the upper and lower jaw are moved forward).
Why it important to treat OSA?
It is important to recognize symptoms and signs of OSA and get it diagnosed. If left untreated, OSA can result in several health complications.
Benefits of treating OSA include:
- Improves sleep quality at nighttime.
- Reduces daytime sleepiness and increases energy and stamina levels during the day.
- Prevention of Cardiovascular problems as OSA causes sudden drops in oxygen levels and thus increases risk of hypertension, coronary heart disease, heart attacks and even stroke.
- It can of major concern during use of specific medicines and when undergoing surgery as OSA can interfere with certain medications such as sedatives, general and narcotic analgesics which relax the upper airways. People who have OSA are at risk of complications during and after surgeries.
- Delays progression of type 2 Diabetes.
- Prevents risk of eye conditions like glaucoma.
- Avoid sleep disruption of partners who share the bed.
















