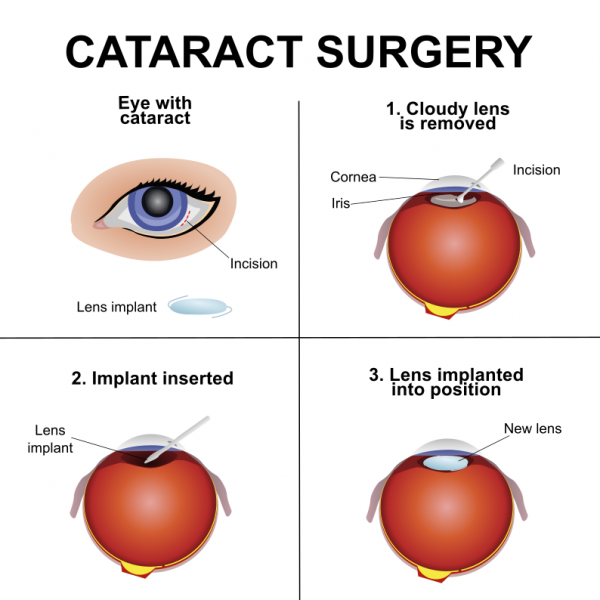
The primary treatment for cataracts is surgical intervention. Cataract surgery involves removing the cloudy lens and replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) to restore clear vision. Here is an overview of the cataract treatment process:
- Preoperative Evaluation: Before the surgery, the ophthalmologist will conduct a thorough evaluation to assess the overall health of the eyes and determine the appropriate type of IOL. Measurements of the eye's dimensions are taken to ensure proper IOL selection.
- Anaesthesia: Cataract surgery is typically performed under local anaesthesia, which involves numbing the eye with eye drops or an injection around the eye. In some cases, general anaesthesia may be used, particularly for children or individuals with certain medical conditions
- Phacoemulsification: The most common technique used in cataract surgery is phacoemulsification. In this procedure, a tiny incision is made in the cornea. An ultrasound device is used to break up the cataract and remove the cloudy lens fragments. The IOL is then inserted through the same incision.
- Intraocular Lens (IOL) Implantation: The IOL is an artificial lens that replaces the natural lens. There are different types of IOLs available, including monofocal lenses that provide clear vision at a single focal distance and multifocal or extended depth of focus lenses that offer a range of focus. The choice of IOL depends on factors such as the patient's lifestyle, visual needs, and any additional eye conditions.
Complications of surgery
While cataract surgery is generally safe and successful, like any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications. It's important to be aware of these possibilities, although they occur relatively infrequently. Some potential complications of cataract surgery include:
- Infection: Infection of the surgical site, known as endophthalmitis, is a rare but serious complication that can lead to vision loss if not promptly treated.
- Swelling or Inflammation: Some individuals may experience temporary swelling or inflammation of the eye, which can cause discomfort and blurry vision. This condition, called uveitis, is usually managed with anti-inflammatory eye drops.
- Retinal Detachment: In rare cases, the surgical procedure can cause the retina (the layer of tissue at the back of the eye) to detach. Retinal detachment requires immediate medical attention to prevent permanent vision loss.
- Dislocated Intraocular Lens (IOL): The artificial lens (IOL) implanted during cataract surgery may shift out of its proper position, causing blurred vision or other visual disturbances. If this occurs, additional surgery may be necessary to reposition or replace the IOL.
- Glaucoma: Cataract surgery can sometimes trigger increased intraocular pressure, leading to glaucoma. This can be managed with medication or additional procedures to control the eye pressure.
It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of cataract surgery with the ophthalmologist before making a decision.
In some cases, if cataracts are not significantly affecting vision or the patient is unable or unwilling to undergo surgery, visual aids such as glasses or contact lenses may be recommended to optimize visual clarity. However, it's important to note that cataract surgery is the only treatment that can remove cataracts completely.
If left untreated, what happens?
If left untreated, cataracts can progressively worsen and significantly impact vision causing a gradual decline in vision, making it increasingly difficult to perform daily activities such as reading, driving, and recognizing faces. Vision may become blurred, cloudy, or hazy, which can affect both distance and near vision. As cataracts progress, they can interfere with the quality of vision as well affecting the ability to engage in hobbies, work, and social activities. Reduced visual acuity and increased sensitivity to glare can limit independence and overall quality of life.
Contributed by
Dr Rashmi Deshmukh
Consultant Ophthalmologist, Cataract, Laser Refractive Surgery (LASIK)
L V Prasad Eye Institute