Cataracts, including congenital cataracts are relatively common in India. According to World Health Organisation (WHO), cataracts are a leading cause of blindness and visual impairment in India. It is estimated that >50% of the blindness cases in India are caused by cataracts. Cataracts can affect people of all age groups, but they are most commonly associated with aging, especially after the age of 50. However, cataracts can also occur in younger age groups, including children and middle-aged adults. Congenital cataracts, are present at birth or develop shortly after birth during infancy.
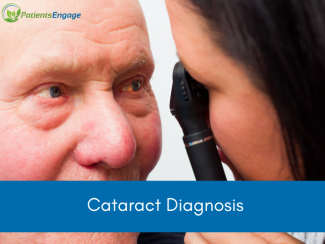
Cataracts are diagnosed through a comprehensive eye examination performed by an ophthalmologist or an optometrist. The diagnosis involves a combination of medical history review, visual acuity tests, and specialized eye examinations.
Here are some common diagnostic tests and procedures used for cataract diagnosis:
- Visual Acuity Test: This test measures the clarity of vision using an eye chart. It helps determine the extent of visual impairment caused by cataracts.
- Slit-lamp Examination: A slit lamp is a specialized microscope that allows the eye care professional to examine the structures of the eye, including the lens. This examination helps identify the presence and characteristics of cataracts.
- Retinal Examination: This examination involves dilating the pupils with eye drops to allow a clear view of the retina at the back of the eye. It helps the eye care professional assess the overall health of the eye and rule out other eye conditions.
- Tonometry: This test measures the pressure inside the eye (intraocular pressure) and helps screen for conditions like glaucoma that may coexist with cataracts.
- Refraction Test: This test determines the refractive error and helps determine the need for glasses or contact lenses to improve vision.
Contributed by
Dr Rashmi Deshmukh
Consultant Ophthalmologist, Cataract, Laser Refractive Surgery (LASIK)
L V Prasad Eye Institute
Changed
08/Apr/2025
Community
Condition