Cataracts, including congenital cataracts are relatively common in India. According to World Health Organisation (WHO), cataracts are a leading cause of blindness and visual impairment in India. It is estimated that >50% of the blindness cases in India are caused by cataracts. Cataracts can affect people of all age groups, but they are most commonly associated with aging, especially after the age of 50. However, cataracts can also occur in younger age groups, including children and middle-aged adults. Congenital cataracts, are present at birth or develop shortly after birth during infancy.

Symptoms and Signs
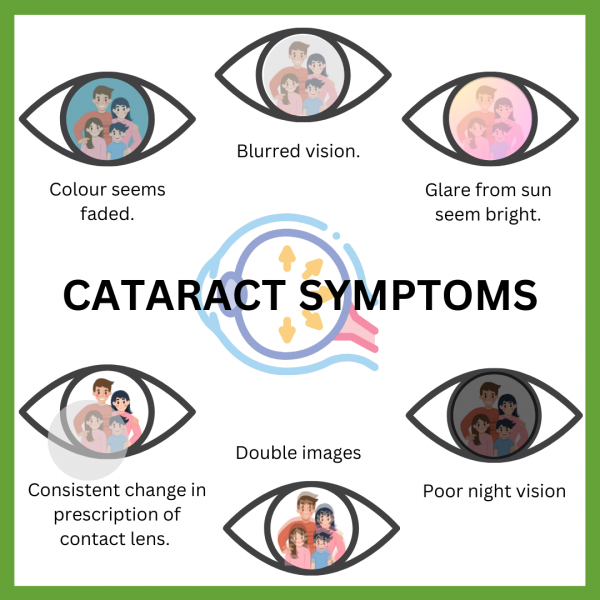
The symptoms and signs of cataracts can vary depending on the type and severity of the cataract.
- One of the primary symptoms of cataracts is a decrease in vision clarity. Vision may appear hazy, blurry, or cloudy, which can make it difficult to perform daily activities like reading or driving. It must be noted, that patients with cataract experience blurry vision despite using updated glass prescription.
- Cataracts can cause increased sensitivity to glare, especially at night or in low-light conditions when the pupils are dilated. Oncoming headlights or streetlights may cause more significant glare or halos, making it challenging to see clearly.
- Another important symptom is difficulty in colour perception and contrast sensitivity. Cataracts can affect colour perception, leading to colours appearing faded or less vibrant than usual. This can make it challenging to distinguish between similar shades or hues.
- Some types of cataracts can cause double vision (diplopia) in one eye. This occurs when the cataract scatters or distorts light entering the eye, resulting in the perception of two images instead of one.
Contributed by
Dr Rashmi Deshmukh
Consultant Ophthalmologist, Cataract, Laser Refractive Surgery (LASIK)
L V Prasad Eye Institute
Changed
08/Apr/2025
Community
Condition