The use of Continuous Glucose Monitor is increasing. The PatientsEngage team has put together useful information that explains the basics of CGM, who it is meant for, what you can expect, how to interpret the data and more.
What Is Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)?
With India fast moving towards becoming the Diabetes capital, newer monitoring techniques for blood sugar have come into play. The Continuous Glucose Monitor or CGM, as its commonly known as, is a wearable sensor that measure glucose levels every 1–5 minutes. This is immensely helpful as it helps provide real-time data that is reflective of the short- and long-term glucose trends. This is immensely helpful in understanding blood sugar fluctuations, response of blood glucose to meals (postprandial responses), and the body’s ability to process and metabolize sugar effectively (metabolic resilience). It is a great tool for patients and doctors alike to map the sugar trends of any person and personalize the treatment plan.
Note: CGM is used interchangeably for Continuous Glucose Monitor and Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Now a days, CGM has many uses but initially it was developed only for people with diabetes. As people are becoming increasing aware and conscious of their health these days many people are using the CGM to track their insulin sensitivity, dietary response to different food consumed, and assessing their risk for cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
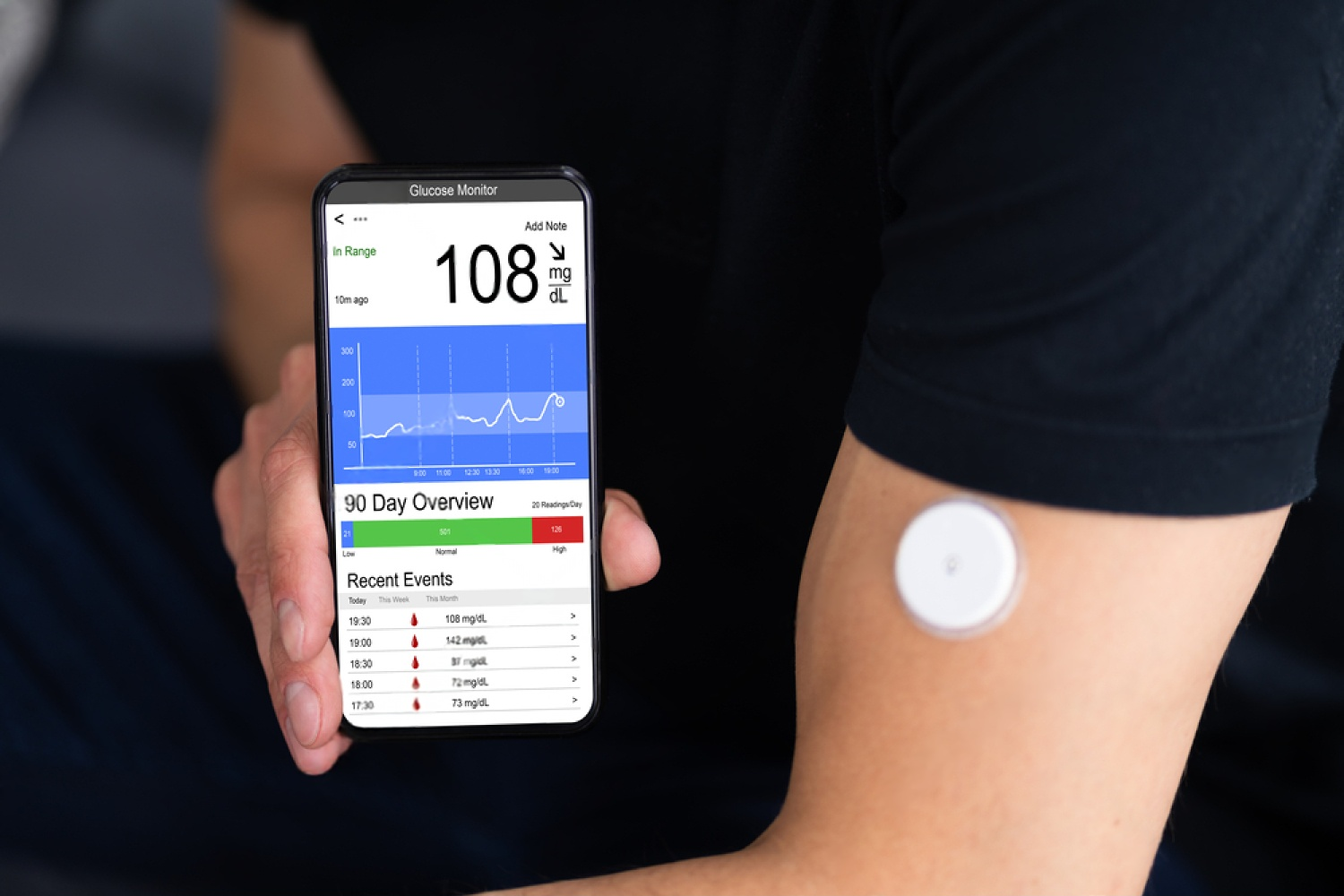
A Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) requires insertion of a small sensor beneath the skin to measure glucose levels. The data from the sensor is sent to a receiver (like a smartphone app) that displays the current glucose level. The sensor also has settings for alarms and alerts if the glucose is higher or lower than the reference range.
What is the CGM used for?
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is a device that helps in providing real time assessment of how the blood sugar spikes and falls with consumption of different food items, in response to stress, and in response to our daily habits like sleep, exercise and mobility. It is a great tool to personalize your diet. It helps an early detection of poor or declining metabolism. - It helps to improve energy levels and support long-term health goals by getting data on your metabolic health.
- It also helps you to understand how our genes, level of physical activity, sleep, mobility, stress management and environment work together to affect your health.
Why I tried out CGM: https://www.patientsengage.com/personal-voices/my-experience-cgm
Who Should Consider Using a CGM?
While CGM is a very helpful tool for people with diabetes who have recurrent episodes of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) and patients on insulin, for others it may not be necessary. The decision is best taken after discussion with your doctor and factoring in the cost, repercussions of information overload and actual need for CGM for any individual.
It is medically indicated for:
- People who have been diagnosed with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, especially those requiring insulin.
- Patients with hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and cannot demarcate the symptoms or have frequent low sugar level episodes.
- Pregnant women with or at risk for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM).
It may be used after discussion with your doctor when:
- You have signs of subclinical metabolic dysfunction (fatigue, brain fog, difficulty losing weight, increased thirst, darkening of skin in armpits or neck, blurred vision, and increased urination, especially at night) despite normal labs.
- If you have a strong family history of metabolic or cardiovascular disease.
- If you are managing body adaptation, persistent fatigue, or mood variability.
- If you experience postprandial (post -meal) hypoglycemia, brain fog, or energy crashes.
- If you want personalized nutrition feedback based on your glucose trends.
My experience with CGM: https://www.patientsengage.com/personal-voices/cgm-active-lifestyle
What are some newer uses for CGMs?
- CGM is also used to detect conditions like prediabetes, polycystic ovarian syndrome, or metabolic syndrome (a group of conditions including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high triglycerides, low HDL cholesterol, and excess abdominal fat, that together increase your risk of cardiovascular disease, Type 2 diabetes and stroke).
- It is a sought-after longevity and healthy aging tool for people who lay focus on preventive health and for fitness enthusiasts.
- Athletes and high performers may use it to optimize fuel utilization and recovery.
- Persons with no diagnosis of diabetes but with a strong family history of diabetes.
Even a short-term CGM trial (10–14 days) can reveal patterns in glucose dynamics that are not captured by static laboratory values.
What should you expect when you start using a CGM?
Initial insights often include:
- Detection of sugar spikes after consuming sugary (high-glycemic) foods.
- Delayed clearance of glucose after periods of being sedentary or after poor sleep.
- Identification of post-exercise hypoglycemia (low sugar) or dawn phenomenon.
Over time the CGM reveals:
- Glycemic impact of specific foods (the sugar levels resulting from different food items).
- Every hormone has a circadian rhythm (24-hour cycle that influences your body’s physiological functions like the sleep-wake cycle, body temperature and release of different hormones) and so does insulin. The CGM helps in detecting any fluctuations in insulin sensitivity that occur over 24-hours in people.
- It also helps in understanding the connection between psychological and physiological stress and glucose fluctuations.
What my CGM experience showed: https://www.patientsengage.com/personal-voices/managing-diabetes-dance-diet
How Should CGM Data Be Interpreted?
Target Ranges (General Recommendations for Non-Diabetic Use):
| Metric | Optimal Range |
| Fasting Glucose | 70–99 mg/dL |
| 1-Hour Postprandial | <140–160 mg/dL |
| 2-Hour Postprandial | <120–140 mg/dL |
| Average Glucose | 100–105 mg/dL (HbA1c 5.1–5.3%) |
How is the CGM Applied?
The CGM has a sensor that is inserted beneath the skin on the abdomen or on the upper arm which is fixed with an adhesive patch around it. The data from the CGM is then sent to a receiver like a smartphone that helps in monitoring the glucose trends continuously. Most sensors last between 7 to 14 days, depending on the brand after which it should be removed and replaced with a new one. The sensor should be discarded in sharps container.
What are the factors that influence the CGM Readings?
There are many factors that can influence the CGM readings that need to be kept in mind when discussing readings with your doctor.
- The macronutrient composition of your meal
- Simple carbohydrates (fruits, milk, and milk products and refined sugar including syrups and candy) cause rapid spikes and drops.
- Consuming fibre, protein, or fat moderates along with sugar changes the impact significantly.
- Postprandial (post meal) physical activity
- Light activity (e.g., 10–20 minutes of walking) significantly improves glucose clearance.
- Circadian rhythm
- Early morning hepatic glucose output (sugar produced by the liver) may elevate fasting glucose which is called the “dawn effect.”
- Evening meals may provoke higher postprandial (post meal) responses due to reduced insulin sensitivity at night.
- Stress physiology
- Cortisol and chemicals like dopamine/adrenaline surges can elevate glucose independently of food intake.
- Hydration status
- Dehydration may falsely elevate interstitial glucose concentrations (the concentration of glucose in the fluid surrounding cells).
- Pharmacologic agents and chronic conditions
- Steroids, beta-blockers, SSRIs, and certain hormonal disorders (e.g., PCOS, hypothyroidism) can skew glucose readings.
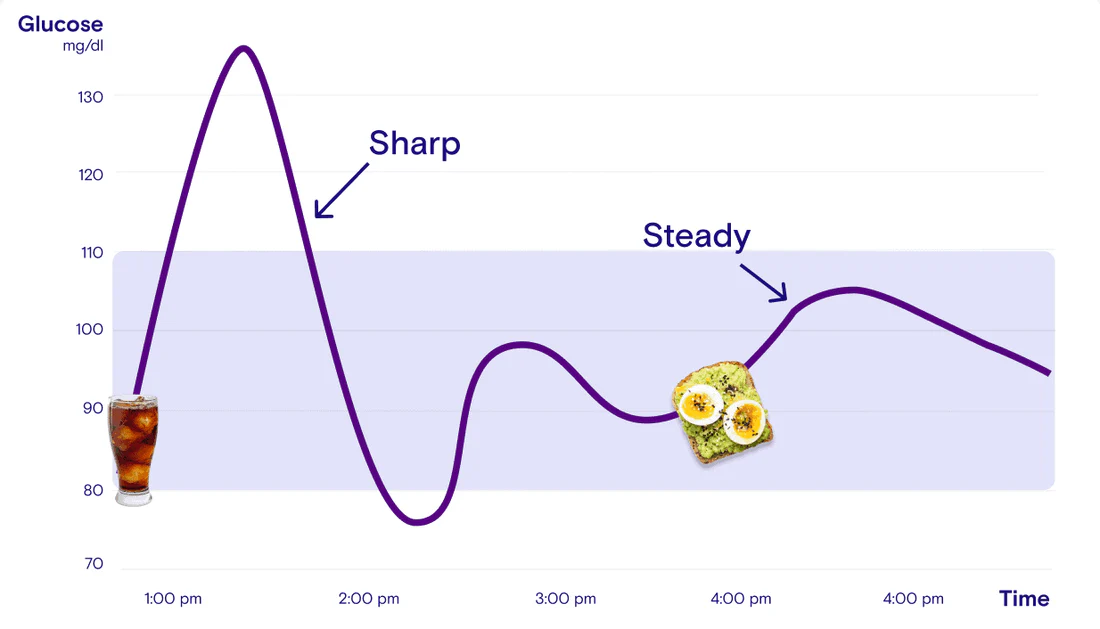
The glucose curve:
A glucose curve is a graph showing how your blood glucose levels change over time. It represents the fluctuations in blood glucose and is read in relation to consumption of meals, physical activity post meals, and other factors like sequence of food consumed etc. This curve helps you to monitor blood sugar levels and also understand how your body responds to glucose.
- A high sugar meal (High-Glycemic meal) causes a sharp spike of the blood sugar.
- A usual meal (Standard meal) shows a moderate peaking of the blood sugar.
- Meal + post-meal walk results in a quicker return to baseline of the blood sugar after the post meal sugar spike.
- Meal with Fiber/Protein consumed first help to flatten the glucose curve the most, meaning slow moderate rise with a gradual fall This doesn’t cause energy crashes or food cravings as the rise and fall are moderate and gradual.
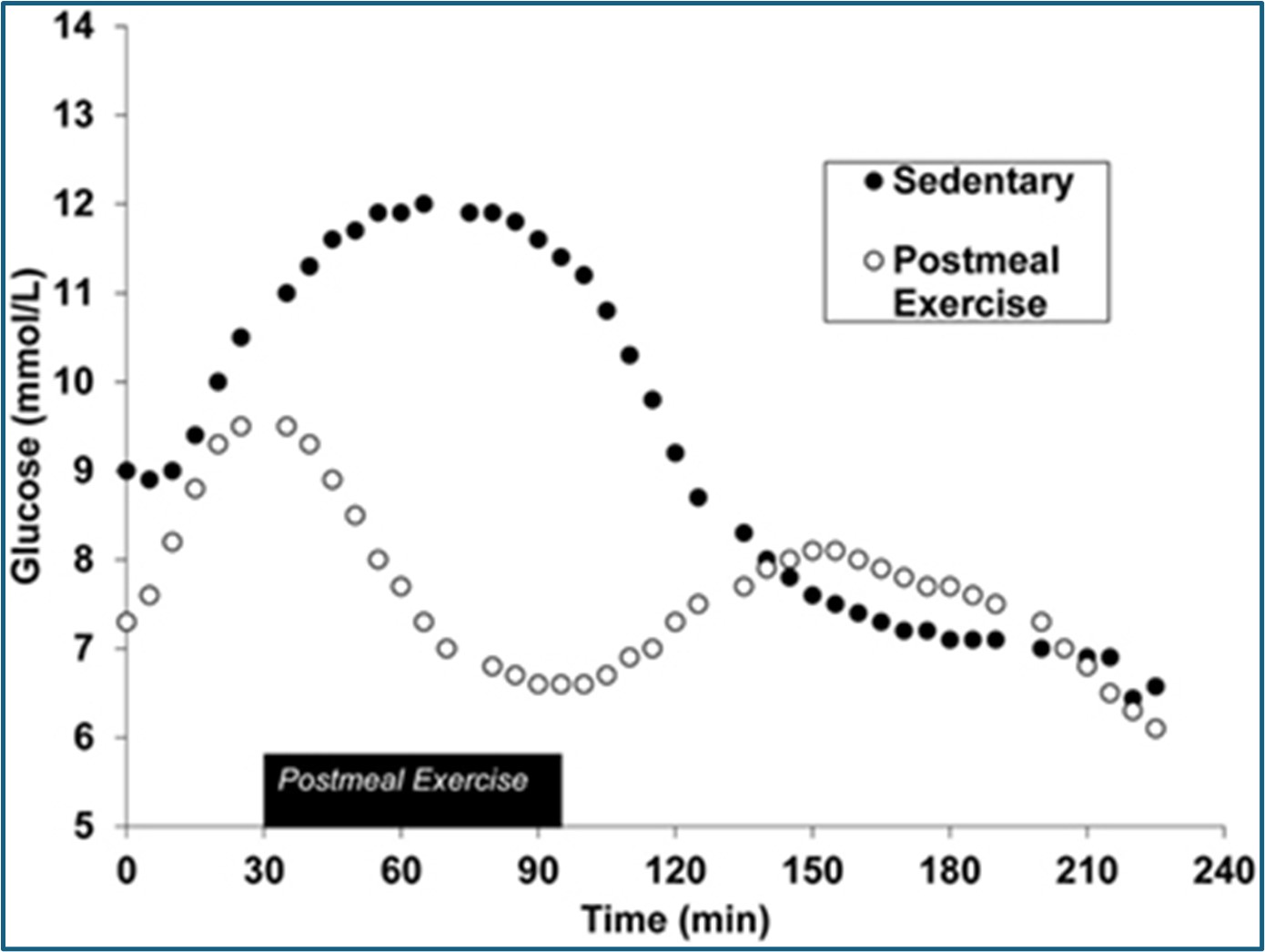
What are some evidence-based strategies to regulate glucose?
- Food sequencing: It’s best to consume fats and protein before eating carbohydrates as this will blunt the glucose spikes thus avoiding sudden spikes and falls which cause energy crashes too.
- Acetic acid intake: A teaspoon of apple cider vinegar before meals may reduce postprandial (post-meal) concentration of sugar in the blood.
- Mobility post meals: Any light movement/activity/walk within 30 minutes after a meal stabilizes the blood sugar and insulin.
- Meal timing: Ideally the larger meals should be eaten earlier in the day to maintain the natural insulin sensitivity.
- Avoid isolated carbohydrates: "Naked carbs" which means carbohydrates consumed without any fat or protein cause rapid glucose spikes and thus should be avoided. Always consume the carbohydrates after protein and healthy fats.
When to consult a Physician while using a CGM?
You must see your doctor if:
- Fasting glucose consistently exceeds 110 mg/dL.
- 1–2-hour postprandial readings are >160–180 mg/dL
- You observe recurrent hypoglycemia (<70 mg/dL), especially in the absence of glucose-lowering medications.
- Your blood sugar reading variability is extreme (>25–30 mg/dL).
- You experience early morning glucose spikes not associated with food intake.
- There is mental distress associated with constant monitoring (e.g., anxiety, obsession).
What your doctor may decide to do:
- The doctor may suggest some more tests: HbA1c, fasting insulin, GGT, lipid profile.
- They may want to establish a diagnosis and rule out insulin resistance or beta-cell dysfunction.
- Adjustment of medications if applicable to you based on readings.
- Referral to a registered dietitian, endocrinologist, or metabolic health coach.
- Recommendation of a prescription CGM.
References:
- Balata, Soleen, et al. "Expanding Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 2 Diabetes." Journal of Primary Care & Community Health, 2025, https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/2633559X241296156.SAGE Journals
- Gómez-Peralta, Fernando, et al. "Impact of Continuous Glucose Monitoring and its Glucometrics in Clinical Practice in Spain and Future Perspectives: A Narrative Review." Advances in Therapy, vol. 41, 2024, pp. 3471–3488, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-024-02943-5
- Flockhart, M., and F. J. Larsen. "Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Endurance Athletes: Interpretation and Relevance of Measurements for Improving Performance and Health." Sports Medicine, vol. 54, no. 2, 2024, pp. 247–255, https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-023-01910-4
- Verywell Health. "FDA Clears the First Implantable Continuous Glucose Monitor That Can Last a Year." Verywell Health, 2024, https://www.verywellhealth.com/eversense-365-cgm-fda-clearance-8718361… Health
- Barron's. "DexCom Stock Rises as Glucose Monitoring System Gets FDA Clearance." Barron's, 2025, https://www.barrons.com/articles/dexcom-stock-fda-glucose-monitoring-sy…
- Seidu, Samuel, et al. "Efficacy and Safety of Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Interventional Evidence." Diabetes Care, vol. 47, no. 1, 2024, pp. 169–179, https://doi.org/10.2337/dc23-1520.Diabetes Journals+1BioMed Central+1
- Diabetologia. "Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis." Diabetologia, vol. 67, 2024, pp. 798–810, https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00125-024-06107-6
- EatingWell. "Falling Asleep After Midnight Could Raise Your Diabetes Risk, New Study Says." EatingWell, 2025, https://www.eatingwell.com/sleep-habits-diabetes-risk-study-11691648.
- International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity. "The Efficacy of Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring as a Behaviour Change Tool in Populations with and without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials." International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 2024, https://ijbnpa.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12966-024-01692-6.
- Klonoff, David C., et al. "CGM Data Analysis 2.0: Functional Data Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence Applications." arXiv preprint, 2025, https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.07885.arXiv
- Lutsker, Guy, et al. "From Glucose Patterns to Health Outcomes: A Generalizable Foundation Model for Continuous Glucose Monitor Data Analysis." arXiv preprint, 2024, https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.11876.
- Huber, Marie-Luise. “Warum Deine Blutzuckerkurve Nicht Immer Gleich Aussieht.” HELLO INSIDE, 8 June 2023, helloinside.com/en/blogs/insider/why-blood-sugar-curves-aren%27t-always-the-same. Accessed 21 May 2025.
- Erickson, Melissa L., et al. “Exercise after You Eat: Hitting the Postprandial Glucose Target.” Frontiers in Endocrinology, vol. 8, 19 Sept. 2017, https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00228.
- Charlot, Anouk, et al. “Beneficial Effects of Early Time-Restricted Feeding on Metabolic Diseases: Importance of Aligning Food Habits with the Circadian Clock.” Nutrients, vol. 13, no. 5, 22 Apr. 2021, p. 1405, dx.doi.org/10.3390%2Fnu13051405, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051405.