This World Thrombosis Day, Dr Manohar B Kalbande, Cardio vascular & thoracic surgeon warns that diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity and sedentary lifestyle increase risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and recommends early diagnosis, complete treatment and regular follow up to get give good relief from this disease.
What is Thrombosis?
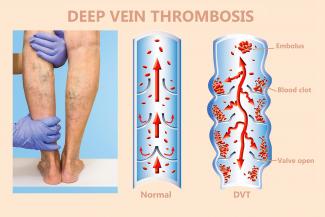
Blood returning to the heart i.e. venous blood is drained by two sets of veins in our body- superficial and deep. The deep veins are located deep in the muscles. When the blood clots in the deep veins produce obstruction to blood returning to the heart, the condition is called Deep Vein Thrombosis [DVT]. The incidence of DVT in India is much more than was previously thought as in some cases the disease goes unnoticed.
What are the signs and symptoms of thrombosis?
A bed ridden patient with DVT may not have any symptoms.
Otherwise, the person usually presents with
- swelling of limb
- onset of acute throbbing or cramping pain of mild to moderate intensity,
- skin feels warm around the painful area
- red or darkened skin around the painful area
- swollen veins that are hard or sore
In chronic cases, there is usually persistent leg edema, hyper pigmentation of skin with thickening is present. Advanced cases may present with large non-healing ulcers. 5-10% patients may have sudden death due to complication called Acute Pulmonary Embolism, wherein large clot from deep veins breaks up and migrates to lung arteries blocking major blood supply to lungs and causing sudden death.
What causes Deep Vein Thrombosis?
DVT occurs due to combination of three factors:
- Sluggish flow of blood due to various reasons
- Injury in the vein wall
- Increased thickness of blood.
Various risk factors associated with DVT are :
- increasing age,
- remaining in one position for long time as it occurs during prolonged travel,anesthesia, operation, paralysis, fracture of bones etc.
Cancer and, in females, use of oral contraceptive drugs are also associated with higher incidence of DVT. Condition called "Thrombophilia Syndrome" wherein the blood becomes thick and more prone for clotting has been recognized as very important factor.
How is DVT diagnosed?
Diagnosis of DVT is usually simple by these non-invasive tests:
-Colour Doppler Examination. It can reveal blood clots in leg veins by using sound waves to check flow in the blood veins.
-The D-dimer test which is a blood test is also done. If blood clots are present, they produce a protein called D-dimer.
-MRI to get a more detailed image of the blood vessels in the legs and lungs.
The only invasive test used sometimes is Venography where a dye is injected into the large vein of the leg and then X-rays images are taken. This is not very commonly performed.
How is thrombosis or blood clots treated?
The goal of treatment is to reduce the size of the clot, prevent it from travelling to the lung and reduce risk of future clots. There are few ways to achieve these goals:
-Start with simple elevation of the affected limb in bed above heart level.
-Blood thinners or anti-coagulants are started immediately. In hospital, initially, injection of Heparin derivative Low Molecular Weight Heparin or LMWH is given for few days. An oral blood thinner then continues for 3-6 months. Commonly these rae warfarin pills which need acute monitoring of doses by a blood test called INR.
-If regular anti-coagulants do not work, Clot-busters or Thrombolytics are prescribed. In case of a severe DVTs, the patient is given the clot-buster via a catheter under imaging which targets to break and suck the clot.
-Surgical thromboectomy or removal by operation is usually not done these days.
-Some individuals who do not tolerate anticoagulant and have clot in deep veins nearer to heart may require placing an umbrella type device called IVC Filter to prevent blood clot from breaking and causing pulmonary embolism.
-Compression stocking must be worn from foot up till the knee to prevent recurrence of clots.
Can lifestyle changes reduce my risk of life-threatening blood clots?
Diabetes mellitus, increased blood cholesterol, obesity, sedentary lifestyle increase risk of DVT. Llifestyle modification can definitely reduce the risk of the disease.
Does deep vein thrombosis increase risk for other health problems?
When not treated or inadequately treated, chronic limb swelling, dark pigmentation, eczema, recurrent ulceration etc occur called as " Post Thrombotic Syndrome" which produces morbidity and reduces functional capacity and leads to loss of working days.
What is the extent of the problem in India?
With the average rate of approximately 150 per lakh population, more than 1.5 million persons may be suffering annually in India from DVT. The disease is more common in females and occurs in lower extremities in >95% cases.
What advice would you give to help control the disease?
The message is early diagnosis, complete treatment and regular follow up can give good relief from this disease.